DAA Unit - 1 🎯Foundations of Algorithm 🔍 40 Top most V.V.i questions 🔄 || CSE 408
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a comprehensive practice session for algorithm and data structure-related MCQs, focusing on key concepts such as time complexity, algorithm characteristics, graph representations, and tree structures. The questions cover a wide range of topics like worst-case time complexity, sorting algorithms, Big O notation, and different data structures used in problem-solving. With clear explanations of correct answers and reasoning, the session helps viewers strengthen their understanding and prepare for exams or interviews related to algorithms and data structures.
Takeaways
- 😀 An algorithm is a step-by-step procedure designed to solve a problem in programming, data structures, or other related fields.
- 😀 A good algorithm must be effective, finite, and have well-defined inputs and outputs. It should also be unambiguous.
- 😀 The worst-case time complexity of an algorithm refers to the longest execution time required on any input.
- 😀 The best-case complexity measures the minimum time taken by an algorithm, often used to understand the algorithm's efficiency in optimal scenarios.
- 😀 Understanding the time complexity of an algorithm is crucial for evaluating how the algorithm's execution time increases as the input size grows.
- 😀 Dynamic programming is one of the most efficient algorithm design techniques, especially useful for optimization problems.
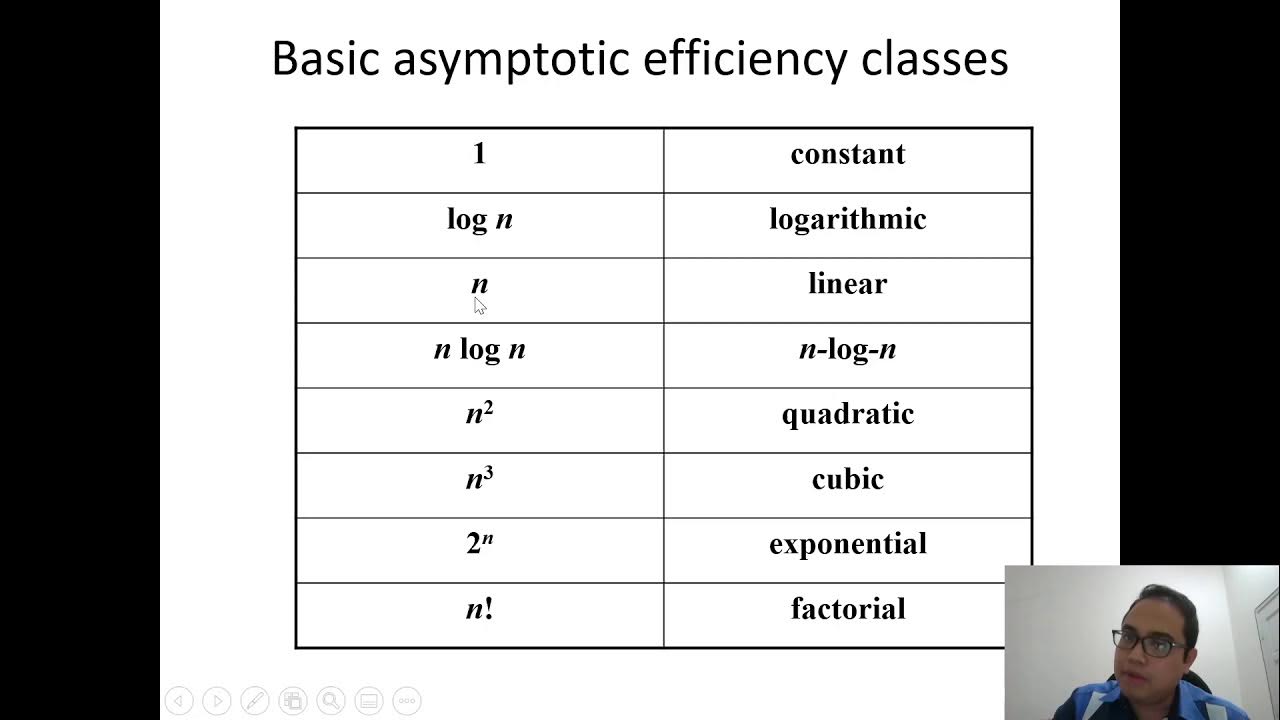
- 😀 The Big O notation represents the worst-case time complexity of an algorithm, providing an upper bound on the running time.
- 😀 The order of growth describes how the running time of an algorithm increases with input size, which is important for analyzing scalability.
- 😀 A tree is a connected acyclic graph, and it can be represented using various data structures such as adjacency lists and matrices.
- 😀 Dijkstra's algorithm is commonly used to find the shortest path in a graph, which is a key application in network routing and graph theory.
Q & A
What is the definition of an algorithm?
-An algorithm is a step-by-step procedure designed to solve a problem or perform a task in a systematic and efficient manner.
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of a good algorithm?
-A good algorithm should be finite, unambiguous, and have well-defined inputs and outputs. It should also be effective. However, ambiguity is not a characteristic of a good algorithm.
What does the worst-case time complexity of an algorithm refer to?
-The worst-case time complexity refers to the longest execution time of an algorithm on any input. It helps in understanding the maximum time the algorithm may take to solve a problem.
What is the best-case time complexity in algorithms?
-The best-case time complexity refers to the minimum time taken by the algorithm to complete the task, assuming the best possible input.
Which step of problem-solving is responsible for defining the input and output of an algorithm?
-The algorithm specification step defines the inputs and outputs of the algorithm. This step ensures that the problem is clearly defined and measurable.
How is the time complexity of an algorithm measured?
-The time complexity of an algorithm is typically measured by the total number of steps executed by the algorithm, which depends on the size of the input.
What is the most efficient algorithm design technique?
-Dynamic programming is considered one of the most efficient algorithm design techniques, especially for solving problems that can be broken down into overlapping subproblems.
What does the order of growth of an algorithm indicate?
-The order of growth of an algorithm indicates how its running time increases as the input size grows. It helps in understanding the scalability of an algorithm.
Which case is most commonly used for analyzing an algorithm?
-The worst-case scenario is most commonly used for analyzing algorithms, as it helps to determine the maximum time an algorithm may take for the largest possible input.
Which data structure follows the LIFO (Last In, First Out) principle?
-A stack follows the Last In, First Out (LIFO) principle, meaning that the most recently added element is the first to be removed.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)