Kajian Keuanan Daerah Sesi III "Manajemen Pendapatan Daerah
Summary
TLDRThis video discusses the management of regional government revenues, emphasizing the importance of understanding fiscal cycles such as revenue identification, administration, collection, accounting, and allocation. It highlights the different sources of income for local governments, including local taxes, retributions, and central government transfers. Strategies to optimize revenue, such as intensification and expansion of tax bases, as well as reducing income leakage, are covered. The session also touches on improving fiscal independence for local governments through better management practices, illustrating these points with findings from a study on fiscal autonomy in West Java.
Takeaways
- 😀 The effective management of regional income is crucial for the provision of public services and governance by local governments.
- 😀 Public financial management in the region is supported by three main pillars: income management, cost management, and financing management.
- 😀 There are five key cycles in regional income management: identification, administration, collection, accounting, and allocation of income.
- 😀 The identification cycle includes determining income sources and potential amounts based on legal regulations.
- 😀 The administration cycle involves categorizing taxpayers and establishing relevant tax and retribution categories.
- 😀 The collection cycle focuses on collecting taxes and fees through official assessment, self-assessment, or joint collection with third parties.
- 😀 The accounting cycle emphasizes proper record-keeping of income, which is crucial for financial transparency and reporting.
- 😀 The allocation cycle determines how much income is directed towards public spending, including operational and capital expenditures.
- 😀 Four main sources of regional income include: regional original income, central government transfers, inter-regional transfers, and other legitimate income sources.
- 😀 Strategies to enhance regional income include intensification (optimizing existing sources), extensification (expanding income sources), and improving public service delivery.
- 😀 Fiscal independence is a key indicator of local government capability to manage its finances, with a focus on reducing reliance on central government transfers.
Q & A
What are the three key pillars for effective public sector financial management?
-The three key pillars for effective public sector financial management are: 1) Revenue management, 2) Cost management, and 3) Financing management.
Why is it important for the government bureaucracy to manage regional revenue effectively?
-It is important for the government bureaucracy to manage regional revenue effectively because revenue significantly impacts public service delivery, the functioning of the regional government, and the implementation of government programs and activities.
What are the five key cycles in regional revenue management?
-The five key cycles in regional revenue management are: 1) Identification of revenue sources, 2) Revenue administration, 3) Revenue collection, 4) Revenue accounting, and 5) Allocation of revenue for regional expenditures.
What are the different systems used in revenue collection by local governments?
-The three main systems used in revenue collection are: 1) Official Assessment System (where the government calculates and collects taxes), 2) Self-Assessment System (where taxpayers calculate and pay taxes themselves), and 3) Joint Collection System (where local government collaborates with third parties to collect taxes, such as PLN for street lighting taxes).
What are the four main sources of regional revenue?
-The four main sources of regional revenue are: 1) Local Revenue (PAD), 2) Transfers from the central government, 3) Transfers between regions, and 4) Other legitimate regional income.
How does local revenue (PAD) contribute to regional financial management?
-Local Revenue (PAD) contributes to regional financial management by covering local government expenses through taxes, levies, and income from asset management. It includes sources such as local taxes, regional retributions, and parts of the profits from the management of regional assets.
What is the difference between taxes and retributions in the context of local government revenue?
-Taxes are mandatory payments made by individuals or entities to the government without direct compensation, used for public services. Retributions, on the other hand, are fees paid in exchange for specific services or permits provided by the government, with a direct benefit to the payer.
What strategies can local governments use to increase Local Revenue (PAD)?
-Local governments can increase PAD by implementing three strategies: 1) Intensification (optimizing existing revenue sources), 2) Extensification (developing new taxable objects and subjects), and 3) Improving public service to attract more investors, thereby boosting revenue from retributions.
What are the four basic principles in regional revenue management?
-The four basic principles in regional revenue management are: 1) Expanding the revenue base, 2) Controlling revenue leakage, 3) Improving the efficiency of tax administration, and 4) Ensuring transparency and accountability in revenue management.
How is fiscal independence determined for regions in Indonesia?
-Fiscal independence for regions in Indonesia is determined by the ratio of Local Revenue (PAD) to total regional revenue, as outlined by the Ministry of Home Affairs (Permendagri) regulations. A higher PAD ratio indicates greater fiscal independence, reducing reliance on central government transfers.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Estágios da Receita Pública - Previsão, Lançamento, Arrecadação, Recolhimento (Aula 14)

Akuntansi Pemerintah SMK Kelas XI - Pencatatan Keuangan Pemerintah Daerah

Praktikum Akuntansi Lembaga Kelas 11 AKL - Pemerintah Pusat Dan Daerah - SMK Doa Bangsa

Desain Perubahan Dana Bagi Hasil (DBH) di UU HKPD (UU 1/2022)
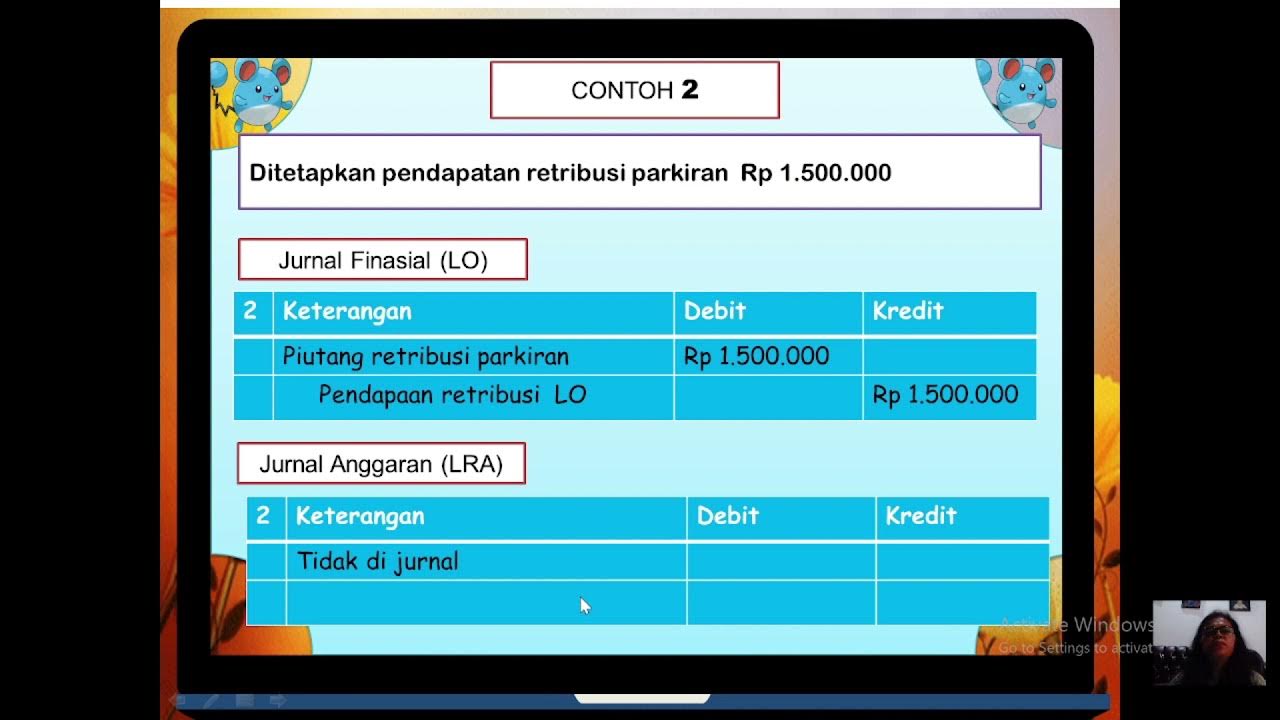
JURNAL SKPD AKUNTANSI PEMERINTAHAN

Konsep Dasar Akuntansi Manajemen
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)