Aprenda a LER um Gráfico de VELOCIDADE X TEMPO | CINEMÁTICA
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Thalis Rodrigues, a physics teacher, explains the analysis of velocity-time graphs for two types of motion: Uniform Rectilinear Motion (MRU) and Uniformly Varied Rectilinear Motion (MRV). He discusses the importance of interpreting these graphs to understand velocity, acceleration, and the distance traveled by an object. Through practical examples, he highlights the concept of positive and negative velocity, the relationship between acceleration and graph slope, and how to calculate distance using area under the curve. The video also addresses common misunderstandings and offers helpful tips for analyzing motion graphs in physics.
Takeaways
- 😀 MRU (Uniform Rectilinear Motion) is characterized by constant speed and straight-line movement. Speed remains unchanged during the motion.
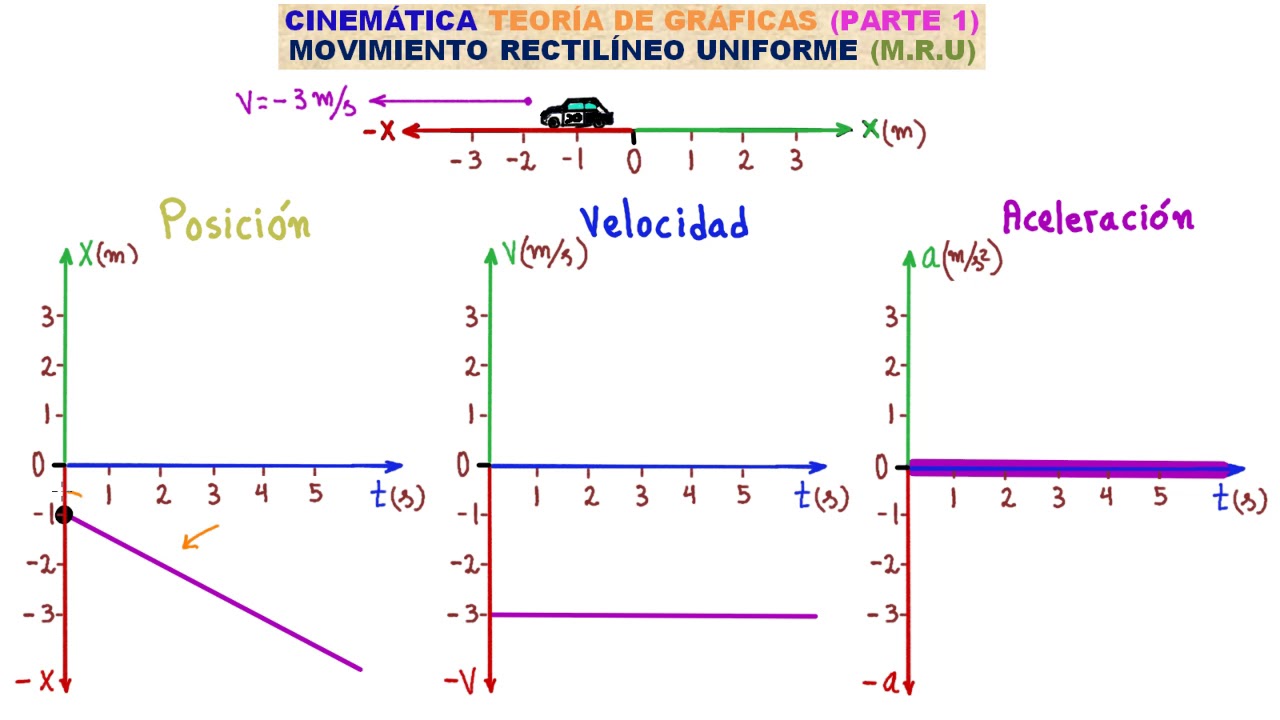
- 😀 In MRU, the velocity can be either positive or negative depending on the direction of movement relative to a reference point.
- 😀 Positive velocity means the object is moving forward (progressive motion), while negative velocity indicates it is moving backward (retrograde motion).
- 😀 The area under a velocity-time graph in MRU represents the distance traveled by the object.
- 😀 In MRU, the velocity-time graph is a horizontal line because the velocity is constant over time.
- 😀 In MRUV (Uniformly Accelerated Rectilinear Motion), acceleration is constant and affects the velocity of the object, causing it to increase or decrease.
- 😀 The velocity-time graph for MRUV is a straight line with a slope, where the slope indicates acceleration.
- 😀 In MRUV, the area under the velocity-time graph still represents the distance traveled, but the graph will be a slanted line due to changing velocity.
- 😀 The sign of velocity (positive or negative) indicates the direction of movement, while the sign of acceleration indicates whether the object is speeding up or slowing down.
- 😀 A decreasing velocity in a velocity-time graph indicates a negative acceleration, meaning the object is decelerating or coming to a stop.
- 😀 To analyze complex graphs (such as curves), one can reflect the graph to better understand the behavior of the object, helping to identify when the motion is accelerated, decelerated, or uniform.
Q & A
What is the definition of Movimento Retilíneo Uniforme (MRU)?
-Movimento Retilíneo Uniforme (MRU) is a type of motion where an object moves in a straight line with constant speed, meaning its velocity does not change over time. The object travels equal distances in equal time intervals.
How is the velocity represented in a velocity-time graph for MRU?
-In a velocity-time graph for MRU, the velocity is represented as a constant value along the y-axis, and the graph is a horizontal line. This indicates that the velocity does not change over time.
What does the area under the velocity-time graph for MRU represent?
-The area under the velocity-time graph for MRU represents the distance traveled by the object. This is because distance equals velocity multiplied by time.
How can we interpret a negative velocity in MRU?
-A negative velocity in MRU indicates that the object is moving in the opposite direction (reverse direction) relative to the reference point. This is considered a retrograde motion, even if the object is not literally moving in reverse, like driving backwards.
What is Movimento Retilíneo Uniformemente Variado (MRUV)?
-Movimento Retilíneo Uniformemente Variado (MRUV) refers to motion in a straight line where the object’s acceleration is constant. In this motion, the velocity changes at a uniform rate over time.
How is the velocity represented in a velocity-time graph for MRUV?
-In a velocity-time graph for MRUV, the velocity increases or decreases linearly with time, resulting in a straight line with a constant slope. The slope of the graph represents the acceleration.
What does the slope of a velocity-time graph represent in MRUV?
-The slope of a velocity-time graph in MRUV represents the acceleration of the object. A steeper slope indicates greater acceleration.
Can you explain the difference between a positive and negative acceleration in a velocity-time graph?
-Positive acceleration means that the velocity is increasing in the direction of motion, while negative acceleration (deceleration) means that the velocity is decreasing. In a graph, positive acceleration results in an upward slope, while negative acceleration results in a downward slope.
What can we conclude about an object if its velocity-time graph is not a straight line?
-If the velocity-time graph is not a straight line, it indicates that the acceleration is not constant. The graph could represent a motion where the object’s acceleration is changing over time.
How would you calculate the distance traveled by an object from a velocity-time graph for MRUV?
-To calculate the distance traveled by an object from a velocity-time graph for MRUV, you find the area under the graph. For a straight line graph, this is typically the area of a triangle (1/2 × base × height), where the base is the time and the height is the velocity.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

FISIKA KELAS X: GERAK LURUS (PART 2) Materi dan Contoh Soal GLB dan GLBB
CINEMÁTICA. GRÁFICAS DEL M.R.U TEORÍA 1 [APRENDE LOS GRÁFICOS DE POSICIÓN, VELOCIDAD Y ACELERACIÓN]

Movimento Retilíneo Uniforme - teoria e exemplo resolvido

Le mouvement rectiligne uniformément accéléré (1/2) | Physique | Alloprof

BAB V Gerak Parabola

Il moto rettilineo uniforme
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)