The Central Dogma: DNA to proteins (an animated lecture video)
Summary
TLDRThis lecture delves into the fundamentals of DNA's role in protein synthesis, exploring the molecular structures of nucleic acids and proteins. It explains the central dogma of molecular biology, detailing the processes of transcription and translation. The lecture also covers the structure of DNA and RNA, the importance of base pairing, and the four-letter genetic code. It further discusses protein structure, including primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary levels, and uses sickle cell anemia as an example of how a single amino acid change can alter protein function, impacting health.
Takeaways
- 🧬 DNA is the genetic material that determines who you are, serving as a template for the synthesis of proteins.
- 📚 The central dogma of molecular biology explains the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to proteins.
- ✍️ Transcription is the process where DNA information is copied into mRNA, which then carries this information out of the nucleus.
- 🔍 The molecular structure of nucleic acids and proteins is crucial for understanding how genetic information is stored and utilized.
- 🔄 DNA replication is essential for cell division, ensuring each new cell receives the same genetic information.
- 🌐 The nitrogenous bases in DNA (adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine) pair specifically (A-T and C-G) to maintain genetic accuracy.
- 🔑 Transfer RNA (tRNA) plays a critical role in translation by matching the mRNA code with the appropriate amino acids.
- 🔗 The primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures of proteins are all important for their function and shape.
- 🌿 RNA, particularly mRNA, is involved in protein synthesis, while ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is a key component of the ribosome where protein synthesis occurs.
- 🌟 The discovery of the DNA double helix by Watson and Crick was a monumental achievement, illustrating how genetic information is physically stored.
- 🧬 Sickle cell anemia is an example of how a change in the primary structure of a protein (hemoglobin) can lead to disease.
Q & A
What is the central dogma of molecular biology?
-The central dogma of molecular biology states that DNA serves as a template for the direct synthesis of a messenger RNA molecule (mRNA), which is then read by transfer RNAs (tRNAs) at a ribosome to assemble a specific chain of amino acids, ultimately generating a protein.
How does DNA replicate itself?
-DNA replication is a process where the double-stranded DNA molecule serves as a template for the creation of two identical DNA molecules. Each new DNA molecule consists of one original and one newly synthesized strand.
What is the role of mRNA in protein synthesis?
-mRNA acts as a genetic messaging molecule that carries the information from DNA to the ribosome, where it is translated into a sequence of amino acids to form a protein.
What is the function of tRNA in the translation process?
-tRNA reads the mRNA sequence at the ribosome and links a specific amino acid to a growing protein chain, ensuring that the amino acids are added in the correct order as specified by the mRNA.
How does the three-dimensional shape of a protein relate to its function?
-The three-dimensional shape of a protein is crucial for its function, as it determines the protein's ability to bind to other molecules, catalyze reactions, or perform other cellular tasks. Any change in the shape can potentially alter the protein's function.
What is the significance of the Chargaff's rules in understanding DNA structure?
-Chargaff's rules revealed that in DNA, the amount of adenine is equal to thymine and the amount of guanine is equal to cytosine. This was a key clue that led to the discovery of the base pairing in the DNA double helix, where adenine pairs with thymine and guanine pairs with cytosine.
How does the process of transcription compare to sending a command to print a document from a computer?
-Transcription is analogous to sending a command to print a document from a computer. In transcription, the information stored in DNA is copied into mRNA, similar to how a computer file is sent as a message to a printer.
What is the difference between DNA and RNA in terms of their sugar component?
-DNA contains deoxyribose sugar, which lacks an oxygen atom at the 2' carbon, while RNA contains ribose sugar, which has a hydroxyl group (-OH) at the 2' carbon.
What are the four levels of protein structure, and how do they contribute to the protein's function?
-The four levels of protein structure are primary (amino acid sequence), secondary (local folding patterns like alpha helices and beta sheets), tertiary (overall three-dimensional shape), and quaternary (interactions between multiple polypeptide chains). These levels contribute to the protein's function by determining its shape and stability, which are essential for its activity within the cell.
How does the sickle cell anemia mutation affect the primary structure of hemoglobin?
-Sickle cell anemia is caused by a mutation in the hemoglobin gene that changes a single amino acid from glutamic acid to valine in the primary structure of the protein. This alteration affects the protein's shape and function, leading to the characteristic sickle shape of red blood cells.
What is the significance of the hydrogen bonding between nitrogenous bases in DNA?
-Hydrogen bonding between nitrogenous bases in DNA, specifically adenine with thymine and guanine with cytosine, is crucial for the stability of the DNA double helix and for accurate replication and transcription processes.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
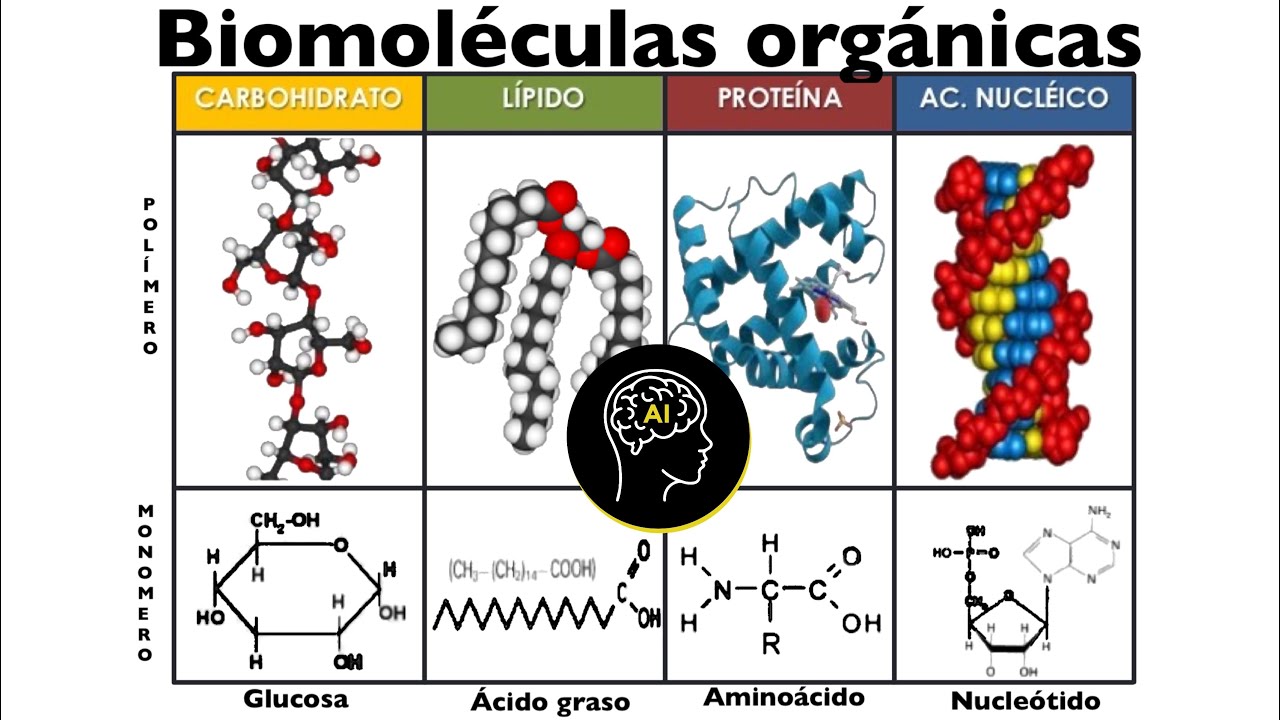
Biomoléculas presentes en células (orgánicas): carbohidratos, lípidos, proteínas y ácidos nucleicos

Chemistry Of Nucleic Acid!B.Sc 2nd Semester Complete Chemistry Maha Class Day-3!Be DKDian

Bio 251 Ch 2B

Genética e Biologia Molecular – Aula 02 – Estrutura e Função do DNA e RNA

LESSON ON DNA, RNA and MUTATION | IN FILIPINO

Genetic Principles
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)