Cahaya dan Alat Optik: Mekanisme Melihat pada Mata Manusia - SMP Kelas 8 | Part 2
Summary
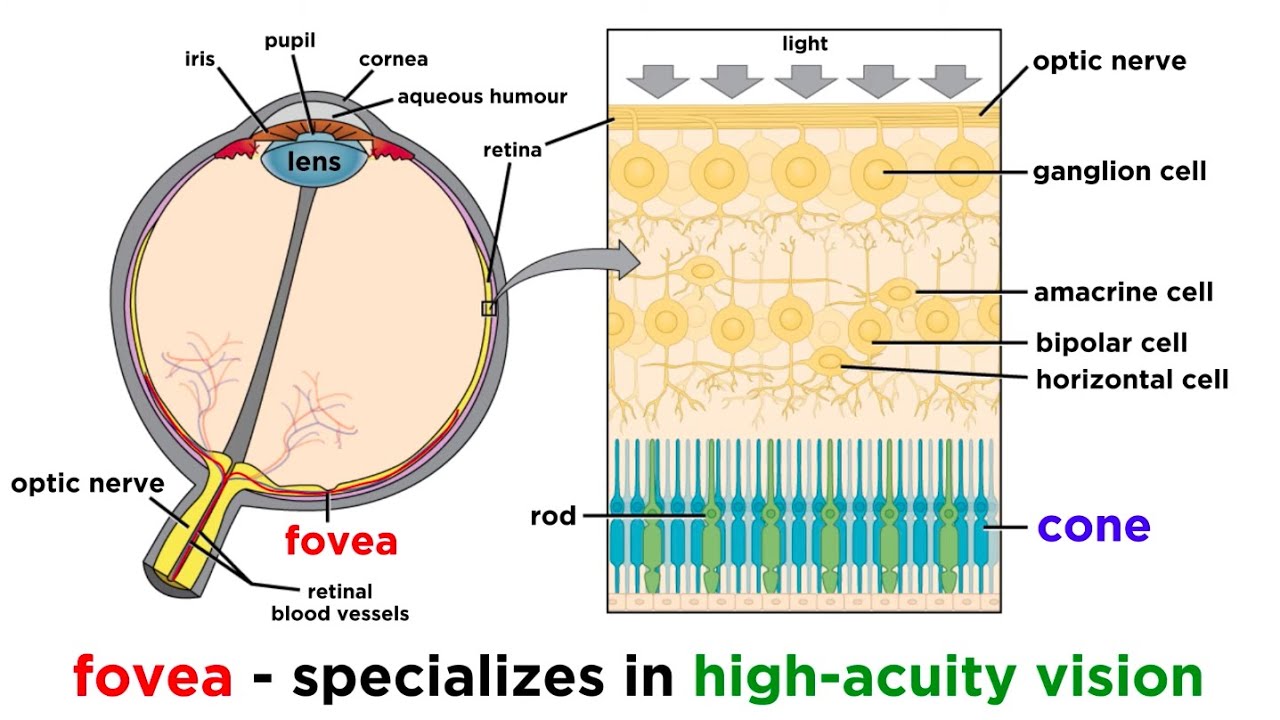
TLDRThis video explains the mechanism of human vision, starting with how light travels and interacts with the eye. It describes how light enters through the cornea, pupil, and lens, focusing on the retina to create an inverted, smaller image. The video also discusses how the brain processes this image to make it appear in its true form. Additionally, the video covers eye accommodation, explaining how the lens changes shape to focus on distant and near objects. Finally, it touches on how the iris and pupil regulate the amount of light entering the eye, adjusting to varying light conditions to protect vision.
Takeaways
- 😀 Light travels straight and bounces off objects before entering the eye.
- 😀 The pupil, the black circular part of the eye, allows light to enter and is key in vision.
- 😀 Light passes through the cornea, pupil, and lens before reaching the retina.
- 😀 The lens focuses light to form an image on the retina, making the image smaller and inverted.
- 😀 The optic nerve transmits the visual image from the retina to the brain for interpretation.
- 😀 The brain processes the image to make it appear as it actually is: correct size, shape, and color.
- 😀 The eye's accommodation ability helps adjust the lens shape for clear vision at different distances.
- 😀 When viewing distant objects, the lens becomes flatter and thinner, focusing the image on the retina.
- 😀 For near objects, the lens becomes thicker and rounder to focus the image properly on the retina.
- 😀 The iris controls the size of the pupil, adjusting it based on light conditions for optimal vision.
- 😀 In dark conditions, the pupil dilates to allow more light in, while in bright conditions, it constricts to reduce light intake and prevent eye strain.
Q & A
What is the pupil of the eye, and what is its role in vision?
-The pupil is the black circular area in the center of the eye. It regulates the amount of light entering the eye, allowing us to see clearly in different lighting conditions.
Can you describe the process of how we see an object?
-First, light travels in a straight line and hits an object. The light then reflects into the eye through the cornea, pupil, and lens. The lens focuses the light so that the image is projected onto the retina. The brain processes this image to help us see the object clearly.
What happens when light enters the eye and reaches the retina?
-When light enters the eye and reaches the retina, a real, inverted, and smaller image is formed. The retinal nerve cells then send the image to the brain, which interprets it to match the object’s true size and orientation.
What is the role of the lens in vision?
-The lens focuses light entering the eye onto the retina, ensuring that the image formed on the retina is clear. The lens changes shape depending on whether the object is near or far, helping us focus on objects at different distances.
What is accommodation in the eye, and why is it important?
-Accommodation is the ability of the eye to change the curvature of the lens to focus on objects at varying distances. This allows us to see both near and far objects clearly by adjusting the lens’s shape.
How does the eye adjust to see distant objects?
-When focusing on distant objects, the eye’s ciliary muscles relax, causing the lens to flatten. This reduces the curvature of the lens, ensuring the light focuses correctly on the retina.
How does the eye adjust to see nearby objects?
-When focusing on nearby objects, the eye’s ciliary muscles contract, causing the lens to become thicker and more curved. This increases the lens’s power to focus light from nearby objects onto the retina.
What is the iris, and what is its function?
-The iris is the colored part of the eye, made of circular muscles that control the size of the pupil. It adjusts the pupil's size in response to light, allowing more or less light to enter the eye.
How does the pupil react in different lighting conditions?
-In dim light, the pupil dilates to allow more light into the eye, improving vision. In bright light, the pupil constricts to limit the amount of light entering, protecting the retina from excessive brightness.
What can happen if too much light enters the eye?
-If too much light enters the eye, it can cause discomfort, leading to glare. Prolonged exposure to excessive light may also damage the retina and lens, impairing vision.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Cahaya dan Alat Optik: Indra Penglihatan Manusia (Bagian-Bagian Mata) - SMP Kelas 8 | Part 1

Vision: Crash Course Anatomy & Physiology #18

Eye Anatomy and Function - Made Easy

Exploring Light Energy - General Science for Kids!

Light | The Dr. Binocs Show | Learn Videos For Kids
Visual Processing and the Visual Cortex
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)