Prategangan DC No 2
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Mohamad Ramdhani walks through the analysis of a BJT transistor circuit with DC voltage. He begins by explaining the identification of transistor terminals (emitter, base, and collector) and determining the type of BJT (NPN). The video covers key concepts such as current direction, assumptions for active operation, and how to calculate various parameters like base current and voltage potential across the transistor. The analysis includes simplifications for DC voltage analysis and practical steps for determining the working regions of the transistor, demonstrating its use in amplification.
Takeaways
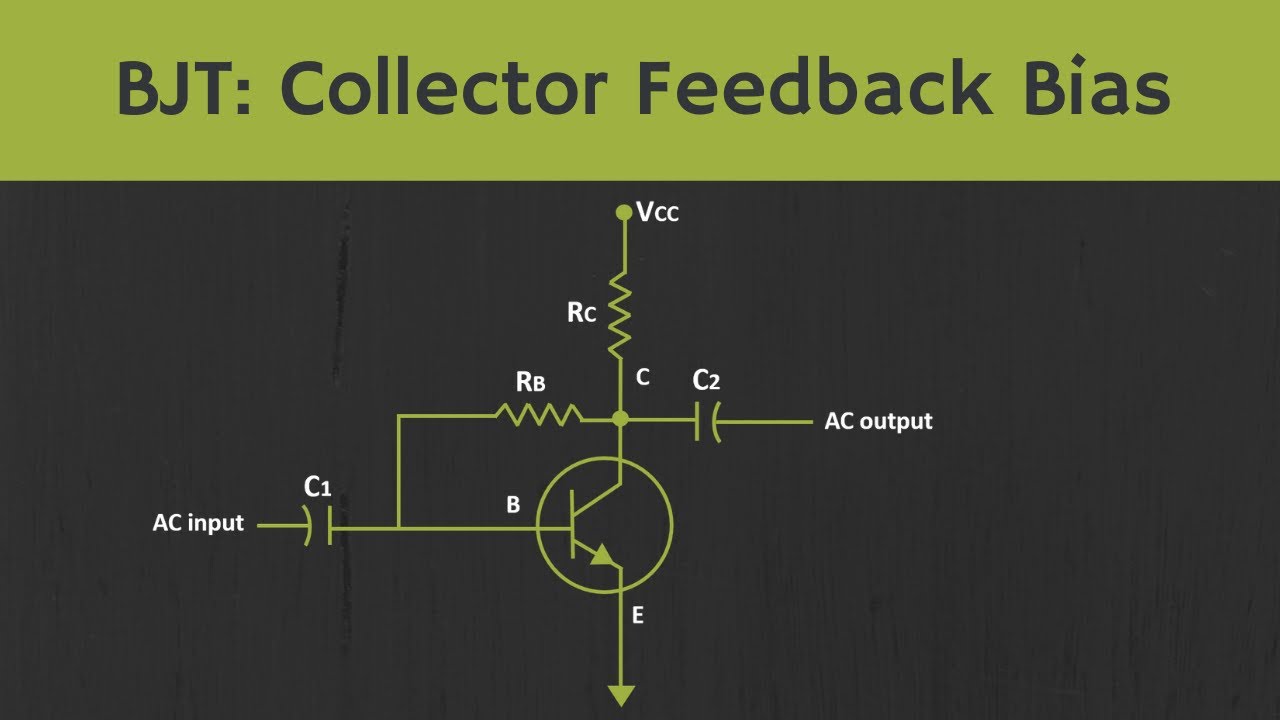
- 😀 The video discusses an analysis of a DC circuit using a BJT transistor.
- 😀 The first step is to identify the terminals of the transistor: base, collector, and emitter.
- 😀 The script emphasizes the importance of identifying the transistor type (NPN) by observing the current flow direction.
- 😀 Assumptions are made that the transistor is active during the analysis.
- 😀 The value of the active transistor's current gain (β) is assumed to be 0.76 for the NPN type.
- 😀 The current at the base (Ib) is calculated as 0.02 mA based on the applied voltage and resistance.
- 😀 The collector current (Ic) is found to be 2.3 mA based on the current at the base and transistor's current gain.
- 😀 Potentials at different terminals are calculated, with the base voltage calculated to be 3V and the collector voltage at 3.1V.
- 😀 The video explains how to analyze the DC potential at various points in the circuit, particularly at the base, collector, and emitter.
- 😀 The BJT is confirmed to be operating in the active region, as the base-emitter and collector-base junctions are forward-biased and reverse-biased, respectively.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the video script?
-The main focus of the video script is performing an analysis of a DC voltage circuit using a Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT), specifically an NPN transistor.
How are the terminals of the transistor identified in the analysis?
-In the analysis, the terminals of the transistor are identified as the base (B), collector (C), and emitter (E). The script outlines the process of determining the direction of current flow through these terminals.
What type of transistor is used in the analysis?
-The analysis is based on an NPN BJT (Bipolar Junction Transistor).
What are the initial assumptions made about the transistor in the circuit?
-The initial assumptions include that the transistor is in the active region and that its β (beta) value is 100. Additionally, the base-emitter voltage (V_BE) is assumed to be 0.7V.
What is the role of the base current (I_B) in the transistor analysis?
-The base current (I_B) plays a crucial role in determining the collector current (I_C) as the collector current is a function of the base current, with I_C = β × I_B.
How is the emitter current (I_E) calculated?
-The emitter current (I_E) is calculated by adding the base current (I_B) and the collector current (I_C), i.e., I_E = I_C + I_B.
What is the significance of the forward biasing of the base-emitter junction?
-The forward biasing of the base-emitter junction is crucial because it allows current to flow from the emitter to the base, enabling the transistor to operate in the active region for amplification.
What is the value of the base voltage (V_B) in the analysis?
-The base voltage (V_B) is calculated as 0.76V, which is derived from the voltage supply minus the drop across the base resistor.
What is the calculated value of the collector current (I_C) in the analysis?
-The collector current (I_C) is calculated to be 2.3 mA, based on the base current and the transistor's β value.
How is the collector voltage (V_C) determined in the circuit?
-The collector voltage (V_C) is determined by subtracting the voltage drop across the collector resistor (R_C) from the supply voltage (V_CC). The final value obtained for V_C is 3.1V.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)