Introduction to BPMN
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an introduction to BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation), explaining its purpose in offering a graphical notation for business processes. BPMN is useful for business analysts, developers, and managers, enabling clear communication across different roles. The video covers various BPMN elements like activities, events, gateways, and sub-processes, illustrating how these components interact in process modeling. Key concepts include sequence flows, tasks, and message exchanges between participants in a process. The video also highlights how BPMN facilitates process management, from initial design to implementation, using real-world examples like ordering and delivering a pizza.
Takeaways
- 😀 BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation) is a standardized graphical notation designed to be understandable by business users, analysts, developers, and managers.
- 😀 BPMN diagrams consist of flow elements such as activities, events, and gateways, all connected by sequence flows.
- 😀 A process in BPMN is depicted as a flow of activities with a clear objective, and sequence flows define the order in which activities are executed.
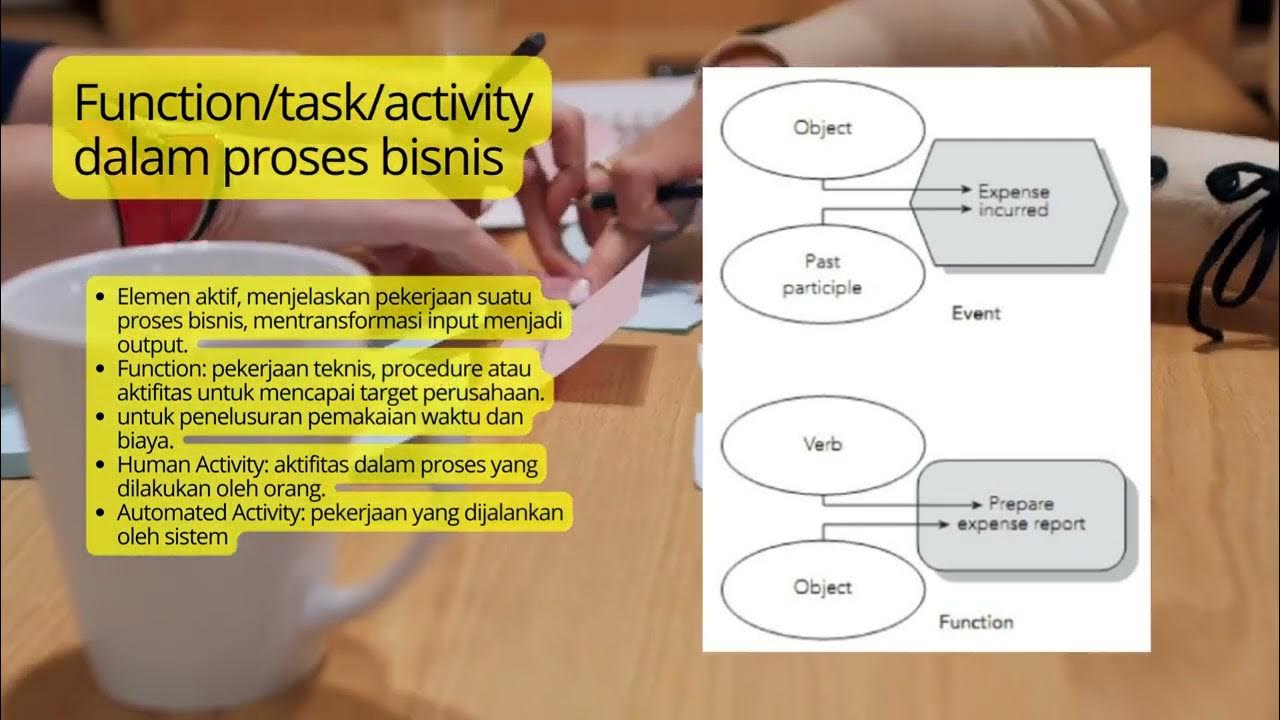
- 😀 Activities in BPMN are the work elements in a process, and can be either atomic (tasks) or non-atomic (sub-processes).
- 😀 BPMN supports various task types, including service tasks, user tasks, manual tasks, business rule tasks, and script tasks.
- 😀 Sub-processes are activities that contain additional process details, and can be either collapsed or expanded within the parent process.
- 😀 Events in BPMN are occurrences that affect the flow, including start, intermediate, and end events, which are triggered by specific conditions.
- 😀 Gateways control the flow of processes, enabling paths to be diverged or merged, and they include types like exclusive, parallel, inclusive, and event-based gateways.
- 😀 Data objects, data stores, and message flows allow for the representation of information and interactions within and across processes.
- 😀 BPMN collaborations are used to describe the interaction between participants in a process, using pools (representing participants) and message flows (representing communication).
Q & A
What is BPMN?
-BPMN stands for Business Process Model and Notation. It is a standardized graphical notation for modeling business processes, created to be understandable by all business users, from analysts to developers and managers.
What is the primary goal of BPMN?
-The primary goal of BPMN is to provide a graphical notation that is easily understandable by all stakeholders involved in business processes, enabling clear communication between business analysts, technical developers, and business managers.
What types of tasks are defined in BPMN, and what are their purposes?
-BPMN defines various task types, including Abstract Task, Service Task, Send Task, Receive Task, User Task, Manual Task, Business Rule Task, and Script Task. These tasks represent different actions in a process, such as executing services, sending or receiving messages, or involving human users.
What is the difference between a sub-process and a task in BPMN?
-A task is an atomic activity, meaning it is a single action that cannot be broken down further. A sub-process is a more complex activity that may have internal details modeled by other activities, gateways, and events. Sub-processes can be shown in collapsed or expanded views.
What is the purpose of gateways in BPMN?
-Gateways in BPMN control the flow of a process. They define conditions for diverging or converging sequence flows, helping to create alternative paths (exclusive, parallel, inclusive) or complex conditions for the process flow.
What are the different types of gateways in BPMN?
-The different types of gateways in BPMN include Exclusive, Parallel, Inclusive, Complex, and Event-based Gateways. These gateways manage the flow based on conditions, synchronization, and events that occur within the process.
How does an Event-based Gateway work?
-An Event-based Gateway triggers different paths based on events. Unlike other gateways, it is activated by an event rather than a condition expression. Once the event occurs, the associated path is followed, and all other paths are invalid.
What is the function of a 'collaboration' in BPMN?
-A collaboration in BPMN describes the interaction between participants in a process. It typically includes multiple pools, which represent participants, and message flows that connect these participants.
What is the role of data objects in BPMN?
-Data objects in BPMN represent physical or informational items that are created, manipulated, or used during the execution of a process. They do not directly affect the flow of the process but are used to model important information within the process.
What are lanes in BPMN, and how are they used?
-Lanes in BPMN are sub-partitions within a pool that are used to organize and categorize activities within a process. Lanes typically represent different roles or responsibilities within a pool, helping to clarify the responsibilities of various participants in the process.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

MPB 10_2 Process Implementation Executable Models

What Kind of Organizational Assets are Business Processes?
RPL 1 1 Proses Bisnis Pengembangan Perangkat Lunak dan Gim

[FR] Introduction au BPM (Business Process Management) et au BPMN (Business Process Model Notation)

Business Process Modeling (BPM): Definisi, Manfaat dan Teknik

BPMN Basics
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)