Megathrust Indonesia: Bagaimana cara menghadapinya?
Summary
TLDRIndonesia, located on the Pacific Ring of Fire, faces a high risk of earthquakes and tsunamis due to its position at the intersection of three major tectonic plates. The video highlights the importance of earthquake preparedness, outlining actions to take during and after an earthquake. It emphasizes safety measures like seeking shelter indoors, staying away from hazardous areas, and following evacuation routes. Additionally, the video discusses Indonesia's seismic zones, megathrust earthquake risks, and the need for effective early warning systems and public education to minimize the impact of such natural disasters.
Takeaways
- 😀 Indonesia is highly susceptible to earthquakes due to its location on the Pacific Ring of Fire, where tectonic plates frequently interact.
- 😀 Earthquakes in Indonesia can lead to tsunamis, making it crucial for the public to understand both earthquake and tsunami risks.
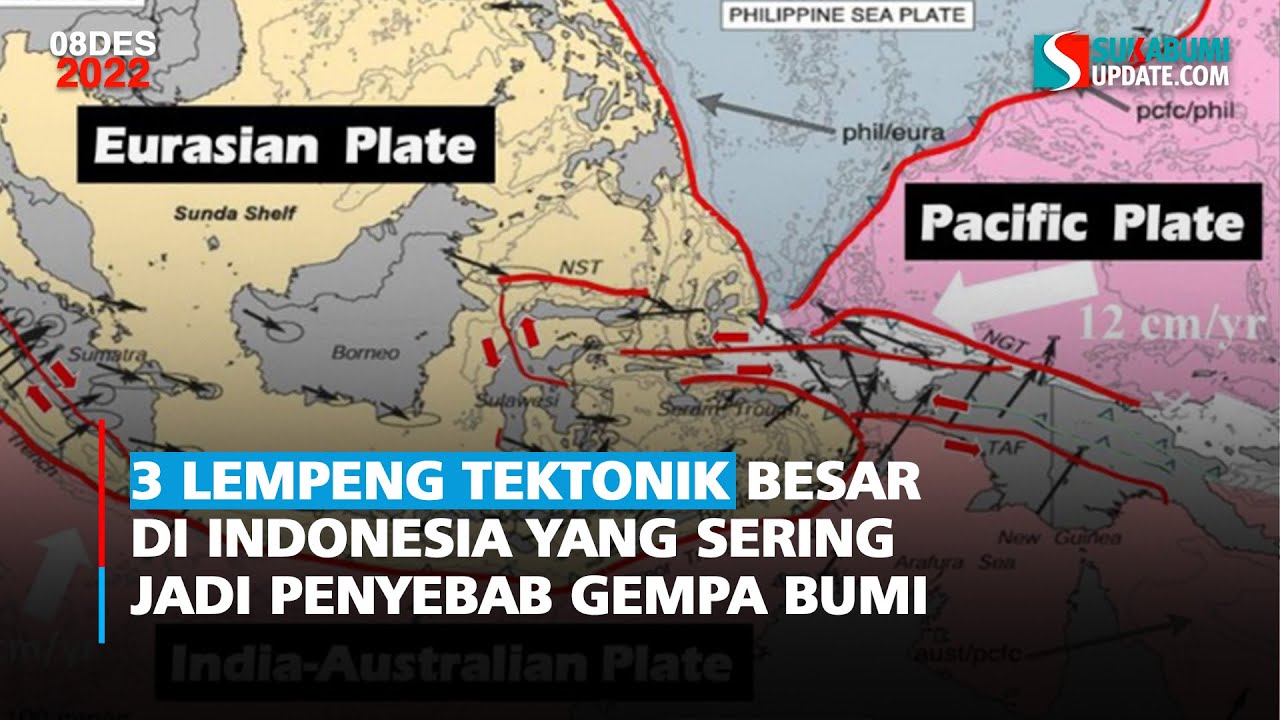
- 😀 Indonesia sits at the intersection of three major tectonic plates: Indo-Australian, Eurasian, and Pacific plates, which increases seismic activity.
- 😀 The country's geography includes several subduction zones, particularly along the Sunda and Banda subduction zones, which are prone to major earthquakes.
- 😀 Earthquake megathrust zones in Indonesia, like Aceh-Andaman and Mentawai-Siberut, pose a high risk of producing large-scale quakes and tsunamis.
- 😀 The Indonesian Meteorological, Climatological, and Geophysical Agency (BMKG) regularly warns of potential megathrust earthquakes, especially in areas that have not experienced significant seismic events for centuries.
- 😀 Although technology can monitor seismic activity, predicting the exact timing of a major earthquake remains impossible.
- 😀 Historical earthquakes, such as the 2004 Aceh earthquake, highlight the ongoing risk of megathrust earthquakes in Indonesia.
- 😀 Disaster preparedness, including education and regular simulation drills, is vital for reducing casualties and increasing public awareness of earthquake risks.
- 😀 Key safety actions during an earthquake include staying calm, seeking shelter under sturdy objects, avoiding windows, and waiting for the shaking to stop before evacuating.
Q & A
What is the Ring of Fire and why is Indonesia at higher risk of earthquakes?
-The Ring of Fire is a group of regions around the Pacific Ocean where frequent seismic and volcanic activity occurs due to the movement of tectonic plates. Indonesia is located in this area and is at a higher risk of earthquakes because it is situated at the intersection of three major tectonic plates: the Indo-Australian, Eurasian, and Pacific plates.
What are the main tectonic zones in Indonesia that cause earthquakes?
-The main tectonic zones in Indonesia include the Sunda subduction zone, the Banda subduction zone, and the megathrust zones such as those along Sumatra, Java, and other regions. These areas are where tectonic plates converge and cause powerful earthquakes and tsunamis.
What is a megathrust earthquake and how does it differ from other types of earthquakes?
-A megathrust earthquake occurs in subduction zones, where one tectonic plate slides beneath another. These earthquakes are particularly powerful, often exceeding a magnitude of 8, and can trigger large tsunamis. They differ from other earthquakes because they involve the movement of oceanic and continental plates at great depths, leading to massive seismic activity.
Why are megathrust earthquakes in Indonesia hard to predict?
-Megathrust earthquakes in Indonesia are hard to predict because there is no technology currently capable of forecasting the exact timing of an earthquake. Although scientists monitor seismic activity, the process of predicting when the energy will be released in a megathrust zone remains uncertain.
What measures should be taken to prepare for a potential megathrust earthquake in Indonesia?
-To prepare for a megathrust earthquake, measures include educating the public about earthquake safety, conducting regular earthquake and tsunami simulations, building earthquake-resistant infrastructure, developing early warning systems, and continuously researching seismic activity to understand the patterns of tectonic movement.
What is the significance of seismic gaps in the context of megathrust earthquakes?
-Seismic gaps are areas in subduction zones where there has been no significant earthquake activity for a long time, potentially signaling an accumulation of tectonic stress. These gaps are considered a warning that a major earthquake might occur once the accumulated stress surpasses the friction between the plates.
What should individuals do if they are inside a building when an earthquake occurs?
-If inside a building during an earthquake, individuals should seek shelter under sturdy furniture, such as a table or desk, to protect themselves from falling objects. They should avoid windows, heavy objects, and elevators. After the shaking stops, they should check for hazards like broken gas lines and electrical wires before exiting the building.
How should individuals respond if they are outside when an earthquake occurs?
-If outside during an earthquake, individuals should move to an open area away from buildings, trees, and power lines. They should avoid taking shelter under bridges or overpasses, as these structures could collapse. It is essential to remain in an open space until the shaking stops.
What are the primary actions to take after an earthquake stops shaking?
-After the shaking stops, individuals should check for injuries and provide first aid if needed. They should look for hazards like fallen debris or broken electrical wires and avoid entering damaged buildings. If near the coast, they should evacuate to higher ground in case of a tsunami warning.
Why is it important to listen to official warnings and information after an earthquake?
-Listening to official warnings and information is crucial after an earthquake to stay informed about potential aftershocks, tsunami risks, and evacuation orders. It ensures that individuals can make safe decisions based on the latest updates from authorities, helping to reduce further risk and harm.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)