Calor Sensible y Calor Latente |Termodinámica| - Salvador FI
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the concepts of sensible and latent heat in thermodynamics. Sensible heat occurs when there is a temperature difference between two systems, transferring heat from the hotter to the cooler system without a phase change. Latent heat, on the other hand, is involved during phase changes at constant temperature and pressure, such as condensation, where energy is added or removed without changing the substance's temperature. The video also introduces the concept of enthalpy of transformation, which refers to the energy required during phase changes. The host invites viewers to explore more thermodynamics content and stay connected on social media.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video introduces thermodynamics, specifically focusing on the concept of heat.
- 😀 Heat manifests in two forms: sensible heat and latent heat.
- 😀 Sensible heat occurs when there is a temperature difference between two or more thermodynamic systems without a phase change.
- 😀 When there is a temperature difference, energy in the form of heat transfers from the higher temperature system to the lower one.
- 😀 The rate of heat transfer increases as the temperature difference between systems grows.
- 😀 Once thermal equilibrium is reached (both systems at the same temperature), heat transfer stops.
- 😀 Thermal equilibrium is different from thermodynamic equilibrium.
- 😀 Latent heat appears during phase changes at constant pressure and temperature.
- 😀 An example of latent heat is condensation, where a substance changes from a gas to a liquid without a temperature change.
- 😀 The flow of energy during a phase change is related to enthalpy of transformation (also known as phase change enthalpy).
- 😀 There are six types of enthalpy of transformation, and further thermodynamics content is available on the channel.
Q & A
What is sensible heat?
-Sensible heat is the heat transferred between two systems that have different temperatures, without any phase change. The energy flows from the system with higher temperature to the one with lower temperature.
How does the temperature difference affect sensible heat transfer?
-The greater the temperature difference between two systems, the higher the rate of heat transfer. A larger temperature gradient leads to faster energy movement between the systems.
What happens when two systems reach thermal equilibrium?
-When two systems reach thermal equilibrium, they are at the same temperature. At this point, no more heat transfer occurs, as there is no longer a temperature difference between the systems.
What is the difference between thermal equilibrium and thermodynamic equilibrium?
-Thermal equilibrium refers specifically to when two systems are at the same temperature and there is no heat transfer. Thermodynamic equilibrium, however, involves a broader state where all other forms of equilibrium (e.g., mechanical, chemical) are also achieved.
What is latent heat?
-Latent heat is the heat energy that is absorbed or released by a substance during a phase change, such as from liquid to gas or gas to liquid, at constant temperature and pressure, without changing the temperature of the substance.
Can latent heat be associated with a temperature change?
-No, latent heat is transferred during a phase change but does not result in a temperature change. For example, during condensation, the substance's temperature remains constant even as heat is released.
What happens during the condensation process in terms of latent heat?
-During condensation, a substance changes from gas to liquid. While the substance releases heat, its temperature remains constant. The heat released during this process is a form of latent heat.
What is meant by the term 'enthalpy of phase change'?
-Enthalpy of phase change refers to the amount of energy required or released during a phase transition, such as when a substance changes state (e.g., from liquid to gas). This energy is typically measured in terms of heat energy.
What are the six types of enthalpy of transformation mentioned in the video?
-The video mentions there are six different types of enthalpy of transformation, but it does not specify them. These types generally correspond to different phase transitions, such as melting, freezing, vaporization, condensation, sublimation, and deposition.
Why is it important to understand the concepts of sensible and latent heat in thermodynamics?
-Understanding sensible and latent heat is crucial because they describe how energy is transferred in different physical processes, such as heating, cooling, and phase changes. This knowledge is essential in fields like engineering, meteorology, and chemistry for designing systems and understanding natural processes.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Calor sensível e calor latente conceitos para entender definitivamente
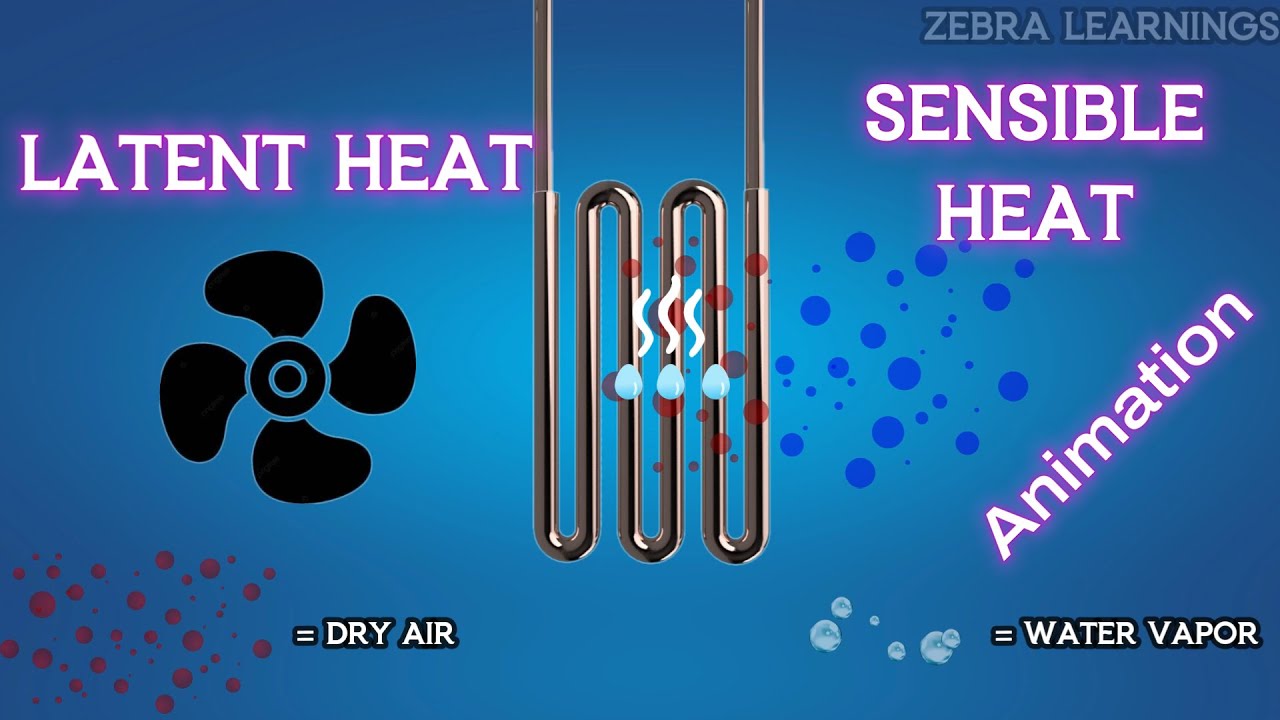
Latent Heat and Sensible Heat Explained | Humidity | Animation | #hvac #hvacsystem #hvacmaintenance

Física - Calor Sensível e Calor Latente

ENG 201 Lecture 4.1.1

3D How Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Works P1 - Components

CALORIMETRIA: UM SUPER MAPA MENTAL | QUER QUE DESENHE
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)