Distribución Y Localización De Planta
Summary
TLDRThe script discusses the critical aspects of plant layout and design, emphasizing factors like safety, efficiency, and worker satisfaction. It outlines different distribution methods including fixed-position, process, and product-based layouts, each with specific applications. Key considerations include optimizing space, minimizing effort, and ensuring safety. The importance of complying with safety and hygiene regulations is highlighted. Furthermore, the script explores plant location strategies, evaluating factors such as proximity to markets, availability of resources, and environmental considerations. Decision-making tools for selecting plant locations are also discussed, covering both quantitative and qualitative methods.
Takeaways
- 😀 The designer's mission is to optimize the layout of work areas and equipment for maximum efficiency, safety, and worker satisfaction.
- 😀 Key objectives for plant distribution include integrating all affecting factors, minimizing effort, ensuring flexibility, and maintaining safety.
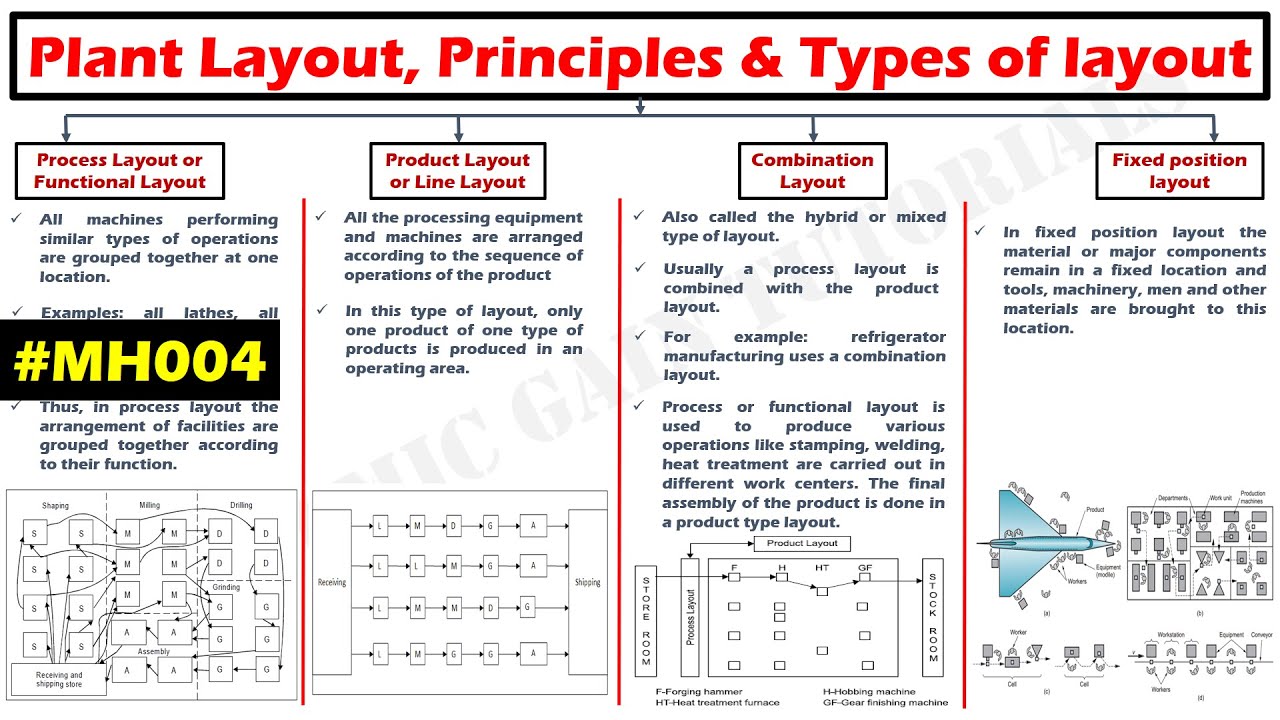
- 😀 Distribution types: Fixed position (for products that cannot be moved), process-based (grouping machines by their characteristics), and product-based (assembly line production).
- 😀 The criteria for plant distribution include functionality, economic efficiency, flow, worker comfort, appropriate lighting, and environmental considerations.
- 😀 Plant distribution methods can be quantitative (based on measurable factors like distances) or qualitative (based on subjective factors like worker preferences).
- 😀 Flows in plant systems (linear or s-shaped) must be optimized to reduce disruptions and ensure continuous production.
- 😀 Adhering to seismic codes is critical to ensuring the safety of workers and minimizing damage during earthquakes.
- 😀 Hygiene and safety regulations aim to protect worker health by eliminating or isolating work-related risks and promoting a proactive safety culture.
- 😀 Plant location decisions should prioritize cost-effectiveness, accessibility to resources, and market proximity.
- 😀 Location alternatives include expanding existing facilities, adding new ones in different locations, or relocating completely. Cost-benefit analysis is crucial in deciding.
- 😀 Factors influencing location selection include labor availability, climate, proximity to suppliers/clients, community regulations, and available resources.
Q & A
What is the primary mission of a designer in plant layout and distribution?
-The designer's primary mission is to find the best arrangement of work areas and equipment to achieve maximum work efficiency, worker safety, and satisfaction.
What are the key objectives to be met in plant layout and distribution?
-The key objectives include integrating all factors affecting distribution, ensuring the smooth circulation of work, utilizing space effectively, minimizing effort and ensuring worker safety, and providing flexibility for adjustments or expansions.
What are the three types of distribution mentioned in the script?
-The three types of distribution are fixed-position or static product distribution, process-based distribution, and product-based distribution (also known as a production line).
What is the focus of fixed-position or static product distribution?
-In fixed-position or static product distribution, the product cannot be moved due to its size or the necessity to complete the work in a specific location, such as water collection tanks in cities.
How does process-based distribution work?
-Process-based distribution involves grouping machines and services according to the characteristics of each, clearly differentiating the steps the raw material undergoes to become the finished product.
What is product-based distribution, and how does it function?
-Product-based distribution, also known as the production line or assembly line, arranges machines, services, and accessories in a continuous sequence so that each process follows immediately after the previous one.
What are some of the criteria for plant layout distribution?
-The criteria for plant layout distribution include functionality, economic considerations (e.g., cost savings from reduced distances), smooth flow of work, comfort for workers, adequate lighting, air circulation, and ease of access.
What is the difference between quantitative and qualitative methods of plant layout distribution?
-Quantitative methods focus on measuring processes and distances to minimize transportation costs, while qualitative methods consider subjective factors like the convenience of department proximity and worker comfort.
How does the plant flow system work in layout design?
-The flow system in layout design governs the circulation based on the physical shape of the facility, with options such as a linear flow or S-shaped flow to ensure efficient movement within the plant.
What are the main factors influencing plant location?
-Factors influencing plant location include labor availability, climate, altitude, proximity to suppliers and customers, community policies, and access to necessary resources.
What are the typical alternatives for plant location selection?
-The three main alternatives for plant location selection are expanding an existing facility, adding new facilities at a different location, or relocating an existing facility to a new site.
What considerations are made during the selection of a new plant location?
-Considerations include evaluating the availability of materials, labor, transportation, public services, and climate, as well as legal factors like taxes, regulations, and land characteristics such as soil type and terrain.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Boost Efficiency with Process Layouts in Manufacturing!
#MH004 Plant Layout, Principles of plant layout & Types of layout.

Pipe Rack Design for Piping : Essential Tips for Piping Engineers

MOTIVASI KERJA DALAM MATA KULIAH MANAJEMEN SUMBER DAYA MANUSIA ll - Manajemen B

DESAIN TATA LETAK (LAYOUT DESIGN)

Lec 19: Plant Layout: Types of Layout
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)