Pengantar Materi Getaran dan Gelombang pada Mata Kuliah Fisika Dasar ITK 2020/2021
Summary
TLDRThis video introduces the concept of simple harmonic motion, explaining it as repetitive motion around an equilibrium point. The script explores key characteristics such as amplitude, frequency, and period, alongside the relationship between circular motion and harmonic motion. The video also addresses energy conservation in simple harmonic motion, emphasizing the role of mechanical energy while highlighting the impact of damping and resonance. Furthermore, it underscores the prevalence of simple harmonic motion in various physical phenomena like guitar strings, electrical oscillations, and atomic systems. Understanding these principles is vital for comprehending waves and other related concepts.
Takeaways
- 😀 Getaran (vibration) is defined as repetitive motion around an equilibrium point, like in a sine wave function.
- 😀 Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) is characterized by amplitude, frequency, and period, and can occur in objects like springs and pendulums.
- 😀 SHM can also be modeled in systems where restoring forces are present, such as springs and pendulums.
- 😀 A circular motion, when projected onto an axis, can be seen as SHM, linking rotational motion to harmonic motion.
- 😀 The phase constant in SHM corresponds to the initial angular position of a circular motion.
- 😀 Energy conservation applies to SHM when there are no dissipative forces like friction, with mechanical energy remaining constant.
- 😀 Kinetic and potential energy in SHM constantly change, while total mechanical energy remains constant.
- 😀 If there are dissipative forces (like friction), amplitude decreases over time, causing the vibration to die out gradually.
- 😀 Conversely, if the frequency of external forces matches the natural frequency of an object, resonance can occur, causing the amplitude to grow.
- 😀 SHM is commonly found in mechanical phenomena, such as the vibrations of guitar strings, bridges, or even the motion of atoms in molecules.
- 😀 Vibrations, including SHM, form the basis of wave phenomena, which will be discussed in the following week's topic.
Q & A
What is simple harmonic motion?
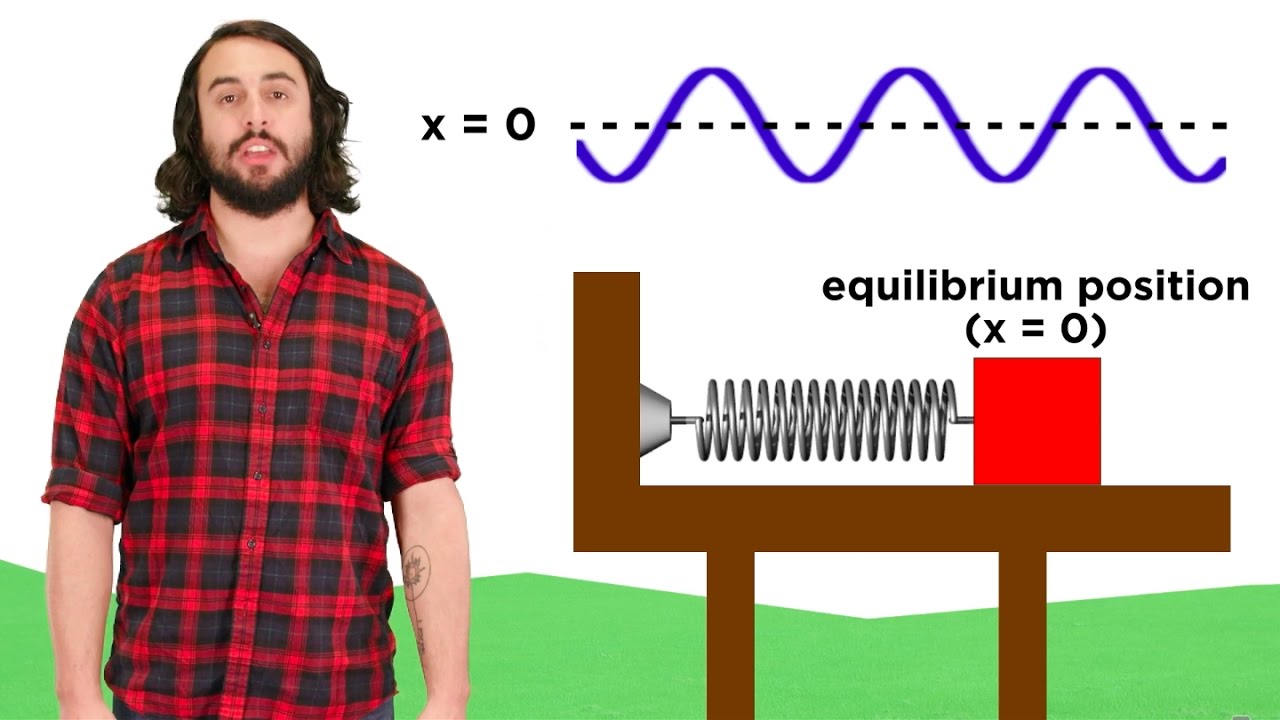
-Simple harmonic motion is defined as repetitive motion around a central equilibrium point, where the object moves back and forth with a sinusoidal function. The object follows a periodic path, often seen in systems such as a mass attached to a spring or a pendulum.
What are the key characteristics of simple harmonic motion?
-The key characteristics of simple harmonic motion include amplitude, frequency, and period. These define the motion's size, how often it oscillates, and the time it takes for one complete cycle.
What does the term 'equilibrium position' mean in the context of simple harmonic motion?
-The equilibrium position in simple harmonic motion refers to the point where the object is at rest, typically represented by x = 0 in a graph of the motion. The object oscillates around this point.
How does simple harmonic motion relate to circular motion?
-Simple harmonic motion can be understood as the projection of circular motion. When an object moves in a circle and its position is projected onto a straight line, it exhibits oscillatory behavior similar to simple harmonic motion.
What is the phase constant in simple harmonic motion?
-The phase constant is the angle in circular motion that represents the initial position of the object in simple harmonic motion. It indicates the starting point of the oscillation.
Does the law of conservation of energy apply to simple harmonic motion?
-Yes, the law of conservation of energy holds in simple harmonic motion, provided there is no friction or dissipative forces. The total mechanical energy (kinetic + potential energy) remains constant, while individual energies may fluctuate.
What happens to the amplitude of simple harmonic motion over time if there is damping?
-If there is damping (e.g., due to friction), the amplitude of the oscillation decreases over time, meaning the motion becomes less pronounced until it eventually stops.
What occurs in simple harmonic motion when the frequency of the oscillating object matches its natural frequency?
-When the frequency of the applied force matches the object's natural frequency, the amplitude of the oscillation can increase significantly, a phenomenon known as resonance.
Why is it important to study simple harmonic motion?
-Studying simple harmonic motion is important because it is commonly observed in various mechanical systems (such as vibrating guitar strings or moving bridges) and can help us understand the behavior of electrical oscillations and molecular vibrations in both physics and chemistry.
How does simple harmonic motion relate to wave phenomena?
-Simple harmonic motion is the basis for understanding wave phenomena. Oscillatory motion generates waves, and understanding the properties of oscillations helps explain the behavior of waves, which will be discussed in further lessons.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Aula 1 – Movimentos Periódicos e Introdução ao MHS

Simple Harmonic Motion Introduction(SHM) via a Horizontal Mass-Spring System

Movimento Harmônico Simples - Aula 02 (Força no MHS)
Simple Harmonic Motion: Hooke's Law

GERAK HARMONIK SEDERHANA: MATERI FISIKA KELAS XI

Drgania, ruch drgający #1 [ Ruch drgający i fale ]
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)