Maxwell's Equations: Crash Course Physics #37
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the groundbreaking contributions of James Maxwell to the field of electromagnetism. It details Maxwell’s four key equations, which unified electric and magnetic phenomena, leading to the prediction of electromagnetic waves. The video also delves into the nature of electromagnetic waves, their energy, and how they propagate through space. With insights into Maxwell’s mathematical approach and the connection to real-world applications like antennas, the video highlights the profound impact of these theories on modern physics, including relativity and quantum mechanics. Ultimately, it emphasizes the lasting legacy of Maxwell’s work in shaping our understanding of the universe.
Takeaways
- 😀 Maxwell’s equations unify the study of electric and magnetic fields into a comprehensive theory of electromagnetism.
- 😀 Michael Faraday demonstrated that a changing magnetic field induces an electromotive force (emf), leading to an electric current.
- 😀 James Maxwell expanded on Faraday’s and other physicists' work, formulating four key equations that govern all electromagnetic interactions.
- 😀 Maxwell predicted the existence of electromagnetic waves, which later proved to be the foundation of technologies like radio, light, and microwaves.
- 😀 Maxwell's first equation is a form of Gauss’s Law for electric fields, stating that electric flux through a closed surface is proportional to the enclosed charge.
- 😀 Maxwell’s second equation describes magnetic flux, emphasizing that magnetic fields always form dipoles and have no 'monopoles'.
- 😀 Faraday’s Law, which Maxwell modified, states that a changing magnetic field induces an electric field, represented by a line integral over a closed loop.
- 😀 Maxwell's third equation addresses how a changing electric field can generate a magnetic field, similar to how electric currents create magnetic fields.
- 😀 The displacement current term added by Maxwell to Ampère’s Law accounts for changing electric fields, even in the absence of physical current flow, like in capacitors.
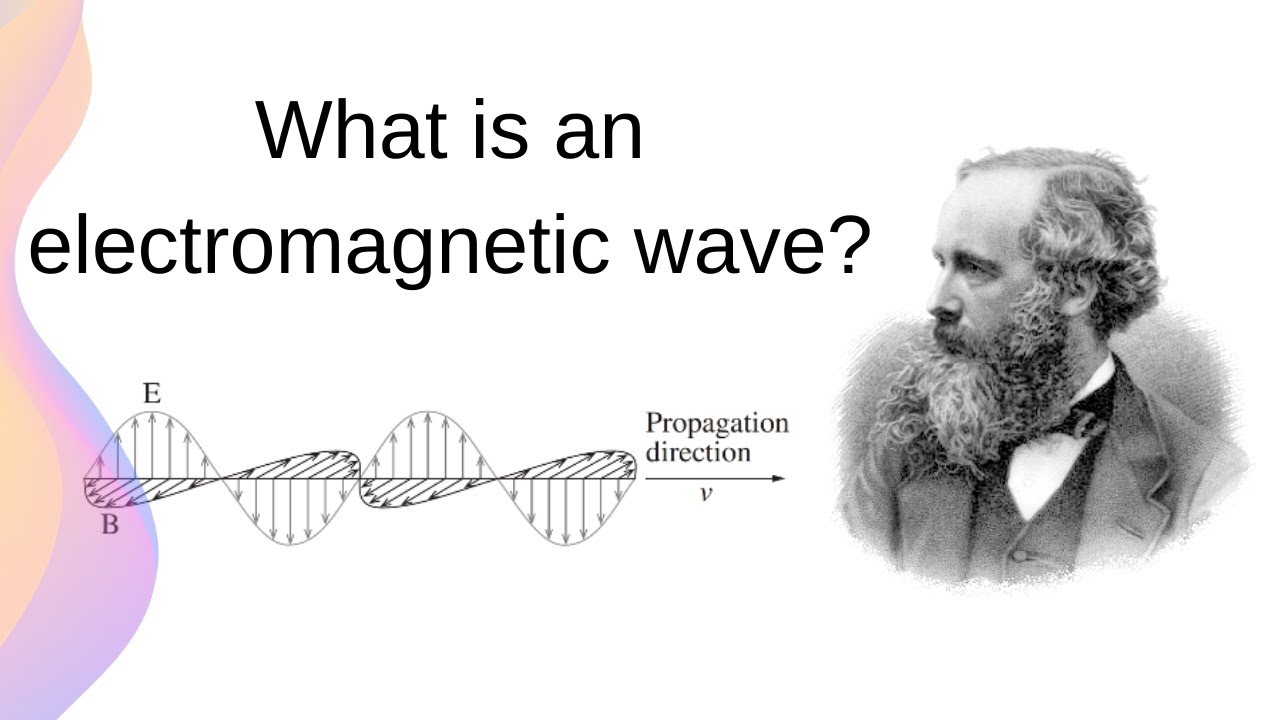
- 😀 Maxwell’s equations describe electromagnetic waves, where oscillating electric and magnetic fields propagate through space at the speed of light (3.00 × 10^8 m/s).
- 😀 The energy carried by electromagnetic waves is proportional to the magnitudes of the electric and magnetic fields, and intensity is the energy transported per unit area and time.
Q & A
What discovery did Michael Faraday make in the early 1800s regarding electromagnetism?
-Michael Faraday discovered that a changing magnetic field induces an electromotive force (emf), which results in an electric current. He also found that electric fields sometimes act like magnetic fields.
What was James Maxwell's contribution to the understanding of electromagnetism?
-James Maxwell developed a set of equations that unified the understanding of electromagnetism, predicting the existence of electromagnetic waves and helping to explain how electric and magnetic fields interact.
What is the significance of Maxwell’s equations in physics?
-Maxwell’s equations are fundamental to physics, similar to Newton’s laws of motion. They provide a complete understanding of how electric and magnetic fields interact, leading to the prediction of electromagnetic waves.
What is Gauss's Law in the context of Maxwell's first equation?
-Gauss’s Law states that the electric flux through a closed surface is proportional to the total charge enclosed by that surface. Maxwell’s first equation is a mathematical form of this law.
How does Maxwell’s second equation differ from his first equation?
-Maxwell’s second equation is similar to the first but applies to magnetic fields. It states that the magnetic flux through a closed surface is always zero, as there are no magnetic monopoles.
What is Faraday's Law and how did Maxwell modify it?
-Faraday's Law states that a changing magnetic field induces an electromotive force (emf) in a wire loop. Maxwell modified this law to show that the induced emf is the line integral of the electric field over a closed loop.
What was the purpose of Maxwell’s modification of Ampère’s Law?
-Maxwell modified Ampère’s Law to account for situations where a magnetic field is induced not by current but by a changing electric field, such as the changing electric field between the plates of a capacitor.
What is the displacement current, and why is it important in Maxwell’s equations?
-The displacement current is a term added by Maxwell to Ampère’s Law to account for the changing electric field between the plates of a capacitor. Though it is not an actual electric current, it behaves mathematically like one, completing Maxwell's equations.
What did Maxwell predict about electromagnetic waves?
-Maxwell predicted the existence of electromagnetic waves, which consist of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. These waves can travel through space, forming the basis for technologies like radio communication, light, and microwave heating.
How does an antenna produce electromagnetic waves?
-An antenna produces electromagnetic waves by alternating the charges between two conductive rods connected to an AC generator. As the charges alternate, they generate oscillating electric and magnetic fields that propagate as electromagnetic waves.
How do electromagnetic waves behave and propagate through space?
-Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves with electric and magnetic fields that oscillate perpendicular to each other and to the direction of wave travel. These waves travel at the speed of light in a vacuum, carrying energy and propagating through space.
What is the speed of light, and how does it relate to Maxwell’s equations?
-The speed of light is approximately 3.00 × 10^8 meters per second. This speed is derived from Maxwell’s equations, which relate the electric and magnetic fields in an electromagnetic wave and lead to the conclusion that electromagnetic waves travel at this constant speed in a vacuum.
What is the electromagnetic spectrum, and how does visible light fit into it?
-The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all types of electromagnetic radiation, from radio waves to gamma rays. Visible light is a small part of this spectrum, with specific wavelengths that are detectable by the human eye.
How do you calculate the energy carried by an electromagnetic wave?
-The energy carried by an electromagnetic wave can be calculated by determining the energy density of the electric and magnetic fields, then combining them to find the total energy per unit volume of the wave.
What is intensity in the context of electromagnetic waves?
-Intensity is the energy transported by an electromagnetic wave per unit time and area. It can be calculated using the energy density of the wave and the distance it travels over time.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)