Biomekadinamika 1
Summary
TLDRThis script provides an in-depth exploration of biomechanics in healthcare, particularly in the context of human movement, with a focus on physical forces and their effects on the body. It covers key concepts such as Newton's Laws of Motion, the role of internal and external forces, and the importance of ergonomics in various healthcare settings. The script highlights the practical applications of biomechanical principles for healthcare professionals, especially midwives and caregivers, in tasks like lifting patients, assisting in childbirth, and ensuring the safety and comfort of both patients and healthcare workers. Additionally, it emphasizes the relevance of proper body positioning and movement to prevent injury and optimize performance.
Takeaways
- 😀 Biomechanics is a field that integrates factors affecting human movement, applying principles of physics, physiology, and engineering to analyze forces within the human body.
- 😀 Newton's First Law (Inertia) states that an object will maintain its state of motion (whether stationary or moving) unless acted upon by an external force.
- 😀 Newton's Second Law explains that an object will accelerate in the direction of an applied force, and this acceleration depends on the force and the object's mass.
- 😀 Newton's Third Law highlights that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction, a principle that can be seen in everyday physical interactions like pushing objects.
- 😀 Forces like friction (static and kinetic) play a crucial role in the movement of objects, with static friction resisting motion and kinetic friction acting during movement.
- 😀 Inertia refers to an object's resistance to change in its motion, which is dependent on its mass and affects how forces are applied.
- 😀 External and internal forces both contribute to movement in the body. External forces include gravity, while internal forces are generated by muscles and other biological processes.
- 😀 The concept of biomechanical analysis in healthcare includes evaluating the forces involved in tasks like lifting, patient positioning, and assisting in childbirth.
- 😀 Proper ergonomic practices, such as correct sitting, standing, and lifting techniques, are essential in preventing injury and ensuring comfort for healthcare workers and patients.
- 😀 Newton's laws have practical applications in healthcare, such as understanding the mechanical forces acting during childbirth, lifting patients, and ensuring that ergonomic tools support health and safety.
Q & A
What is the definition of biomechanics as discussed in the script?
-Biomechanics, or biomedicine biomechanics, is a field of study that integrates various factors influencing human movement. These factors are analyzed based on basic knowledge in physics, mathematics, physiology, anatomy, and engineering principles to analyze the forces occurring in the human body, whether in healthy or sick conditions.
What are the three fundamental principles of biomechanics mentioned in the script?
-The three fundamental principles of biomechanics are: 1) Newton's First Law (Inertia), which states that an object will remain at rest or in uniform motion unless acted upon by an external force. 2) Newton's Second Law, which explains that an object will experience acceleration in the direction of the applied force. 3) Newton's Third Law, which states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
Can you explain Newton's First Law (Inertia) in the context of biomechanics?
-Newton's First Law, or the law of inertia, explains that an object will maintain its state of motion or rest unless a force is applied to change that state. In biomechanics, this is important for understanding how the body resists changes in movement, such as when a person moves or stops moving, or how external forces like gravity or muscle forces act on the body.
What is the difference between static and kinetic friction in biomechanics?
-Static friction refers to the frictional force that resists the initiation of motion, like when an object is at rest and you apply force to move it. Kinetic friction occurs once the object starts moving and resists the ongoing motion. In biomechanics, these types of friction are relevant when considering how objects or body parts move or stay in place under various forces.
How is inertia related to the human body in the context of biomechanics?
-Inertia refers to the tendency of an object to resist changes in its state of motion. In the human body, this principle explains why a body resists sudden movements or why certain postures or movements require more force to overcome the body's natural resistance, such as when lifting a heavy object or adjusting posture.
What role do external and internal forces play in the biomechanics of the human body?
-External forces, like gravity, act on the body from the outside, such as when a person stands up or walks. Internal forces, like muscle forces or electrical impulses from the nervous system, cause movement within the body and are essential for activities like lifting, walking, or even the function of internal organs like the heart.
How does gravity affect the human body in biomechanics?
-Gravity is an external force that impacts the human body by constantly pulling it down toward the Earth. This force affects posture, balance, and movement. In biomechanics, understanding gravity helps in analyzing movements like standing, walking, and lifting, as well as how gravity influences the forces on bones, muscles, and joints.
What is the importance of understanding the position of the body in healthcare professions?
-In healthcare professions, understanding body position is critical to prevent injury and improve effectiveness. Proper positioning can reduce strain on muscles and joints, facilitate movement, and enhance the quality of patient care, such as during labor and delivery or when lifting and positioning patients.
What is the role of biomechanics in improving ergonomic practices for healthcare workers?
-Biomechanics plays a significant role in ergonomics by helping healthcare workers understand and apply the principles of force, posture, and movement. Proper ergonomics, such as maintaining a correct sitting or standing posture and lifting techniques, can prevent injury and ensure the comfort and safety of healthcare professionals.
How does Newton's Third Law apply to the movement of babies during childbirth?
-Newton's Third Law, which states that every action has an equal and opposite reaction, applies to childbirth when the baby exerts a force on the surrounding environment (e.g., the womb or amniotic fluid), and in return, the environment provides a reactive force. This can help the baby move or shift during delivery.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Learning outcomes and module design

What is Biomechanics?

Biomekanika Olahraga : Tumpuan
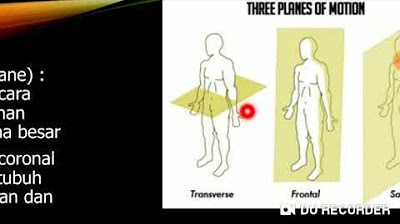
ANATOMI GERAK MANUSIA (BAG. 1) : ISTILAH ARAH, BIDANG ANATOMIS DAN SUMBU ANATOMIS.

Nasionalisme dan Jati Diri Bangsa | BAB 3 | IPS KELAS 8 SMP/MTs | KURIKULUM MERDEKA

What is Biomechanics? Biomechanics in Life & Sports
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)