BIO428: Genetics Chapter 2B 2023
Summary
TLDRThis lecture explores the intricacies of the cell cycle, highlighting its regulation by cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases, and inhibitors. It discusses the checkpoints in G1 and G2 phases, the importance of cyclin accumulation, and the differences between diploid and haploid cells. The lecture also covers meiosis, detailing unique features like synapsis, homologous recombination, and reduction division. Additionally, the processes of spermatogenesis and oogenesis are explained, showcasing gametogenesis in males and females. The lecture ties these processes together, demonstrating their role in sexual reproduction and genetic diversity.
Takeaways
- 😀 The cell cycle is highly regulated, and disruptions can lead to diseases like cancer.
- 😀 Cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), and CDK inhibitors play a key role in controlling the cell cycle.
- 😀 The cell cycle consists of four phases: G1 (growth), S (synthesis), G2 (preparation for division), and M (mitosis or meiosis).
- 😀 The G1 to S phase and G2 to M phase transitions are tightly controlled by checkpoints to ensure cell readiness for division.
- 😀 Cyclin accumulation is crucial for cell cycle progression; inappropriate expression can trigger premature division or impede progression.
- 😀 The difference between diploid and haploid cells is highlighted, with somatic cells being diploid (46 chromosomes) and gametes being haploid (23 chromosomes).
- 😀 Polyploidy, where organisms have more than two sets of chromosomes, is beneficial for plants but harmful to animals.
- 😀 Meiosis reduces the chromosome number by half, and involves key processes like synapsis, homologous recombination, and reduction division.
- 😀 Meiosis involves two stages: Meiosis I (reduction division) and Meiosis II (equational division), resulting in four haploid daughter cells.
- 😀 Spermatogenesis and oogenesis are processes of gamete formation, with spermatogenesis occurring in the testes and oogenesis in the ovaries.
Q & A
What is the role of cyclins and CDKs in regulating the cell cycle?
-Cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) are key positive regulators of the cell cycle. They activate cell cycle factors that are essential for the progression through different phases of the cell cycle, ensuring that the cycle proceeds in an orderly and regulated manner.
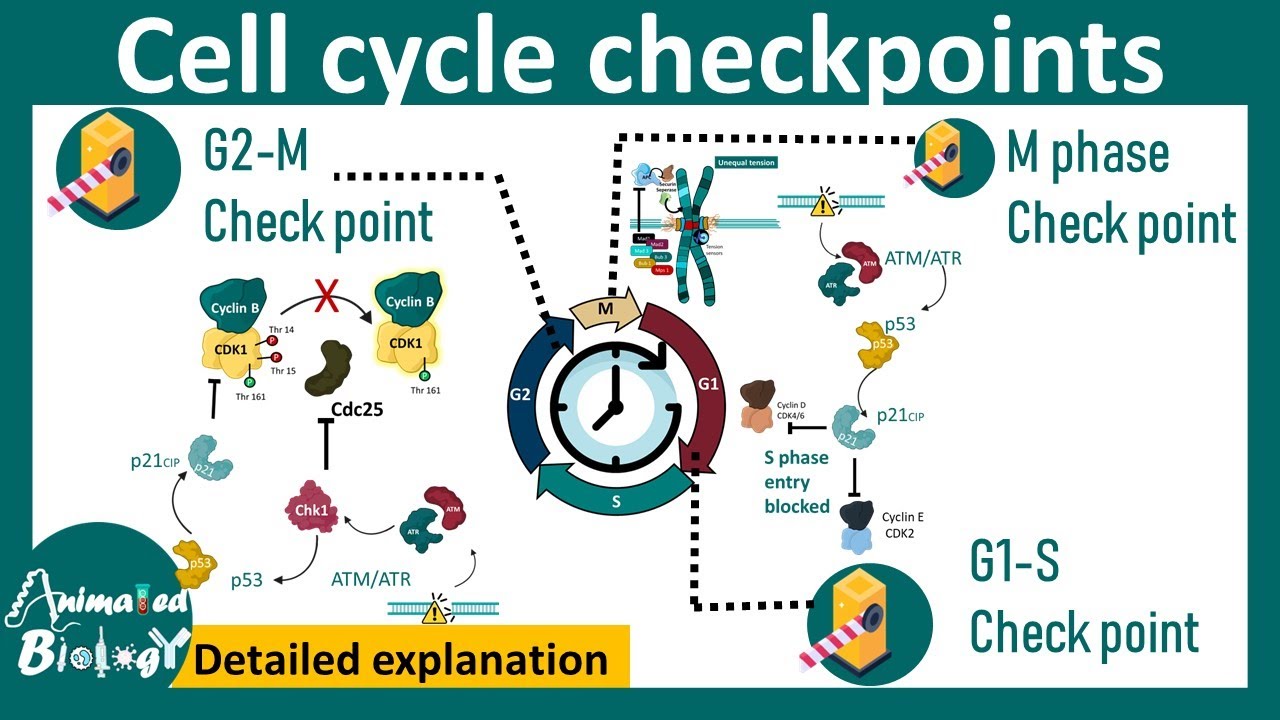
Why are G1 and G2 checkpoints critical in the cell cycle?
-The G1 and G2 checkpoints are essential for ensuring that the necessary materials are available before proceeding to the next phase. In the G1 phase, cell size, protein, and RNA synthesis are checked to ensure that enzymes for DNA synthesis are available. In the G2 phase, the materials required for cellular division are verified before mitotic division.
What is the significance of the transition from G1 to S phase and from G2 to M phase?
-These transitions are crucial checkpoints in the cell cycle. They assess intrinsic signals and are governed by cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK2 and CDK1), ensuring that the cell only proceeds to the next phase when it is properly prepared.
What is the difference between diploid and haploid cells?
-Diploid cells contain two sets of chromosomes (one from each parent), whereas haploid cells have only one set of chromosomes. Somatic cells are diploid, while gametes (sperm and egg cells) are haploid.
What occurs during fertilization of gametes?
-Fertilization involves the fusion of two haploid gametes (sperm and egg), resulting in a diploid zygote with a full set of chromosomes (46 chromosomes in humans).
How does polyploidy differ in plants and animals?
-Polyploidy, which is the presence of more than two sets of chromosomes, is beneficial in plants as it can lead to better traits, but it is generally detrimental in animals, leading to genetic defects and abnormalities.
What is the difference between somatic cells and gametic cells?
-Somatic cells are non-reproductive cells that contain a diploid number of chromosomes, while gametic cells (sperm and egg cells) are reproductive cells and contain a haploid number of chromosomes.
What are the three unique features of meiosis?
-The three unique features of meiosis are synapsis (the pairing of homologous chromosomes), homologous recombination (genetic exchange between homologous chromosomes), and reduction division (where chromosome number is halved, leading to haploid cells).
What is the role of synapsis and crossing over in meiosis?
-Synapsis is the process where homologous chromosomes pair up during prophase 1 of meiosis. This allows crossing over, or the exchange of genetic material, which leads to genetic variation.
What is spermatogenesis, and how does it differ from oogenesis?
-Spermatogenesis is the process by which male gametes (sperm cells) are produced in the testes, involving mitosis and two meiotic divisions. Oogenesis, on the other hand, is the production of female gametes (eggs) in the ovaries, and it involves the formation of one mature egg and polar bodies through meiotic divisions.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Cyclins and CDKs Cell Cycle Regulation

Cyclin and CDK in cell cycle progression | How Cyclin CDK works?

4.7 Regulation of the Cell Cycle - AP Biology

Cell Cycle & Regulation, Mitosis, Cyclins, RB, P53 & Tumor Suppressors (USMLE Esssentials)
Cell cycle checkpoints | DNA damage checkpoint | spindle assembly checkpoint | Cell biology
The Cell Cycle and its Regulation
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)