O que é a Síndrome de Turner? Saiba mais! | SAG UEL
Summary
TLDRIn this video, we explore Turner Syndrome, a genetic condition that affects only females due to a missing or altered X chromosome, leading to 45 chromosomes instead of the usual 46. The video covers its causes, common clinical signs like short stature and infertility, and how it's diagnosed through karyotype analysis. We also discuss the importance of early treatment, such as hormone replacement therapy and support for growth and development. Viewers are encouraged to reach out for more information and to subscribe for further educational content on genetic disorders.
Takeaways
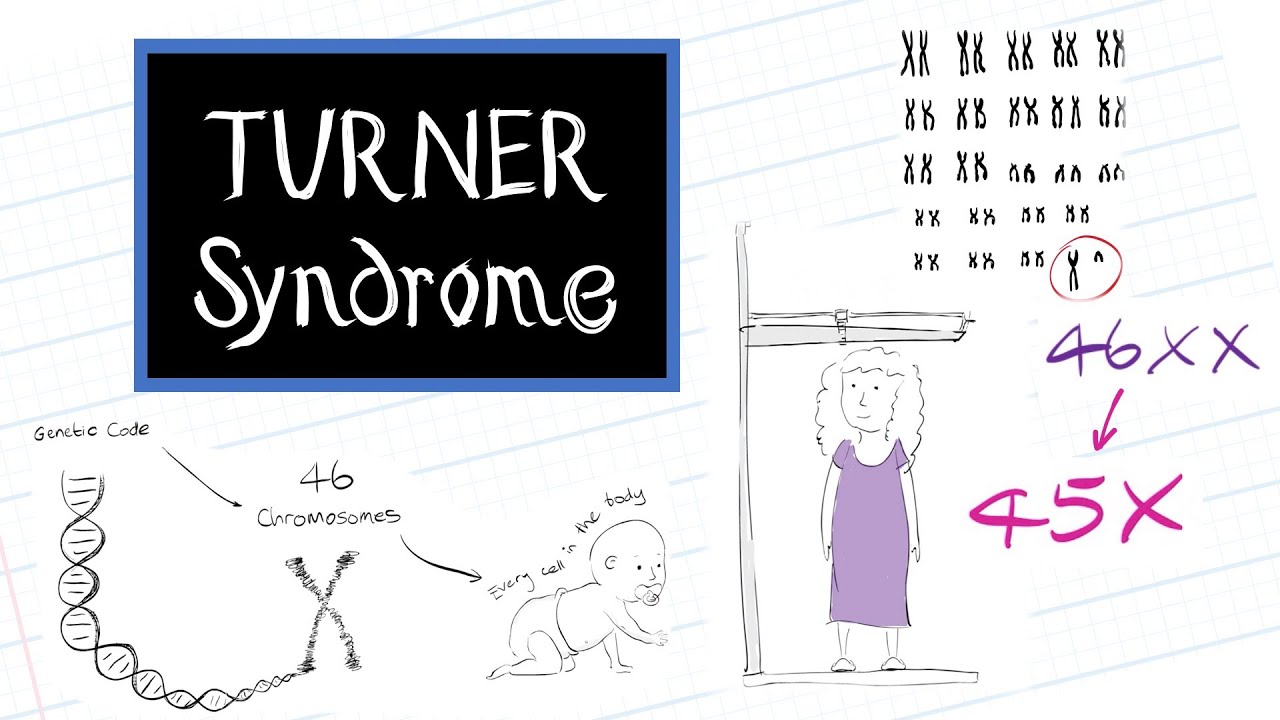
- 😀 Turner Syndrome is a genetic disorder that only affects females, resulting from an alteration in one of the sex chromosomes.
- 😀 People with Turner Syndrome have 45 chromosomes instead of the usual 46, with one X chromosome either missing or altered.
- 😀 Advanced maternal age (35 years or older) is a known risk factor for Turner Syndrome, though prenatal screenings are essential for early detection.
- 😀 There are different degrees of Turner Syndrome, depending on the nature of the chromosomal alteration (classic or mosaic forms).
- 😀 The classic form of Turner Syndrome involves all cells having 45 chromosomes, leading to more pronounced clinical features like short stature, webbed neck, and ovarian abnormalities.
- 😀 The mosaic form of Turner Syndrome involves a mix of cells with 45 and 46 chromosomes, which leads to more variable symptoms.
- 😀 Infertility is a common symptom of Turner Syndrome, particularly in the classic form where ovarian development is impaired.
- 😀 Women with Turner Syndrome cannot naturally conceive due to the lack of certain structures required for pregnancy, despite treatment starting from puberty.
- 😀 The diagnosis of Turner Syndrome is confirmed through a karyotype test, often performed during puberty, especially when there is no menstruation by age 16 or a cessation of menstruation.
- 😀 Early intervention with hormone replacement, growth promotion, and psychological support can improve quality of life for individuals with Turner Syndrome.
- 😀 For more information or inquiries about Turner Syndrome, individuals can reach out through the provided contact methods, including WhatsApp and social media.
Q & A
What is Turner syndrome?
-Turner syndrome is a genetic condition that only affects females. It is caused by the alteration of one of the sex chromosomes, where one X chromosome is either partially altered or missing.
How does Turner syndrome affect the chromosomes?
-In Turner syndrome, there are typically 45 chromosomes instead of the usual 46. One of the sex chromosomes (X) is either missing or altered, leading to a change in the person's karyotype.
What are the main causes of Turner syndrome?
-The primary factor linked to the increased risk of Turner syndrome is the mother's advanced age, particularly 35 years or older. However, genetic alterations during cell division can also contribute.
What are the different types of Turner syndrome?
-There are two main types: the classical form, where all cells have 45 chromosomes, and a mosaic form, where some cells have 45 chromosomes and others have 46. The severity of symptoms depends on the number of affected cells.
What are some common clinical signs of Turner syndrome?
-Common clinical signs include short stature, webbed neck, and gonadal developmental issues, which can lead to infertility. The severity of these symptoms varies depending on the karyotype of the individual.
Can individuals with Turner syndrome have children?
-In the classical form of Turner syndrome, infertility is common due to gonadal developmental issues. However, individuals with the mosaic form may have a chance to conceive if their gonadal cells are not affected.
How is Turner syndrome diagnosed?
-Turner syndrome is diagnosed through a karyotype test using lymphocytes. If the karyotype is normal but Turner syndrome is still suspected, further tests are conducted to check for mosaicism.
At what stage of life is Turner syndrome usually diagnosed?
-Although Turner syndrome can be diagnosed at any stage of life, it is most commonly diagnosed during puberty, especially when there is a delay in menstruation or when menstruation stops prematurely.
What treatments are available for Turner syndrome?
-Treatment options for Turner syndrome may include hormone replacement therapy to promote sexual development and growth, as well as psychological and social support. Early treatment can help alleviate symptoms like short stature and other secondary sexual characteristics.
Why is early treatment important for individuals with Turner syndrome?
-Starting treatment early can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with Turner syndrome. It can help manage symptoms such as short stature and underdeveloped secondary sexual characteristics.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)