Uji PERMEABILITAS TANAH #tekniksipilindonesia
Summary
TLDRThis video demonstrates a soil permeability test using the constant head method for sandy soil. The process includes preparing the necessary equipment, such as the permeability cell, porosity stones, and sample preparation. The soil sample is saturated with water, and the test begins by measuring the water flow rate through the soil. The experiment involves multiple steps, including the precise measurement of water levels and the calculation of water discharge over time. The procedure is repeated for several trials to gather reliable data, which is then analyzed to determine the soil's permeability rate.
Takeaways
- 😀 The permeability test is being conducted to measure the flow of water through soil, specifically using the constant head method for coarse-grained soil samples like sand.
- 😀 The equipment needed includes a permeability testing apparatus, porosity stone, porosity paper, spring, burette, and a measuring glass.
- 😀 Before starting the test, the soil sample is mixed with a small amount of water to ensure it isn't too dry.
- 😀 The soil sample is placed into the permeability cell, and the process of saturation begins to ensure the soil pores are filled with water.
- 😀 The burette is filled with water, and the water level is maintained constant during the test to ensure accurate measurement of water flow through the sample.
- 😀 The constant head method requires that the water level in the burette remains steady throughout the test, indicating a constant flow rate.
- 😀 During the test, the amount of water that flows out of the soil sample is measured every 60 seconds, and the results are recorded to calculate the soil's permeability.
- 😀 The permeability test continues for a duration of 30 minutes to ensure accurate data collection for coarse-grained soil samples like sand.
- 😀 The output water is measured using a glass graduated with 200 mL increments, and the volume is used to calculate the permeability coefficient.
- 😀 The process is repeated multiple times to get consistent results, and the final calculation of permeability is based on the average water output measurements.
- 😀 The test results can help determine the hydraulic conductivity of the soil, which is important for understanding its drainage properties in real-world applications.
Q & A
What is the purpose of the permeability test mentioned in the transcript?
-The purpose of the permeability test is to measure the rate at which water can pass through soil. This helps in understanding the soil's ability to allow water infiltration, which is important for civil engineering and environmental studies.
What are the two methods used for conducting permeability tests?
-The two methods used for conducting permeability tests are the constant head method and the falling head method. The constant head method is suitable for coarse-grained soils like sand, while the falling head method is used for fine-grained soils.
Why is the constant head method chosen for this test?
-The constant head method is chosen for this test because the sample used is coarse-grained soil, such as sand, which allows water to flow through it steadily, making this method appropriate for measuring water permeability in such soils.
What is the purpose of saturating the soil sample before the test?
-The purpose of saturating the soil sample is to ensure that there are no air pockets in the soil, allowing for accurate measurement of water flow through the fully saturated pores of the soil.
What equipment is required for conducting the constant head permeability test?
-The equipment required includes a permeability cell, soil sample (sifted through a 20-mesh sieve), burette, graduated cylinder, filter paper, porous stone, spring, stopwatch, and water supply.
How is the soil sample prepared before the test?
-The soil sample is prepared by moistening it slightly, ensuring it is not too dry before starting the test. This helps in achieving consistent results by preventing the soil from being too compact or overly dry.
Why is it important to ensure the water level in the burette remains constant during the test?
-It is important to keep the water level in the burette constant to maintain steady water flow into the soil. This ensures that the permeability test results are accurate and reliable, reflecting true soil behavior under constant water input.
What is measured during the permeability test and how is the data recorded?
-During the permeability test, the volume of water passing through the soil over fixed intervals is measured. The height of the water in the burette is recorded at each interval, and the data is used to calculate the permeability rate of the soil.
How long does the constant head permeability test typically last?
-The constant head permeability test typically lasts for up to 30 minutes, though the duration may vary depending on the type of soil and the experimenter's requirements. The test is repeated for multiple trials to ensure accuracy.
What is the significance of recording the water volume at regular intervals during the test?
-Recording the water volume at regular intervals is essential for calculating the flow rate of water through the soil. This data helps determine the soil's permeability, which is crucial for understanding its drainage properties and suitability for various applications.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Unconfined Aquifer - Permeability of soil - Field test

Cara mencangkok pohon jambu air menggunakan tanah lebih cepat keluar akar (lengkap)
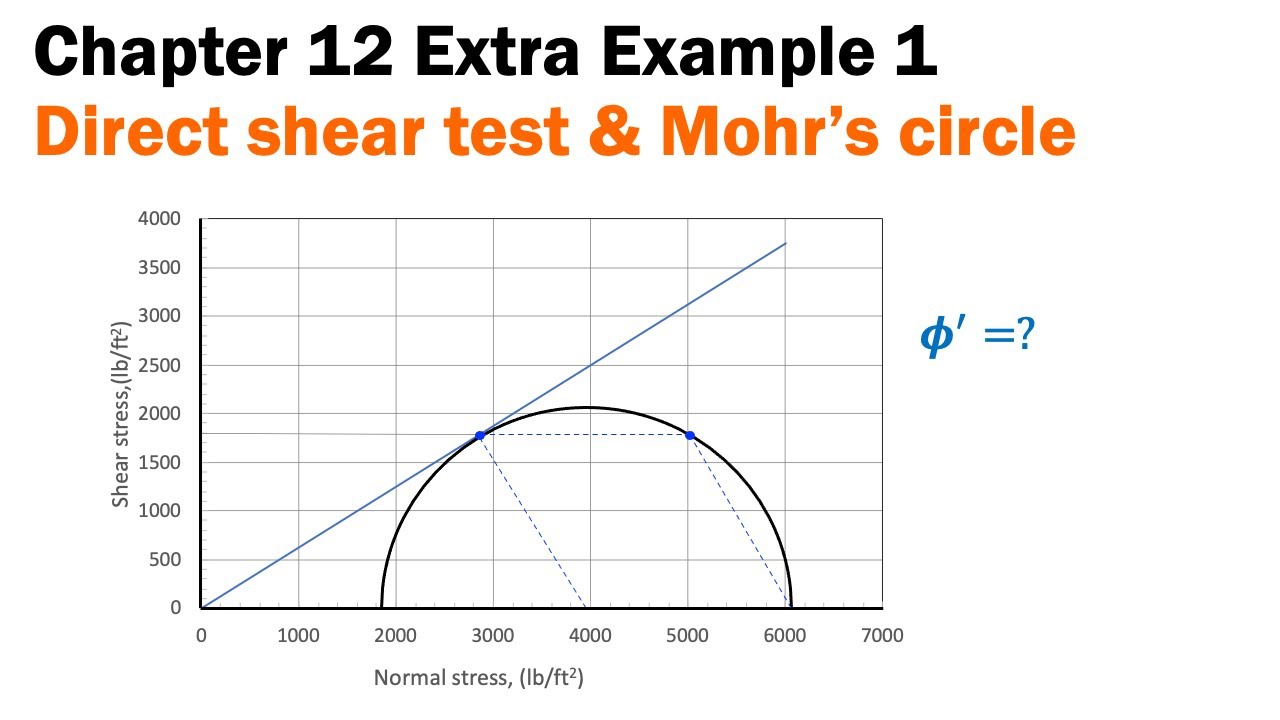
Chapter 12 Extra Example 1 - Direct shear test and Mohr's circle at failure
Soil Permeability - Darcy's Law

Soil Texture - Environmental Science

Cara Menguji Kualitas Tanah Metode Sederhana
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)