Sistem Analog dan Digital (Sistem Digital)
Summary
TLDRThis video script explores the fundamental concepts of digital and analog systems in science and technology. It explains the key differences between continuous (analog) and discrete (digital) representations of quantities like speed, temperature, and voltage. Through examples like speedometers and thermometers, the script highlights how analog signals vary continuously, while digital systems use step-wise increments. The script also defines digital systems, focusing on logic levels and waveforms, and discusses the advantages of digital systems, such as precision, programmability, and resilience to noise. Overall, it emphasizes the importance and benefits of digital systems in modern technology.
Takeaways
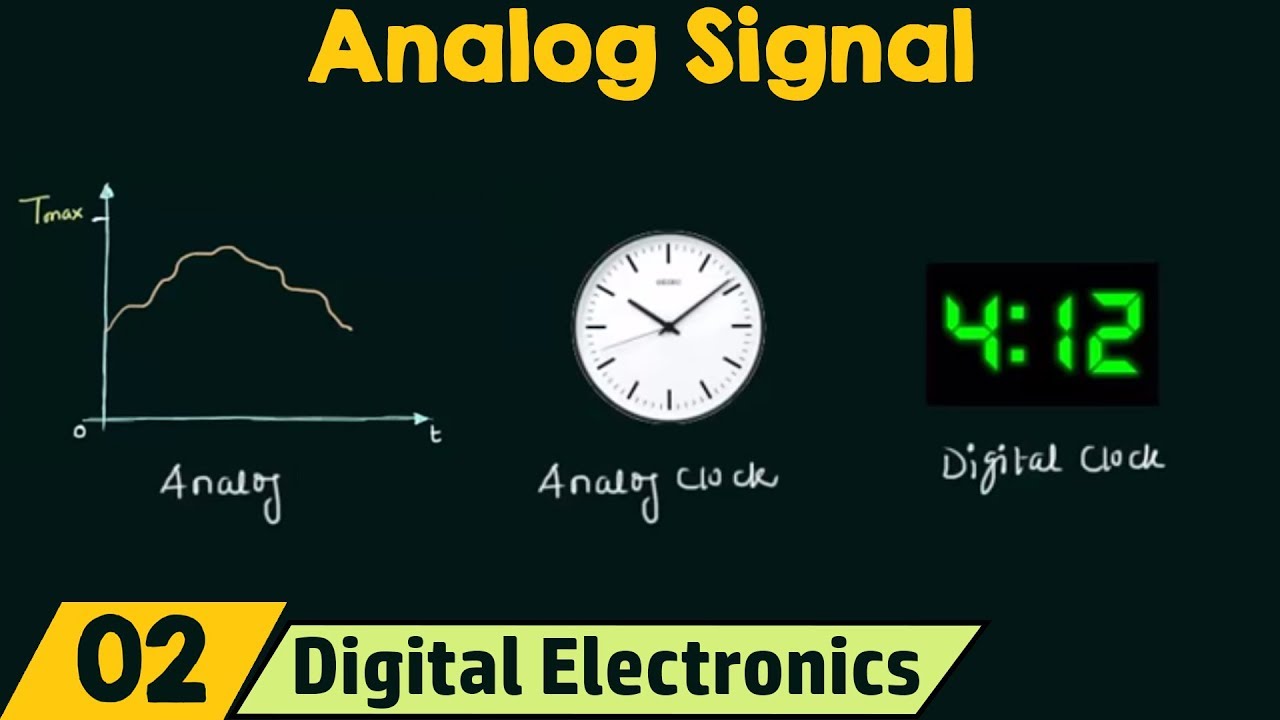
- 😀 Digital systems represent quantities using discrete values, while analog systems represent them continuously.
- 😀 Analog systems show data through continuous values like speedometers and thermometers with mercury or needles.
- 😀 Digital systems show data in discrete steps, with examples like digital clocks and digital thermometers.
- 😀 A speedometer's needle moves continuously in an analog system, representing real-time speed changes.
- 😀 In a digital system, data is displayed in discrete increments, like reading 5 km/h intervals on a digital speedometer.
- 😀 Analog signals are continuous, whereas digital signals are represented by discrete values or intervals.
- 😀 Digital systems offer advantages like easier design, higher accuracy, programmability, and better resistance to noise.
- 😀 The digital system uses logic levels (0 and 1) to represent two states: 'on' or 'off,' with corresponding voltage levels.
- 😀 Systems like voltmeters and ammeters can be either analog or digital, displaying voltage and current in different forms.
- 😀 Digital signals are quantized, meaning they take specific, separate values, unlike analog signals that can vary smoothly.
- 😀 Digital systems are often more efficient in storing and processing data due to their ability to handle more content in smaller space.
Q & A
What is the main difference between analog and digital systems?
-The main difference is that analog systems represent values continuously, whereas digital systems represent values in discrete steps. Analog systems use proportional values, and their waveforms are continuous, while digital systems process data in intervals and display values as discrete digits.
Can you explain the concept of analog representation with an example?
-Analog representation involves displaying a physical quantity in a continuous manner. For example, an analog speedometer shows the speed of a vehicle by the continuous movement of a needle that represents the actual speed value.
How does a digital representation differ from an analog one in terms of measurement?
-In digital systems, the measured values are shown as discrete digits, typically on a display. For instance, a digital thermometer shows the temperature in numerical values, and a digital speedometer will display speed in fixed increments, unlike the continuous movement of an analog needle.
What is the significance of using discrete values in a digital system?
-Using discrete values allows for easier data processing and storage, as digital systems work with well-defined, specific units of measurement. This discrete nature also helps in reducing errors, as the system can focus on fixed intervals and is less affected by noise compared to analog systems.
What is an example of an analog measuring instrument, and how does it work?
-An example of an analog measuring instrument is a thermometer that uses mercury. The level of mercury rises in response to temperature changes, and the height of the mercury column is used to read the temperature on a scale.
How do digital devices like digital voltmeters display their readings?
-Digital devices like digital voltmeters display their readings in numerical form, showing the exact value of voltage being measured. These readings are presented in a series of digits that correspond to the voltage levels, offering clear and precise data.
What are the key advantages of digital systems over analog systems?
-Digital systems are generally easier to design, offer higher accuracy, are less prone to interference (noise), and can store data more efficiently. Additionally, they can be programmed for specific tasks and are more resistant to degradation over time.
What does the term 'system digital' refer to, and what components does it consist of?
-A digital system refers to an electronic system that processes discrete signals. It consists of logic gates, electronic components, and circuits that handle the digital data, allowing for operations such as switching, calculation, and information storage.
What are the typical voltage levels used to represent logic 0 and logic 1 in digital systems?
-In digital systems, logic 0 is typically represented by a low voltage, such as 0 to 0.8 volts, while logic 1 is represented by a higher voltage, usually between 2 and 5 volts.
What is the role of logic gates in a digital system?
-Logic gates are the fundamental building blocks of digital systems. They perform basic logical functions (such as AND, OR, and NOT) to process binary data, enabling decision-making and control of electronic operations in digital devices.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)