Electromagnetic waves | Physics | Khan Academy
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into the fascinating world of electromagnetic waves, exploring how they are generated and why they vary in different forms such as radio waves, infrared, and visible light. It explains how accelerating charges, like those in wifi antennas, generate these waves, and how frequency and wavelength are related. The video further discusses how these waves are used in wireless communication, from modulating signals in radio waves to the digital modulation used in wifi. Ultimately, it showcases how understanding electromagnetic waves is key to modern communication technologies.
Takeaways
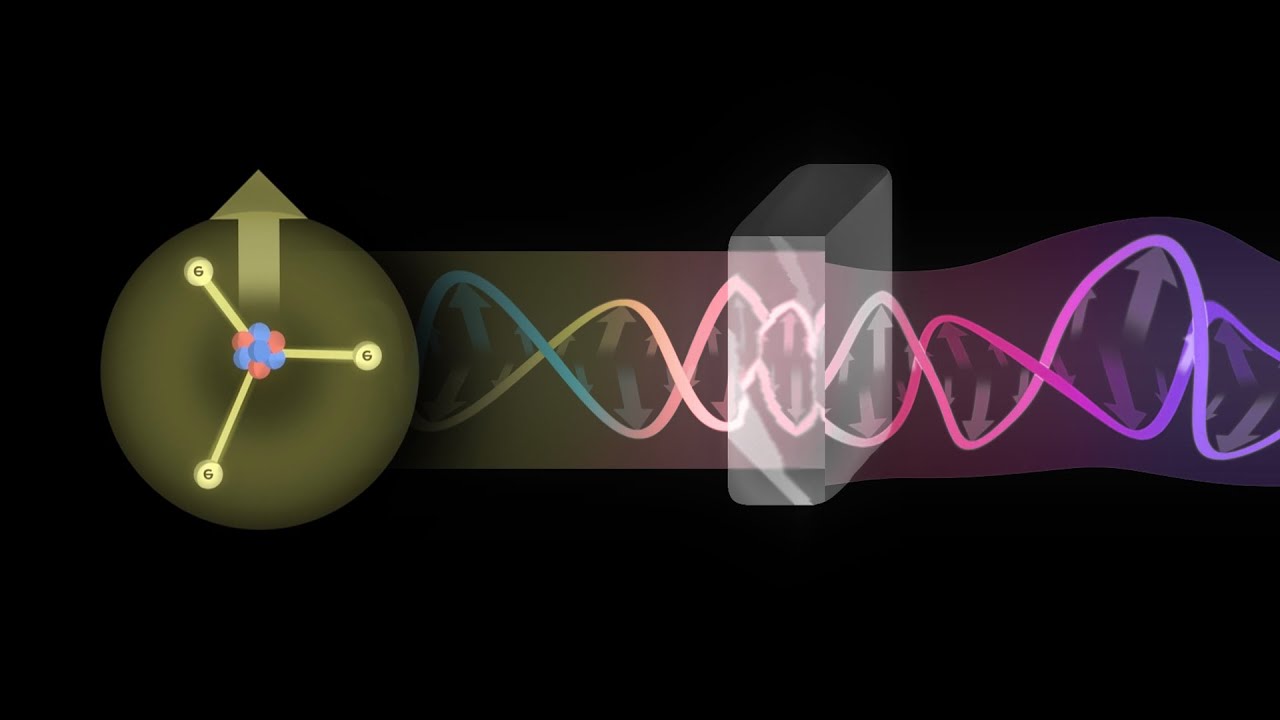
- 😀 Electromagnetic waves consist of oscillating electric and magnetic fields, which propagate energy through a vacuum.
- 😀 Accelerating charges produce electromagnetic waves, with examples such as the oscillating electrons in wifi antennas, our bodies, and incandescent bulbs.
- 😀 Different frequencies of oscillating charges result in different types of electromagnetic waves, such as radio waves, infrared radiation, and visible light.
- 😀 Key properties of electromagnetic waves include amplitude (height), phase (synchronization of points on the wave), wavelength (distance between peaks or valleys), and frequency (number of waves passing a point per second).
- 😀 The speed of electromagnetic waves in a vacuum is constant at approximately 3 × 10^8 meters per second, independent of the wave's frequency or wavelength.
- 😀 The relationship between frequency and wavelength is inversely proportional in electromagnetic waves: high frequency corresponds to short wavelengths, and low frequency corresponds to long wavelengths.
- 😀 For example, wifi signals operate at frequencies around 1 billion hertz, generating radio waves, while visible light is at frequencies around 10^14 hertz.
- 😀 When electromagnetic waves encounter an antenna (like in a phone), they transfer energy by causing the electrons in the receiver to oscillate.
- 😀 Wireless communication, such as wifi, transfers information by modulating electromagnetic waves. This can be done through amplitude modulation (AM) or digital modulation (as used in wifi).
- 😀 Digital modulation involves encoding information in discrete values (0s and 1s) and using variations in the wave's properties (such as amplitude) to represent the data being transmitted.
- 😀 Understanding electromagnetic waves and modulation techniques is fundamental to modern wireless communication technologies, including wifi, satellite communication, and more.
Q & A
What are electromagnetic waves?
-Electromagnetic waves are disturbances that consist of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. These waves can propagate through a vacuum without requiring any medium and carry energy, such as how energy from the sun reaches us.
How are electromagnetic waves produced?
-Electromagnetic waves are produced when charges are accelerated. This acceleration changes the electric and magnetic fields, leading to the generation of electromagnetic waves. For example, electrons moving up and down generate waves.
Why do different objects emit different types of electromagnetic waves?
-Different objects emit different types of electromagnetic waves because the frequency at which their charges oscillate varies. For example, Wi-Fi antennas produce radio waves due to low-frequency oscillations, while incandescent bulbs produce visible light due to higher frequencies.
What is the difference between amplitude, wavelength, and frequency in an electromagnetic wave?
-Amplitude refers to the maximum strength of the electric or magnetic field in the wave, wavelength is the distance between consecutive points that are in phase, and frequency is the number of waves that pass a point per second.
How are frequency and wavelength related in electromagnetic waves?
-In electromagnetic waves, the frequency and wavelength are inversely related. As the frequency increases, the wavelength decreases, and vice versa. This relationship is crucial for understanding different types of electromagnetic waves.
What is the speed of electromagnetic waves in a vacuum?
-The speed of electromagnetic waves in a vacuum is constant and is approximately 3 × 10^8 meters per second, often referred to as the speed of light (C). This speed is independent of the wave’s frequency or wavelength.
How can the speed of a wave be calculated from its frequency and wavelength?
-The speed of a wave can be calculated by multiplying its frequency (number of waves per second) by its wavelength (distance between consecutive peaks). The formula is: speed = frequency × wavelength.
What happens to electromagnetic waves when they interact with objects, such as the antennas in Wi-Fi or a phone?
-When electromagnetic waves interact with antennas, they cause electrons in the antenna to vibrate. In a transmitter antenna, this vibration generates electromagnetic waves, while in a receiver antenna, the waves cause electrons to vibrate, transferring energy.
How is information transferred using electromagnetic waves in wireless communication?
-In wireless communication, information is transferred by modulating the electromagnetic wave. This can be done by altering properties such as amplitude, frequency, or phase to encode the information, such as sending data in binary form (1s and 0s).
What is the difference between analog and digital modulation in communication?
-Analog modulation involves continuous changes in properties like amplitude to transmit a signal. Digital modulation, on the other hand, involves sending discrete values (like 1s and 0s) to encode information, with the signal's properties changing accordingly.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Fizyka od podstaw: Czy Fale elektromagnetyczne, promieniowanie, światło jest tym samym?

Fisika kelas 12 | Gelombang Elektromagnetik (GEM)
The origin of Electromagnetic waves, and why they behave as they do

GCSE Physics Revision "Uses of EM waves"

Le onde e lo spettro

SCIENCE 10 (Quarter 2-Module 1): DIFFERENT FORMS OF ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)