Os Elementos Químicos - Carbono
Summary
TLDRIn this episode of the series on chemical elements, the focus is on carbon, a key element essential to life. Carbon, with an atomic number of 6, is known for its versatility, forming bonds with a wide range of elements. It exists in various forms, such as graphite and diamond, and plays a critical role in organic chemistry and the environment. Carbon is central to energy cycles and forms compounds that are vital to living organisms. Despite concerns over carbon emissions, which contribute to climate change, it remains fundamental to life on Earth and technological advancements.
Takeaways
- 😀 Carbon is a chemical element with the symbol C, atomic number 6, and an atomic mass of 12 units.
- 😀 Carbon is solid at room temperature and has been known since ancient times, dating back to around 3750 BC.
- 😀 The name 'carbon' was proposed by Lavoisier in 1774, and its chemical behavior was later explained by scientists such as Kekulé and Cooper.
- 😀 As a member of Group 14 in the periodic table, carbon is a non-metal and is tetravalent, meaning it can form four covalent bonds.
- 😀 Carbon has three natural isotopes: Carbon-12, Carbon-13, and Carbon-14, with Carbon-14 being radioactive.
- 😀 Carbon is remarkable for its ability to form long chains and even cyclic structures, allowing it to create a wide variety of compounds.
- 😀 Carbon’s versatility allows it to form compounds with oxygen (e.g., CO2) and hydrogen (e.g., hydrocarbons), essential for life and industry.
- 😀 Carbon is a fundamental component of all life on Earth, including the molecules that make up DNA and proteins.
- 😀 Carbon is also responsible for the creation of diamond, the hardest known substance, and graphite, a more fragile and cheap form.
- 😀 Carbon's ability to form layered structures, such as graphite and nanotubes, has important technological applications in materials science.
- 😀 Despite its vital role in life, excessive carbon release into the atmosphere through human activity is causing dangerous environmental imbalances.
Q & A
What is the atomic number and atomic mass of Carbon?
-Carbon has an atomic number of 6 and an atomic mass of 12.
Who proposed the name 'carbon' and when?
-The name 'carbon' was proposed by Antoine Lavoisier in 1774.
What is the significance of carbon being tetravalent?
-Carbon being tetravalent means it can form four covalent bonds with other atoms, which gives it the ability to create complex molecules and structures.
What are the three isotopes of carbon?
-The three isotopes of carbon are Carbon-12, Carbon-13, and Carbon-14.
What is Carbon-14 known for?
-Carbon-14 is a radioactive isotope of carbon, used in radiocarbon dating to determine the age of ancient organic materials.
How does the atomic structure of carbon contribute to its versatility in forming compounds?
-Carbon’s small atomic radius allows it to form stable bonds with a variety of elements, leading to the creation of long chains, rings, and diverse compounds, such as hydrocarbons and carbonates.
What are some common forms of carbon and how do they differ?
-Two common forms of carbon are graphite and diamond. Graphite is soft and used in pencils, while diamond is the hardest known natural material.
What role does carbon play in the environment and life on Earth?
-Carbon is crucial for life, as it is a fundamental part of organic molecules like DNA, proteins, and fatty acids. It also plays a vital role in processes like photosynthesis and the carbon cycle, which supports plant growth and sustains life on Earth.
How does carbon contribute to the formation of fuels and energy?
-Carbon combines with hydrogen to form hydrocarbons, which are essential for producing fuels such as gasoline, natural gas, and oil, all critical for energy production and transportation.
What environmental concerns are associated with carbon emissions?
-Excessive carbon emissions, particularly in the form of carbon dioxide (CO2), contribute to climate change by increasing the greenhouse effect, which leads to global warming and disruptions in ecosystems.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

CHIMICA FACILE 3 - I Composti e le reazioni chimiche

Why is All Life Carbon Based, Not Silicon? Three Startling Reasons!

Biogeochemical Cycling
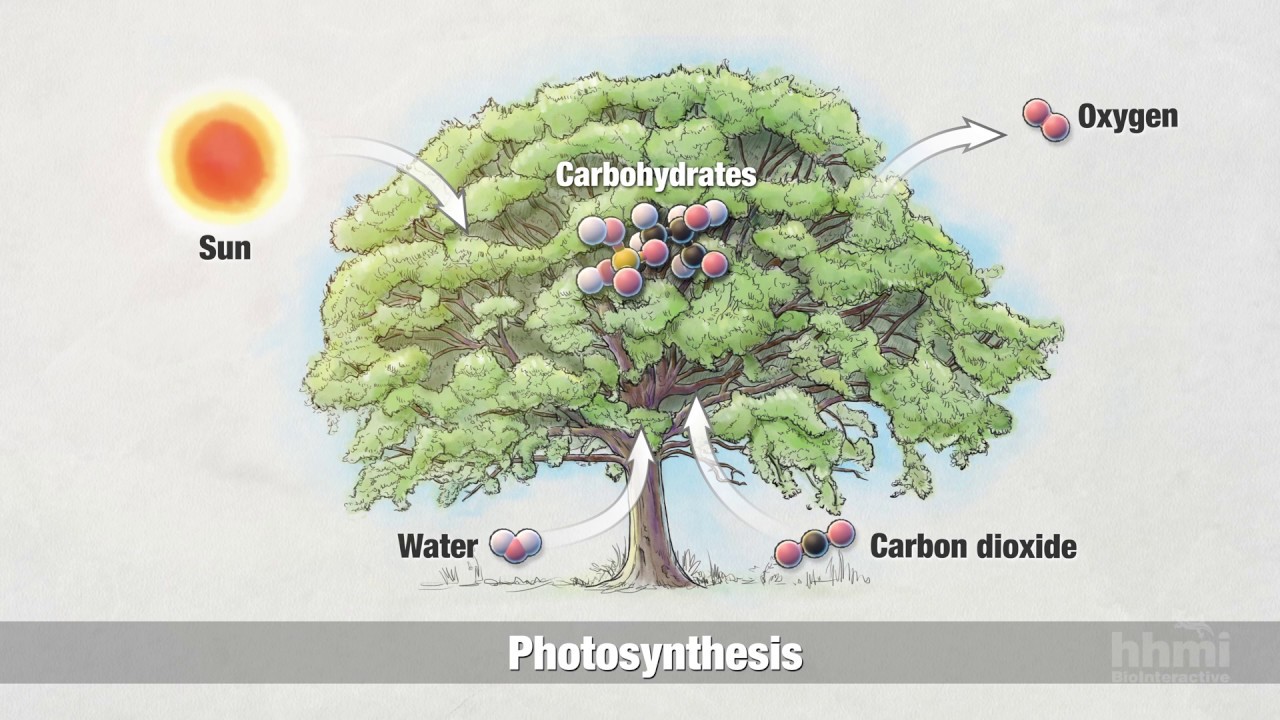
Photosynthesis: Part 2: Chemical Process | HHMI BioInteractive Video

Chemistry: Introduction to the Periodic Table - Dmitri Mendeleev

Carbon Element 💎 - Periodic Table | Properties, Uses & More!
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)