Materi Validitas dan Reliabilitas || Part 1 || Statistika Penelitian || Pertemuan 4
Summary
TLDRThis transcript explains the concepts of validity and reliability in research, focusing on their importance in data collection instruments like questionnaires. It outlines the difference between primary and secondary data, emphasizing that primary data requires validity and reliability testing, while secondary data does not. The video discusses how to test these aspects using statistical methods such as correlation tests for validity and Cronbach's alpha for reliability. It also provides a practical example of studying the impact of compensation on employee performance, showing how to create and test a valid and reliable survey instrument.
Takeaways
- 😀 Validity refers to whether an instrument measures what it is intended to measure, such as using the correct tool for the specific measurement (e.g., using a scale to measure weight).
- 😀 Reliability is about the consistency of measurement results when the same instrument is used multiple times under similar conditions.
- 😀 Primary data is directly collected by researchers (e.g., interviews, questionnaires, or observations), while secondary data comes from already published sources (e.g., financial reports, government statistics).
- 😀 To ensure the validity of a research instrument, it must measure the right variables or concepts accurately and appropriately.
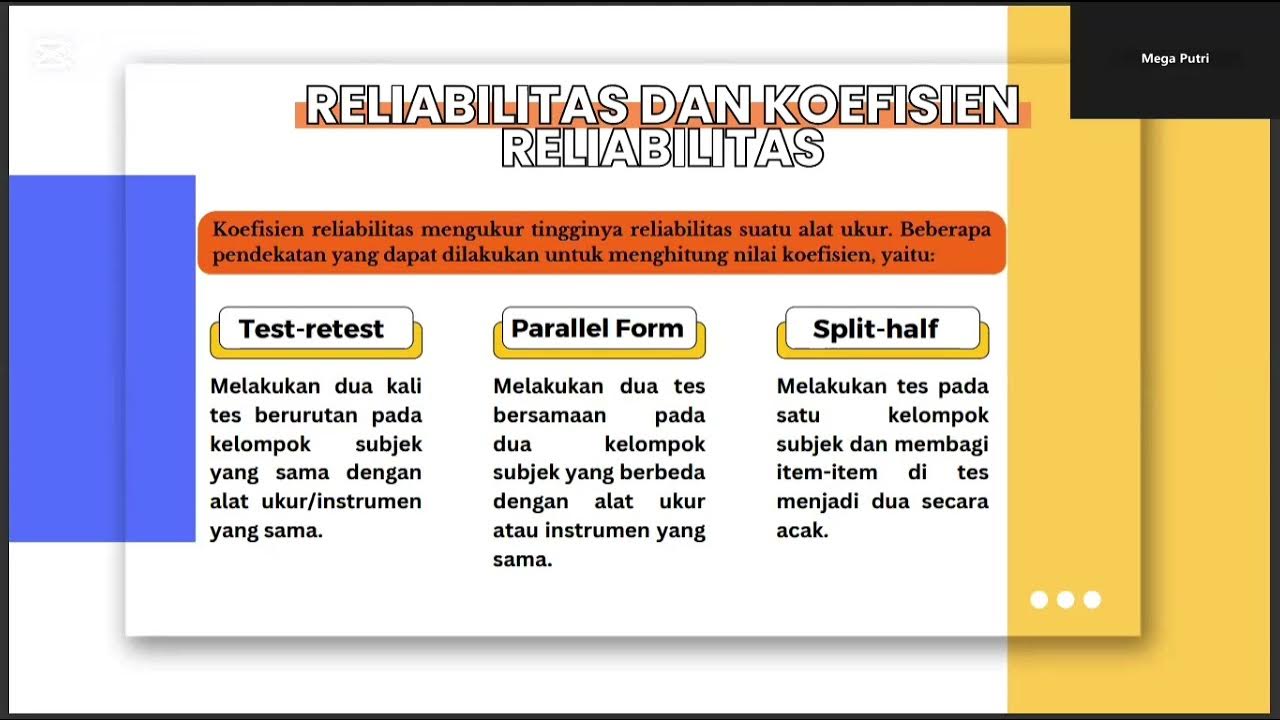
- 😀 When testing reliability, an instrument is considered reliable if it produces consistent results over time, like a stable scale giving the same weight reading for the same object.
- 😀 Secondary data typically does not require testing for validity and reliability because it has already been published and vetted, unlike primary data.
- 😀 An example of a valid and reliable research instrument is a questionnaire designed to measure employee performance, which must use the right indicators for performance and compensation.
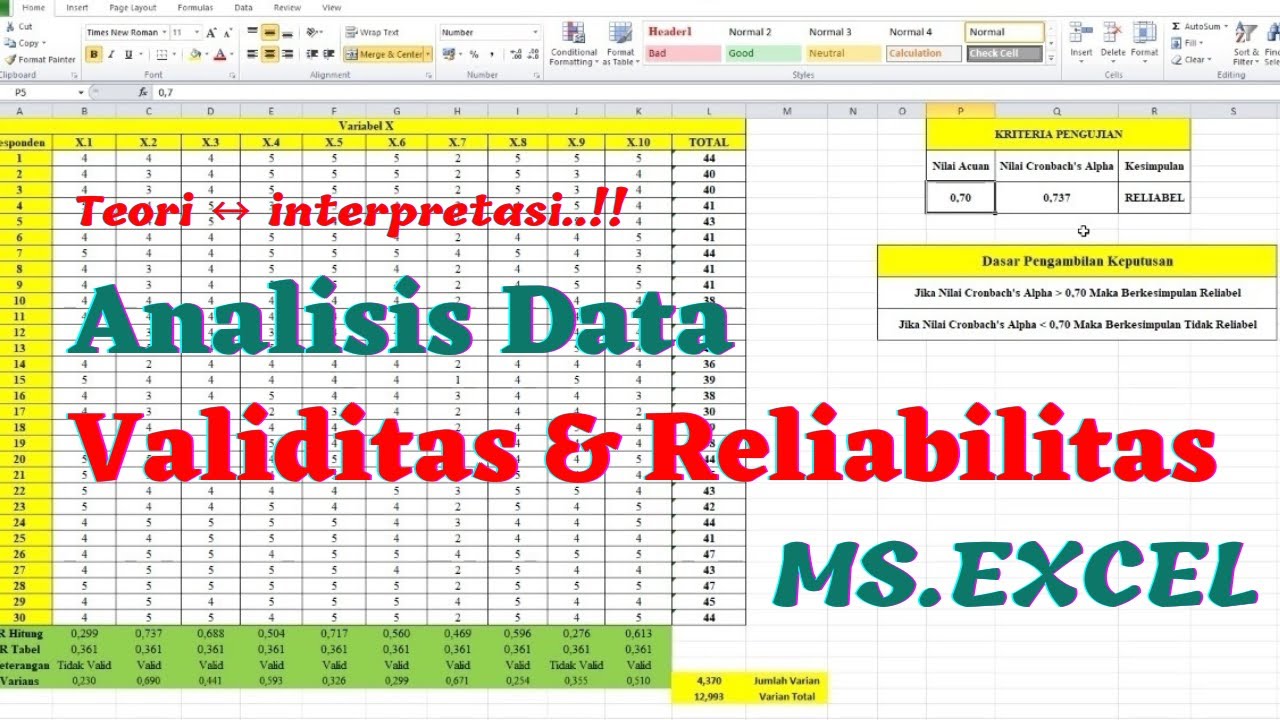
- 😀 When performing hypothesis testing for validity, the correlation between the item statements and the construct is assessed, with a threshold of 0.361 for 30 respondents indicating validity.
- 😀 For testing reliability, the Cronbach’s alpha statistic is commonly used. An instrument is considered reliable if Cronbach’s alpha is above 0.6 or 0.7, depending on the reference used.
- 😀 In research, 30 respondents are commonly used in pilot testing of instruments, such as questionnaires, to check both validity and reliability before the main data collection phase.
- 😀 It’s essential to understand the statistical thresholds used for validity and reliability to ensure that your instruments provide accurate and dependable data in research.
Q & A
What is the difference between primary and secondary data in research?
-Primary data is directly collected by the researcher through methods like interviews, questionnaires, or observations. Secondary data, on the other hand, refers to pre-existing data that has already been published or collected by other sources, such as financial reports or data from institutions like BPS.
Why is it important to assess the validity of an instrument in research?
-Validity ensures that the instrument accurately measures what it is intended to measure. For example, using a meter to measure length is valid, but using it to measure weight would not be valid. This is crucial for ensuring that the research results are meaningful and accurate.
How is reliability different from validity in research instruments?
-Reliability refers to the consistency of the results when the same instrument is used multiple times to measure the same object. If the instrument yields the same results consistently, it is considered reliable. Validity, on the other hand, focuses on whether the instrument measures what it is supposed to measure.
Can secondary data be tested for validity and reliability?
-No, secondary data is considered to have already undergone its own validation and reliability testing by the source from which it originates. Researchers using secondary data generally do not need to re-test its validity or reliability.
What statistical methods are used to test the validity of research instruments?
-To test validity, researchers often use correlation tests like the product-moment correlation, and statistical software like SPSS. If the p-value is less than 0.05, the item is considered valid.
How do you determine whether a research instrument is reliable?
-Reliability is assessed using Cronbach's Alpha. An instrument is considered reliable if its Cronbach's Alpha value is greater than 0.6 (or 0.7, depending on the chosen threshold). Higher values indicate greater reliability.
Why is the sample size for validity and reliability testing typically 30 respondents?
-A sample size of 30 is commonly used because it is considered statistically sufficient to ensure the reliability and validity of the instrument. This allows for more accurate generalizations about the data.
What role do indicators play in measuring compensation and employee performance?
-Indicators help break down abstract concepts like compensation and employee performance into measurable components. For example, salary and incentives are indicators for compensation, while quantity, quality, and creativity are indicators for employee performance.
How do you interpret the correlation value in validity testing?
-A correlation value greater than 0.361 (for n = 30) indicates that the item being tested is valid. If the correlation is lower than this threshold, the item is considered invalid.
What are the key sources referenced for determining the thresholds for validity and reliability in the script?
-The script references sources like Eko Putro Widoyoko's book on research techniques (for a Cronbach's Alpha threshold of 0.7) and Wiratna Sujarweni's book on business and economics education (for a threshold of 0.6).
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)