Asam karboksilat dan ester
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the concepts of carboxylic acids and esters, focusing on their structures, naming conventions, and reactions. Carboxylic acids contain a carboxyl group (-COOH), and their names depend on the number of carbon atoms, such as Methanoic Acid for one carbon and Ethanoic Acid for two carbons. Esters, formed through esterification, are known for their fragrant properties and are named by combining the alkyl group from alcohol and the alkanoate group from carboxylic acid. The video also covers the synthesis and hydrolysis of esters, using examples like Methyl Pentanoate and Ethyl Hexanoate, which represent floral and fruity fragrances respectively.
Takeaways
- 😀 Organic compounds like carboxylic acids and esters are discussed, with their general formula CNH2n.
- 😀 Carboxylic acids have a functional group -COOH, which includes a carboxyl group (C=O and OH), and their pH is less than 7, making them acidic.
- 😀 Esters are characterized by the -COO functional group, which is often surrounded by alkyl groups.
- 😀 Carboxylic acids are named with 'acid' followed by the number of carbon atoms in the molecule (e.g., methanoic acid for one carbon, ethanoic acid for two).
- 😀 The naming for esters follows the format 'alkyl alkanoate' where the alkyl group comes from alcohol and the alkanoate group comes from carboxylic acid.
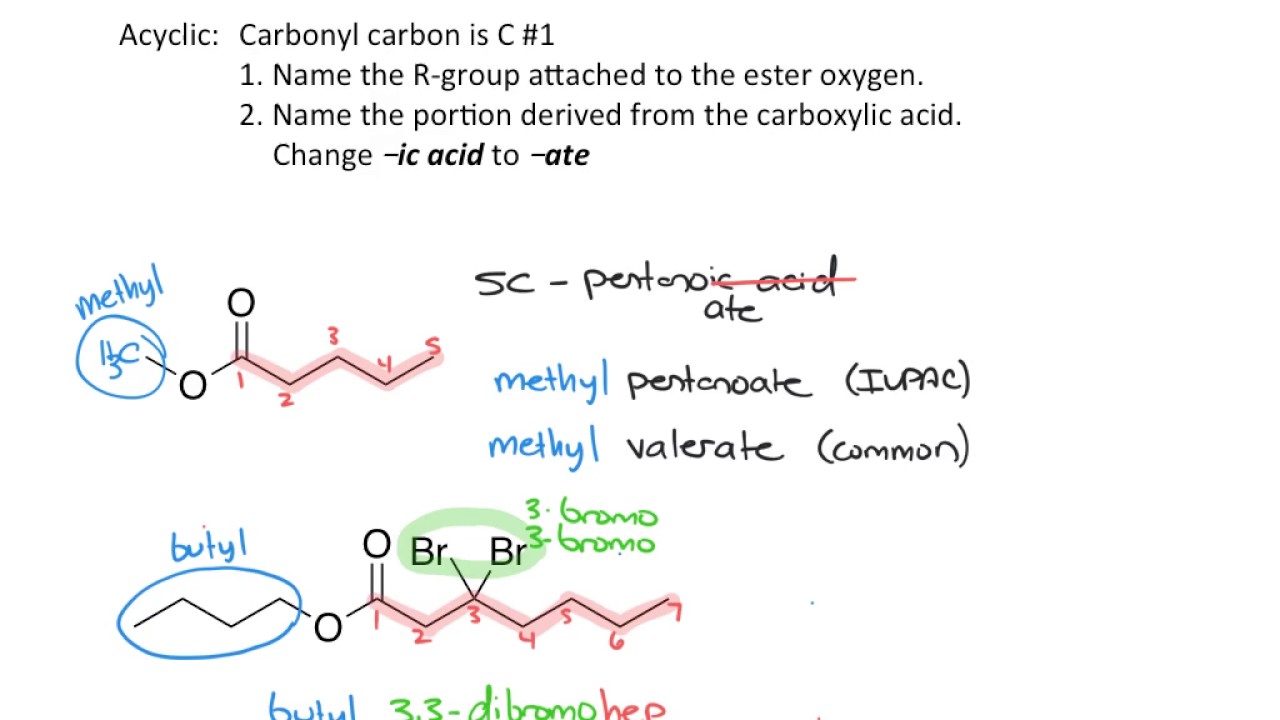
- 😀 Ester compounds, such as methyl pentanoate, have distinctive fragrances like the scent of flowers or fruits.
- 😀 Esters are typically created through a process called esterification, where a carboxylic acid reacts with alcohol, producing an ester and water.
- 😀 Esterification can be reversed by hydrolysis, splitting the ester into a carboxylic acid and alcohol using water.
- 😀 For example, to synthesize methyl pentanoate (which smells like flowers), methanol reacts with pentanoic acid.
- 😀 Ester synthesis allows for creating different scents like pineapple, apple, and others by mixing specific alcohols with corresponding carboxylic acids.
- 😀 The esterification reaction is key in creating fragrances without needing to extract them from their natural sources, such as mixing ethanol and hexanoic acid to create ethyl hexanoate (pineapple scent).
Q & A
What are carboxylic acids and esters?
-Carboxylic acids and esters are organic compounds. Carboxylic acids contain a carboxyl group (-COOH), while esters contain an ester group (-COO). Both compounds have distinct functional groups and are important in organic chemistry.
What is the general formula for carboxylic acids and esters?
-Both carboxylic acids and esters share the general formula CnH2n+2 for their alkyl or alkanoat components. Carboxylic acids specifically include a carboxyl group (-COOH), while esters include a COO group.
How do you name carboxylic acids?
-Carboxylic acids are named by identifying the number of carbon atoms in the molecule. The prefix 'acid' is used, followed by the name of the alkanoic acid based on the number of carbon atoms, such as 'methanoic acid' for one carbon, 'ethanoic acid' for two, etc.
How do you name esters?
-Esters are named by combining the names of the alkyl group (derived from the alcohol) and the alkanoate group (derived from the carboxylic acid). For example, 'methyl methanoate' comes from methanol and methanoic acid.
What is the difference in naming between carboxylic acids and esters?
-Carboxylic acids are named using the suffix '-oic acid,' based on the number of carbon atoms, while esters are named using the combination of an alkyl group and '-oate' derived from the carboxylic acid, such as 'ethyl pentanoate.'
What is esterification?
-Esterification is a chemical reaction where a carboxylic acid reacts with an alcohol to form an ester and water. It is a reversible reaction and can be achieved by mixing the acid and alcohol under specific conditions.
What are some examples of esters and their fragrances?
-Esters are often used in fragrances. Examples include butyl butyrate (which smells like pineapple), ethyl hexanoate (which smells like pineapple), and methyl pentanoate (which has a floral scent).
How do esters differ from carboxylic acids in terms of their functional groups?
-Carboxylic acids contain a carboxyl group (-COOH), while esters contain an ester group (-COO). The ester group includes a bond between oxygen and carbon, with the carbon attached to an alkyl group from the alcohol.
How is methyl pentanoate synthesized?
-Methyl pentanoate is synthesized by esterification. This involves reacting methanol (CH3OH) with pentanoic acid (C5H10O2), where the alcohol and carboxylic acid combine to form the ester, methyl pentanoate.
What is the process for making ester with a specific scent, like pineapple or apple?
-To make an ester with a specific scent, such as pineapple, you combine the alcohol and carboxylic acid associated with that scent. For example, to make ethyl hexanoate (pineapple scent), you combine ethanol with hexanoic acid.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)