Atoms to Ions | Atom | Lesson 6 | National 5 Chemistry
Summary
TLDRThe video explains the concept of electron arrangement and how atoms achieve stability by gaining or losing electrons to form ions. It covers the electron configurations of various elements such as lithium, beryllium, aluminium, nitrogen, oxygen, and fluorine. The video also highlights how metal atoms lose electrons to form positive ions and non-metal atoms gain electrons to form negative ions. The process of ionic bonding between these ions is also discussed, along with examples like sodium chloride formation. The importance of achieving a full, stable outer electron shell is emphasized throughout.
Takeaways
- 😀 All elements aim to have a full stable outer electron shell, similar to noble gases in group 8 of the periodic table.
- 😀 The number of electrons in an atom's outermost energy level determines its electron arrangement and stability.
- 😀 The first energy level can hold a maximum of 2 electrons, the second can hold 8, and the third also aims for 8 electrons.
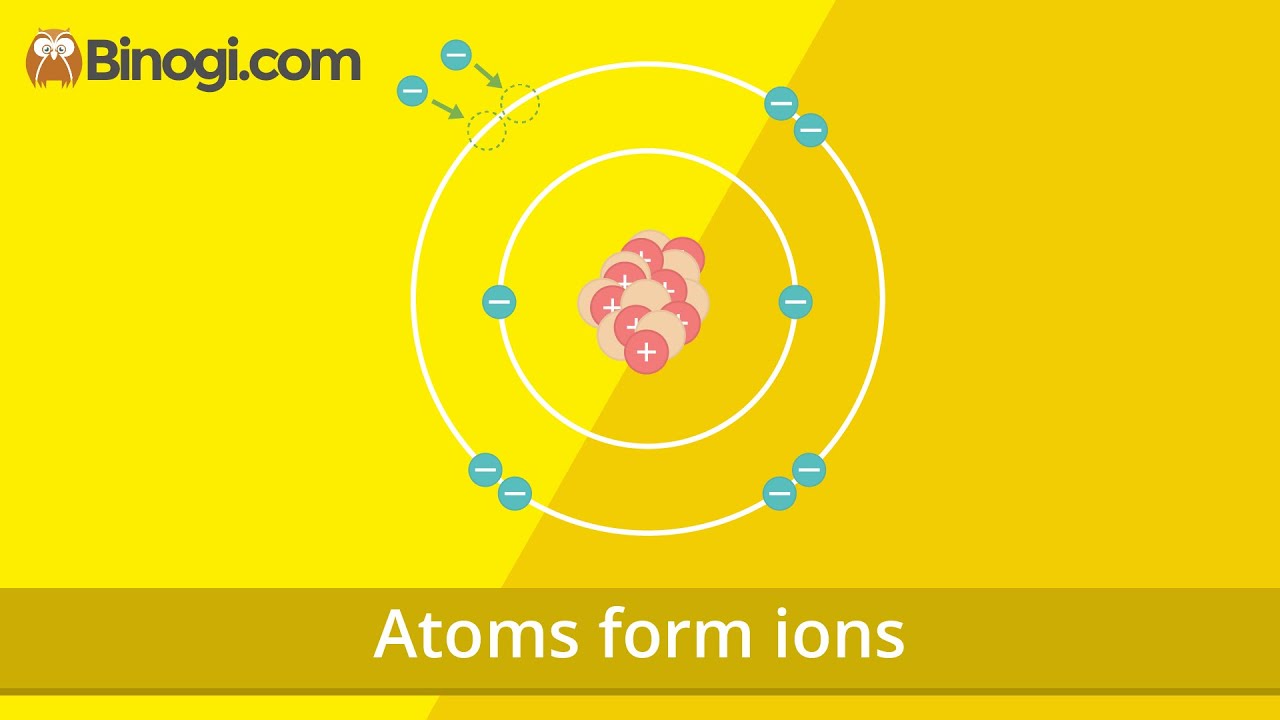
- 😀 Metal elements, located on the left side of the periodic table, tend to lose electrons and form positive ions.
- 😀 The lithium atom, with the electron arrangement 2, 1, loses one electron to become a positive ion with a +1 charge.
- 😀 Beryllium (with electron arrangement 2, 2) loses two electrons to form a 2+ ion.
- 😀 Aluminium (with electron arrangement 2, 8, 3) loses three electrons to form a 3+ ion.
- 😀 Non-metal elements, found on the right side of the periodic table, tend to gain electrons and form negative ions.
- 😀 The noble gases (group 0) already have a stable electron arrangement and do not form ions.
- 😀 When a nitrogen atom (electron arrangement 2, 5) gains three electrons, it forms a 3- ion.
- 😀 Chlorine gains an electron from sodium to achieve a stable electron arrangement, forming a chloride ion (Cl-).
- 😀 In ionic bonding, metal atoms lose electrons to non-metal atoms, forming positive and negative ions that attract each other through electrostatic forces.
Q & A
Why do all elements aim to have a full stable outer electron shell?
-Elements aim to achieve a full stable outer electron shell because it provides them with stability, similar to the noble gases in group eight of the periodic table, which already have a stable configuration.
How many electrons can the first energy level hold?
-The first energy level can hold a maximum of two electrons.
How many electrons can the second and third energy levels hold?
-Both the second and third energy levels can hold a maximum of eight electrons.
What happens to the lithium atom when it aims for stability?
-The lithium atom has an electron arrangement of 2,1 and will lose one electron to achieve a stable configuration, resulting in a positively charged ion (Li+).
What is the electron arrangement of beryllium, and how does it achieve stability?
-Beryllium has the electron arrangement 2,2 and achieves stability by losing two electrons to form a Be2+ ion.
How does aluminum achieve a stable electron arrangement?
-Aluminum has the electron arrangement 2,8,3 and achieves stability by losing three electrons to form an Al3+ ion.
What is the behavior of non-metal elements in terms of electron loss or gain?
-Non-metal elements gain electrons to form negative ions, unlike metals that lose electrons to form positive ions.
How does the nitrogen atom achieve a stable electron arrangement?
-Nitrogen has the electron arrangement 2,5 and achieves stability by gaining three electrons to form a negatively charged nitrogen ion (N3-).
What is the electron arrangement of oxygen, and how does it achieve stability?
-Oxygen has the electron arrangement 2,6 and achieves stability by gaining two electrons to form an O2- ion.
How does fluorine achieve stability?
-Fluorine has the electron arrangement 2,7 and achieves stability by gaining one electron to form a fluoride ion (F-).
What is the process of ionic bonding as described in the transcript?
-Ionic bonding occurs when metal atoms lose electrons to form positive ions, and these electrons are transferred to non-metal atoms, which form negative ions. The opposite charges of the ions create an electrostatic attraction that holds them together.
How does chlorine achieve a stable electron arrangement when it reacts with sodium?
-Chlorine has the electron arrangement 2,8,7, and it gains one electron from the sodium atom to achieve a stable electron arrangement, becoming a chloride ion (Cl-).
What is the significance of the atomic number in determining the properties of an element?
-The atomic number of an element is equal to the number of protons in its nucleus and determines the element's identity and many of its chemical properties.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

KESTABILAN UNSUR (PENGANTAR IKATAN KIMIA - KIMIA SMA KELAS 10)

Partikel Penyusun Benda dan Makhluk Hidup (Part-2) Konfigurasi Elektron, Ion dan Ikatan Ion

GCSE Chemistry - What is Ionic Bonding? How Does Ionic Bonding Work? Ionic Bonds Explained #14
Atoms form ions (Chemistry) - Binogi

GCSE Chemistry - Formation of Ions #13

What's an Ion?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)