How to Solve a Parallel Circuit Problem 🔋🔌
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the speaker explains how to solve a parallel circuit problem, focusing on key concepts like voltage, current, and resistance. The video walks viewers through the steps of understanding how current splits across different branches, with each branch sharing the same voltage. The speaker covers how to calculate the current in each branch using Ohm's law and the two methods for determining total resistance: using total voltage and current or by summing the inverse resistances. The video provides a thorough breakdown of these concepts, ensuring viewers grasp the essentials of solving parallel circuit problems.
Takeaways
- 😀 In a parallel circuit, multiple loops exist, allowing current to split and flow through different branches.
- 😀 Each branch in a parallel circuit experiences the same voltage drop, which is equal to the total voltage of the power source.
- 😀 Current splits when it reaches the junction in a parallel circuit, flowing through different branches based on their resistance.
- 😀 Ohm's Law (V = IR) is used to calculate the current through each branch in a parallel circuit, with voltage divided by resistance.
- 😀 The total current in a parallel circuit is the sum of the currents through each branch.
- 😀 To calculate total resistance in a parallel circuit, the inverses of each branch's resistance are summed.
- 😀 The total current can be found by adding up the individual currents in the branches after applying Ohm's Law.
- 😀 For simpler problems, the total resistance can be calculated directly using Ohm's Law (R = V/I).
- 😀 The more universal method for finding total resistance in a parallel circuit is by summing the inverses of the resistances and then inverting the result.
- 😀 To sum the inverses, you can either manually find the common denominator or use a calculator for easier calculation.
- 😀 Both methods (using Ohm's Law directly or summing inverses) should yield the same result for total resistance when calculated correctly.
Q & A
What is the key difference between a parallel circuit and a series circuit?
-A parallel circuit has multiple loops for current to flow through, while a series circuit has a single path for current to travel. In a parallel circuit, the current splits at junctions, while in a series circuit, the current flows through all components in sequence.
How does the voltage behave in a parallel circuit?
-In a parallel circuit, the voltage is the same across all branches. Each branch receives the same voltage drop as the total voltage supplied by the power source.
What happens to the current when it reaches a junction in a parallel circuit?
-At a junction in a parallel circuit, the total current splits into separate branches. Each branch carries a portion of the total current, depending on the resistance of that branch.
Why is it necessary to understand the concepts before solving the math for a parallel circuit?
-Understanding the concepts, such as how current splits and how voltage remains constant across branches, makes the mathematical calculations easier and more intuitive, leading to more accurate results.
How do you calculate the current in each branch of a parallel circuit?
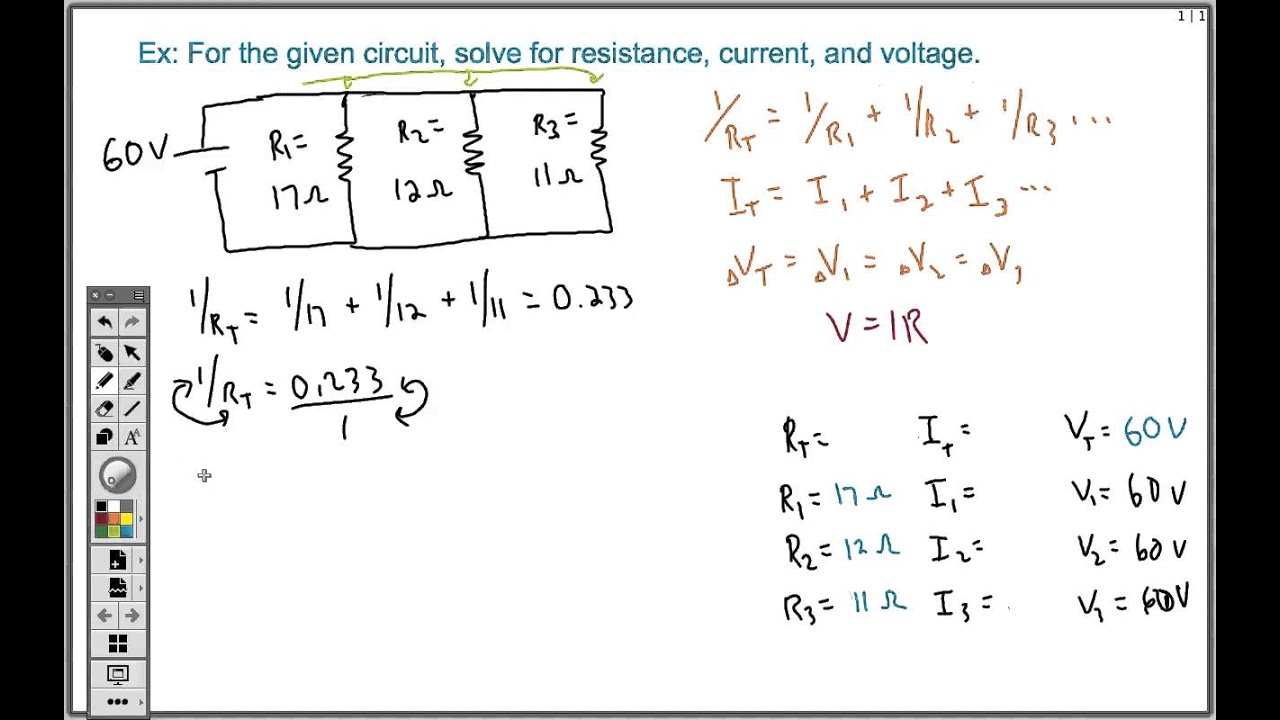
-To calculate the current in each branch of a parallel circuit, use Ohm's law: I = V/R, where V is the voltage across the branch (which is the same for all branches) and R is the resistance of that particular branch.
What is the process to find the total current in a parallel circuit?
-To find the total current in a parallel circuit, you calculate the current through each branch using Ohm's law and then add them up. The total current is the sum of the currents in all branches.
What is the formula used to calculate the total resistance in a parallel circuit?
-The total resistance in a parallel circuit is calculated using the formula: 1/Rt = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3 + ..., where Rt is the total resistance and R1, R2, R3, etc., are the resistances of the individual branches.
What is the easier method to find the total resistance in a parallel circuit if you know the total voltage and current?
-If you know the total voltage and current, the easiest method is to use Ohm's law in the form: Rt = V/I, where V is the total voltage and I is the total current.
What does the second method to find the total resistance involve?
-The second method involves adding the reciprocals of each branch's resistance, then taking the reciprocal of the total. This method is more universal and doesn't require knowledge of the total voltage and current.
Why might someone prefer to use a calculator when calculating the sum of reciprocals for total resistance?
-Using a calculator simplifies the process and reduces the chance of making errors when adding fractions or finding the common denominator. It is especially helpful when working with resistances that are more complex or involve decimals.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

ASSOCIAÇÃO DE RESISTORES: em série e em paralelo | Cortes dos Aulões do Enem | Física | Antônio
How to Solve a Parallel Circuit (Easy)

DC Resistors & Batteries: Crash Course Physics #29

Listrik Dinamis-Rangkaian Listrik (Hukum Ohm) (Part 3)

Chapter 3 Summary - Simple Resistive Circuits

Aula 8 - Circuito em série e paralelo
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)