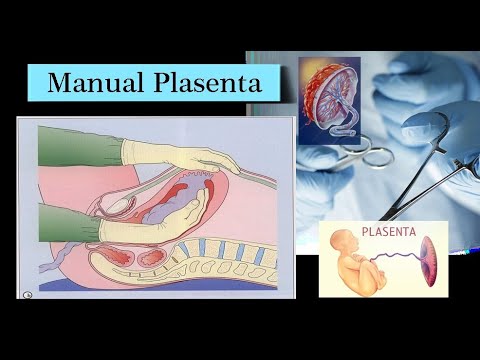
Kompresi Bimanual Interna dan Eksterna (KBI/KBE)
Summary
TLDRThis medical script outlines the step-by-step procedures for managing uterine atony in a laboring mother. It describes actions like internal and external bimanual compression, the use of a hydrostatic catheter, and related interventions, including the administration of uterotonics, oxygen, and IV fluids. The script emphasizes careful monitoring of bleeding, patient positioning, and the preparation of necessary medical equipment. The entire process involves sterilization, infection control, and close observation, ensuring the patient’s safety while stabilizing the condition. The sequence of interventions aims to control hemorrhage and ensure a successful outcome for both the mother and baby.
Takeaways
- 😀 The procedure is performed on mothers experiencing uterine atony after childbirth.
- 😀 The preparation includes informing the patient and family about the condition and the planned procedures.
- 😀 Full protective equipment is required, including a mask, gloves, sterile instruments, and a protective suit.
- 😀 The necessary tools for the procedure include sterile gloves, gauze, sterile cotton, and various medications like oxytocin, methylergonovine, and misoprostol.
- 😀 Medical staff should wash hands thoroughly and wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) before beginning the procedure.
- 😀 The patient should be placed in a dorsal recumbent position, and the vulva should be cleaned properly.
- 😀 A Nelaton catheter is used to empty the bladder to ensure it's not the source of bleeding.
- 😀 Internal bimanual compression (KBBI) is performed by inserting the hand into the uterus to apply pressure and stop bleeding.
- 😀 After KBBI, the bleeding is reassessed, and if it doesn't stop, external bimanual compression (KB) is applied.
- 😀 In case of persistent bleeding, the hydrostatic catheter technique is used, involving a condom catheter and an infusion of saline or other fluids to control bleeding.
- 😀 The procedure requires continuous monitoring of vital signs and regular observation of the patient every 15 minutes to check for bleeding control.
Q & A
What is the primary goal of the procedures mentioned in the script?
-The primary goal is to manage uterine atony during labor, specifically addressing postpartum hemorrhage through a series of compression techniques and catheterization to control bleeding.
What is bimanual compression, and how is it applied internally (KBBI)?
-Bimanual compression involves the simultaneous use of both hands to apply pressure to the uterus. Internally, the procedure is done by placing one hand in the uterus and using the other hand on the abdomen to compress the uterus and control bleeding.
How should the patient be positioned for the procedures?
-The patient should be positioned in the dorsal recumbent position, which is a lying down position with the back flat and knees bent.
What are the essential tools and materials required for the procedure?
-The required tools and materials include sterile gloves, sterile cotton, Nelaton catheter, lubricant, uterotonic medications like oxytocin, Misoprostol, Methergin, infusion sets, antiseptic, oxygen equipment, and various instruments for compression and catheter insertion.
What is the role of the Nelaton catheter in this procedure?
-The Nelaton catheter is used for urinary catheterization to empty the bladder and ensure it is not distended during the procedure, which could interfere with uterine compression.
How is external bimanual compression (KB) performed?
-External bimanual compression involves the assistant standing next to the patient and applying pressure with both hands on the abdomen to help control bleeding while the primary care provider manages internal compression.
What actions should be taken if bleeding persists after initial compressions?
-If bleeding continues after the first round of bimanual compression, additional interventions such as repeating internal compression, administering uterotonic medications, or preparing for catheterization and referral should be carried out.
How is the hydrostatic catheter inserted, and what is its purpose?
-The hydrostatic catheter involves the insertion of a condom catheter into the cervix, connected to an infusion set with saline or other fluids. The catheter helps apply pressure to the cervix and control bleeding by inducing hydrostatic pressure.
What precautions should be taken before starting the procedures?
-Precautions include thoroughly washing hands with soap and water, wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) like gloves, masks, and face shields, ensuring proper positioning of the patient, and preparing all required medical tools.
What should be done if bleeding stops after compression?
-If the bleeding stops after compression, the healthcare team should observe the patient for at least two minutes to ensure stability and continue monitoring vital signs at regular intervals, such as every 15 minutes.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)