LABORATORIO Cadute nel tubo di Newton AMALDI ZANICHELLI
Summary
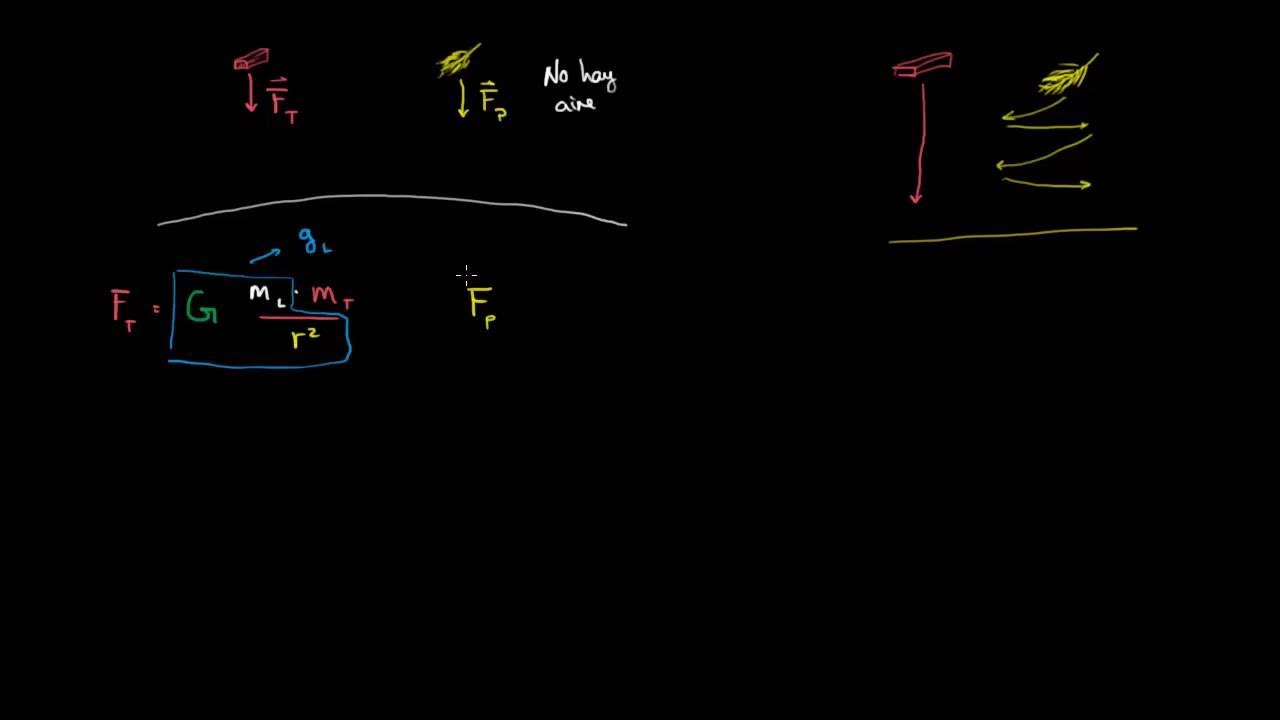
TLDRThis experiment demonstrates that in a vacuum, objects of different masses, shapes, and sizes fall at the same rate due to gravity. Using a glass tube, a valve, and a vacuum pump, objects such as a metal piece, cork, and feather are dropped. In the presence of air, the metal piece reaches the bottom first, followed by the cork and feather due to air resistance. However, after the air is removed, all objects fall nearly simultaneously, illustrating Galileo's principle that gravity acts equally on all objects in the absence of air resistance.
Takeaways
- 😀 The experiment demonstrates that in a vacuum, objects of different masses, shapes, and sizes fall together with the same acceleration.
- 😀 A glass tube with an opening, a valve, and a vacuum pump is used in the experiment to create a vacuum environment.
- 😀 The experiment starts by testing the falling objects with the valve open, showing that the metal piece hits the bottom first, followed by the cork and feather.
- 😀 When the vacuum pump is connected to the tube and the air is evacuated, the valve is closed, and the pump is removed.
- 😀 After creating the vacuum, the tube is inverted, and the objects now fall almost simultaneously, with the metal piece falling slightly faster.
- 😀 In the vacuum environment, all objects experience nearly identical fall times, demonstrating the same acceleration due to gravity.
- 😀 The metal piece precedes the other objects by only a tiny fraction of time in the vacuum.
- 😀 In the presence of air, friction affects the falling objects differently: it has minimal effect on the metal piece, but a greater effect on the cork and feather.
- 😀 The core principle being demonstrated is that, in a vacuum, all objects are subject to the same gravitational acceleration, regardless of their properties.
- 😀 This experiment highlights the importance of eliminating air resistance in studying the effects of gravity on different objects.
Q & A
What is the main objective of the experiment described in the script?
-The main objective of the experiment is to qualitatively demonstrate that objects with different masses, shapes, and sizes fall with the same acceleration in a vacuum.
What objects are used in the experiment to demonstrate the effect of gravity?
-The objects used in the experiment are a metal piece, a cork, and a feather.
How does the presence of air affect the objects' fall in the experiment?
-When air is present, the objects fall at different rates due to air resistance, with the metal piece hitting the bottom first, followed by the cork, and then the feather.
What role does the vacuum pump play in the experiment?
-The vacuum pump is used to remove the air from the tube, creating a vacuum environment where air resistance no longer affects the falling objects.
What happens to the objects' fall when the vacuum is created?
-In the vacuum, the objects fall nearly simultaneously, with the metal piece touching the bottom just slightly before the others, demonstrating that they are all subject to the same gravitational acceleration.
Why does the metal piece fall slightly faster than the other objects in the vacuum?
-The metal piece falls slightly faster due to its higher mass and density, but the difference is so small that all objects effectively fall with the same acceleration in the vacuum.
What is the key scientific principle demonstrated by this experiment?
-The key principle demonstrated is that in the absence of air resistance (in a vacuum), all objects fall at the same rate regardless of their mass or size, due to gravity.
How does air resistance affect the fall of the objects in the tube when air is present?
-Air resistance affects the fall by slowing down lighter and less dense objects, such as the cork and the feather, more than denser objects like the metal piece.
What would happen if the experiment were conducted in a different medium, like water?
-In a medium like water, the objects would fall slower due to the increased resistance from the denser medium. However, the relative differences in fall times would still depend on the density and shape of the objects.
What conclusion can we draw from this experiment regarding gravity and mass?
-The conclusion is that gravity accelerates all objects equally in a vacuum, regardless of their mass, which disproves the idea that heavier objects fall faster than lighter ones when air resistance is eliminated.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)