KALKULUS | FUNGSI TRANSENDEN | EKSPONEN ASLI (Turunan dan Integral)
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the concept of the natural exponential function, its relationship with the natural logarithm, and how to compute its derivatives and integrals. It covers the basic properties of the exponential function, including its graph and characteristics like monotonicity and concavity. The video also demonstrates how to find derivatives using the chain rule and integrates exponential functions, with step-by-step examples. The tutorial concludes with various exercises, including solving integrals using substitution and handling exponential functions in practical problems.
Please replace the link and try again.
Q & A
What is the natural exponential function, and how is it related to the natural logarithmic function?
-The natural exponential function is the inverse of the natural logarithmic function. While the natural logarithm has the base 'e' (approximately 2.718), the natural exponential function is denoted as e^x. The two functions are inverses of each other, meaning that one undoes the effect of the other.
How is the graph of the natural exponential function related to the graph of the line y = x?
-The graph of the natural exponential function is the reflection of the line y = x across the line y = x. This means that the exponential curve mirrors the linear function along the line y = x, showing a different growth pattern.
What are the properties of the natural exponential function?
-The natural exponential function has the following properties: e^0 = 1, e^-1 = 1/e, and it is always monotonically increasing and concave up. Additionally, it passes through the point (0, 1) and has a horizontal asymptote at y = 0.
How do you calculate the derivative of the natural exponential function?
-The derivative of the natural exponential function e^x is simply e^x itself. More generally, for a function of the form e^f(x), its derivative is e^f(x) multiplied by the derivative of f(x) using the chain rule.
What is the derivative of e^(4x^2)?
-The derivative of e^(4x^2) is found by applying the chain rule. The derivative of the exponent, 4x^2, is 8x. Therefore, the derivative is 8x * e^(4x^2).
What rule is used to differentiate the product of two functions involving the natural exponential function?
-To differentiate the product of two functions involving the natural exponential function, the product rule is applied. If u(x) and v(x) are two functions, the derivative is u'(x)v(x) + u(x)v'(x), where the derivatives of u and v are calculated individually.
How do you integrate the natural exponential function?
-The integral of e^x with respect to x is simply e^x + C, where C is the constant of integration. For more complex expressions, substitution or other integration techniques may be necessary.
What is the integral of e^(-4x)?
-The integral of e^(-4x) is found by using substitution. By substituting u = -4x, we get the integral e^u du, which equals e^(-4x)/-4 + C.
How do you solve the integral of e^(2x)sin(2x)?
-To solve the integral of e^(2x)sin(2x), the product rule is applied along with integration by parts. The result is a combination of the exponential and trigonometric functions, where the integrals are simplified step by step.
What happens when you apply integration limits to an exponential function?
-When applying limits to an exponential function, you evaluate the integral at the upper and lower bounds and subtract the results. For example, in the case of integrating e^(-3x) with limits from 0 to ln(2), the result is calculated by substituting these values into the antiderivative and subtracting.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
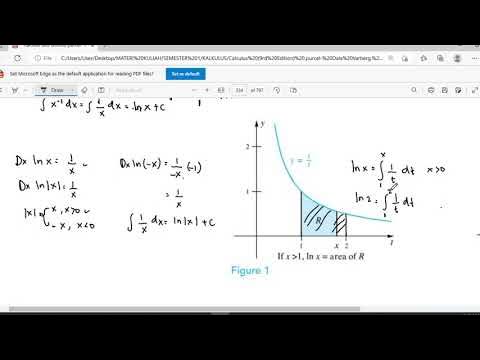
Fungsi Transenden 1 (Logaritma Natural/Ln)
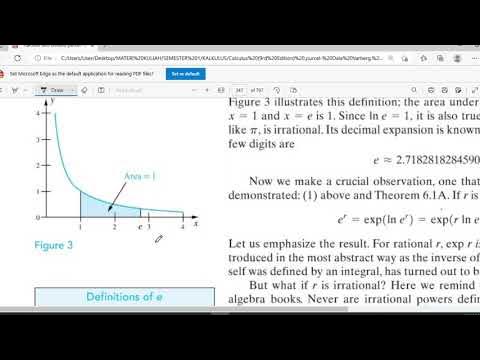
Fungsi Transenden 3 (Fungsi Eksponensial Natural)

KALKULUS | FUNGSI TRANSENDEN | LOGARITMA ASLI (Turunan dan Integral)
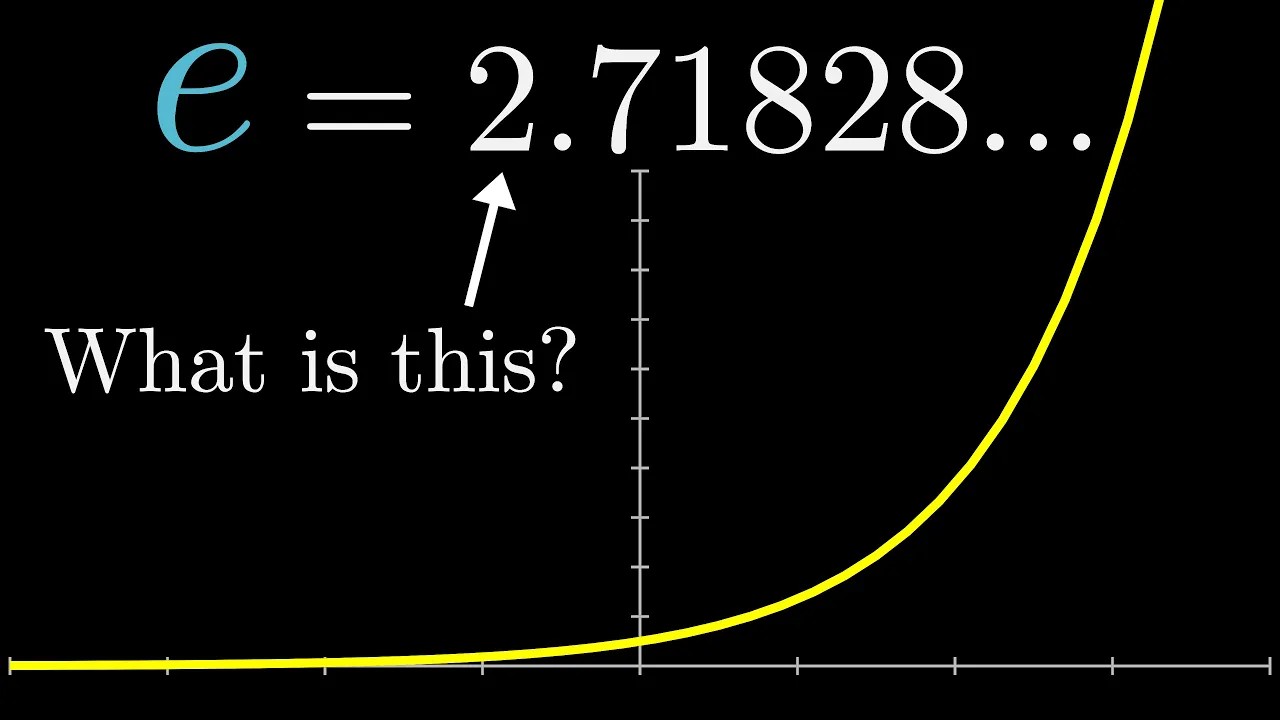
What's so special about Euler's number e? | Chapter 5, Essence of calculus

Derivatives of inverse functions | Advanced derivatives | AP Calculus AB | Khan Academy

Matematika Teknik I: 101 Fungsi Logaritma Natural - Definisi ln x dan turunannya
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)