MATERI KULIAH: SEJARAH PENGELOLAAN HUTAN
Summary
TLDRThis lecture provides a comprehensive overview of the history and evolution of forest management practices, from timber mining in ancient civilizations to modern community forestry. It explores key milestones, such as the development of forest laws in Europe, the rise of forest resource management strategies, and the shift from centralized control to community involvement in Indonesia. The lecture emphasizes the importance of balancing ecological preservation with sustainable forest use, highlighting the significance of participatory management in today’s forestry practices. The session concludes with exercises to reinforce the concepts discussed.
Takeaways
- 😀 Forest management history is crucial for understanding current practices and policies, both globally and in Indonesia.
- 🌍 The history of wood extraction dates back to ancient civilizations like Babylon and expanded during the Roman Empire in Europe.
- 🌳 In Europe, early forestry laws like the 1376 'Ordinance The Melon' in France and the 1543 'Forest Act' in England laid the groundwork for forest management.
- 📚 The 19th century saw the emergence of silviculture and forest planning, with new forest management systems like moniculture and planned rotations.
- 💡 Early forest management systems aimed to maximize timber production but often led to ecological issues like vulnerability to pests and diseases.
- 🌱 The concept of social forestry was introduced in 1978, highlighting the importance of community participation in forest management and ecosystem sustainability.
- 🤝 In modern forestry, community-based management approaches, such as 'Hutan Desa' and 'Hutan Kemitraan' in Indonesia, give local people more control over forest resources.
- 🌎 Forest management models have shifted from centralized, profit-driven approaches to more inclusive, ecosystem-based strategies that prioritize environmental protection.
- ⚙️ Sustainable forest management focuses on balancing timber production with ecosystem services, such as biodiversity conservation and water regulation.
- 👩🌾 Decentralized forest governance in Indonesia emphasizes local participation in forest decision-making and management, aligning with global trends in community-based forestry.
- 📈 The evolution of forest management reflects a broader understanding of the role of forests in both local and global environmental and economic systems.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the lecture in the transcript?
-The main focus of the lecture is the history of forest management, both globally and in Indonesia. It covers topics such as timber mining, forest resource management, forest ecosystem management, and community-based forestry.
When did timber mining first begin in the world according to the lecture?
-Timber mining began around the year 200 CE in the Euphrates and Tigris valleys during the Babylonian kingdom.
How did timber mining evolve in Europe?
-Timber mining expanded in Central and Western Europe during the third century when the Roman Empire began to develop its territories. This led to the creation of forestry laws such as the Ordonnance The Melon in France in 1376 and the Forest Act in 1543.
What was the significance of timber mining in Indonesia?
-Timber mining in Indonesia began during the colonial period when the country was under Dutch, Portuguese, and Spanish rule, marking the introduction of forest management practices in the region.
What is the 'monoculture' approach mentioned in the lecture, and what are its advantages and disadvantages?
-Monoculture is a forestry approach where a single species of tree is planted across large areas. Its advantage is that it simplifies planning and can reduce costs, but its disadvantages include increased vulnerability to pests and diseases and reduced environmental protection.
What was the shift in forest management towards social forestry?
-Social forestry emerged as a shift towards managing forests for the benefit of local communities. It emphasizes the involvement of local people in the planning and management of forest resources, aiming to balance environmental sustainability and community needs.
What is the difference between conventional forestry and social forestry?
-Conventional forestry focuses on timber production, often benefiting businesses, while social forestry emphasizes the welfare of local communities and the sustainable use of forest resources, incorporating local needs and environmental protection.
How did forest management evolve from the 8th Congress of Forestry in 1978?
-The 8th Congress of Forestry in 1978 marked the formal recognition of social forestry, emphasizing forest management that benefits local communities and involves them in decision-making processes, with a broader focus on various forest products beyond timber.
What is the concept of 'forest ecosystem management'?
-Forest ecosystem management focuses on managing forests as entire ecosystems, prioritizing environmental protection, biodiversity, and ecological functions rather than just economic output from timber. It includes considering the role of forests in hydrology, wildlife, and overall environmental stability.
How has forest management evolved in Indonesia according to the transcript?
-Forest management in Indonesia has evolved from state-controlled, centralized systems to community-based models, such as social forestry, where local communities play a key role in managing and benefiting from forest resources. Various government policies have supported this shift, including laws that allow local people to manage forested areas under different schemes.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Overview of FAO Forestry’s work on social forestry
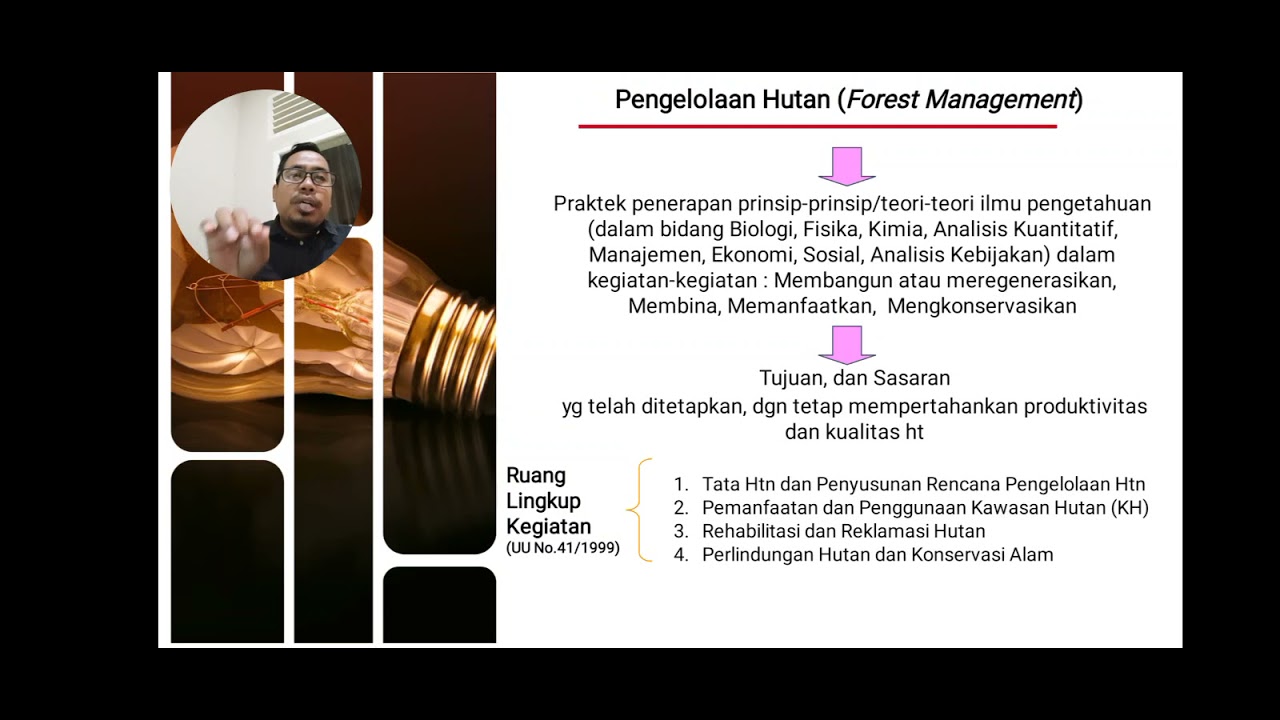
kebijakan Kehutanan Part 5

PENGANTAR MANAJEMEN PART #2 - PERKEMBANGAN TEORI MANAJEMEN || JURUSAN MANAJEMEN - Albert Steinado

TEKNIK SILVIKULTUR ||Memahami apa sih Teknik Silvikultur Itu? Jenis dan Aplikasinya di lapangan?||

História da Administração

Video Pertemuan 1.PENDAHULUAN
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)