DAUR BIOGEOKIMIA/DAUR AIR/DAUR FOSFOR/DAUR SULFUR/DAUR NITROGEN/DAUR KARBON DAN OKSIGEN/SMA KELAS X
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an informative overview of biogeochemical cycles, highlighting their crucial role in maintaining life on Earth. The speaker explains various cycles, including the water cycle, sulfur cycle, phosphorus cycle, nitrogen cycle, and carbon-oxygen cycle. Each cycle is described in detail, emphasizing the movement of elements between biotic and abiotic components of ecosystems. The video explores how processes like evaporation, photosynthesis, and decomposition contribute to sustaining ecosystems, offering viewers a comprehensive understanding of the natural processes that support life on our planet.
Takeaways
- 😀 Biogeochemical cycles are continuous processes that involve the movement of chemical elements between abiotic (non-living) and biotic (living) components of the Earth.
- 😀 The water cycle involves the movement of water through evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and transpiration, ensuring water availability on Earth.
- 😀 Sulfur in the environment is cycled through various forms, including sulfur dioxide and hydrogen sulfide, with bacteria playing a key role in its reduction.
- 😀 Phosphorus is an essential element for life, found in rocks and soil, and is absorbed by plants, which are then consumed by herbivores and decomposers.
- 😀 The nitrogen cycle involves the transformation of nitrogen in the atmosphere into usable forms like ammonia and nitrates, which plants absorb and animals consume.
- 😀 Nitrogen fixation by bacteria like Azotobacter and Rhizobium converts atmospheric nitrogen into forms that plants can use for protein synthesis.
- 😀 The carbon cycle involves plants using carbon dioxide from the atmosphere for photosynthesis, releasing oxygen, which is used by animals for respiration.
- 😀 Carbon is also stored in fossil fuels formed from decomposed organic matter, which when burned, release carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere.
- 😀 Sulfur compounds can contribute to acid rain, impacting ecosystems and soil quality, and affecting the sulfur cycle’s dynamics.
- 😀 Decomposers play a crucial role in recycling nutrients, breaking down organic matter from dead plants and animals into simpler compounds like ammonium and nitrates.
- 😀 Biogeochemical cycles are interconnected, meaning changes in one cycle (e.g., carbon or nitrogen) can affect other cycles and overall environmental balance.
Q & A
What is biogeochemical cycling?
-Biogeochemical cycling refers to the continuous movement of elements or chemical compounds from abiotic components (non-living) to biotic components (living) and back, with the help of organisms and chemical reactions in the abiotic environment.
What is the main function of biogeochemical cycles?
-The primary function of biogeochemical cycles is to sustain life on Earth by ensuring that essential materials, like water, sulfur, nitrogen, and phosphorus, are available to all living and non-living components of the ecosystem.
Can you explain the water cycle briefly?
-The water cycle, or hydrological cycle, is the continuous circulation of water through Earth's atmosphere, land, and bodies of water. Water evaporates from the surface, condenses into clouds, and precipitates as rain, where it may return to the surface, be absorbed by plants, or flow into rivers and oceans.
How does sulfur cycle in nature?
-Sulfur in nature is mainly found in inorganic forms. It is reduced into sulfides by bacteria and can be released as sulfur dioxide or hydrogen sulfide through processes like fossil fuel combustion or volcanic activity. This sulfur can form sulfuric acid and precipitate as acid rain, which is then absorbed by plants.
What role does phosphorus play in ecosystems?
-Phosphorus is an essential element for all living organisms as it is a key component of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is vital for energy metabolism. Phosphorus cycles through the environment by eroding rocks, being absorbed by plants, and eventually returning to the soil as decomposed organic matter.
What is the process of nitrogen fixation?
-Nitrogen fixation is the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen (N2) into forms usable by living organisms, like ammonia or nitrates. This process is facilitated by bacteria such as Azotobacter and Rhizobium that help plants absorb nitrogen.
What are the stages involved in the nitrogen cycle?
-The nitrogen cycle involves several key processes: nitrogen fixation (conversion of N2 into usable forms), nitrification (conversion of ammonia to nitrites and then to nitrates by bacteria), assimilation (plants absorbing nitrates), ammonification (decomposers breaking down dead organisms), and denitrification (conversion of nitrates back into N2).
How does the carbon and oxygen cycle work?
-In the carbon and oxygen cycle, carbon dioxide (CO2) is absorbed by plants during photosynthesis and converted into glucose, releasing oxygen (O2) in the process. Organisms then use oxygen to respire, releasing CO2 back into the atmosphere, continuing the cycle. Long-term storage occurs in fossil fuels.
What impact does the burning of fossil fuels have on the biogeochemical cycles?
-Burning fossil fuels releases carbon dioxide (CO2) and sulfur dioxide (SO2) into the atmosphere, which contributes to the carbon cycle and can lead to acid rain through sulfur emissions, impacting the sulfur cycle. This disrupts natural balances and can cause environmental damage.
How does the movement of water in the cycle relate to ecosystems?
-Water movement through the hydrological cycle supports ecosystems by providing hydration to plants and animals, regulating temperature, and enabling processes like transpiration in plants, which further contributes to atmospheric moisture and rainfall patterns.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Biogeochemical Cycles Carbon Hydrogen Nitrogen Oxygen Phosphorus Sulfur

KELAS 10 : MATERI EKOSISTEM BAG. 2 (Daur Biogeokimia)

Daur BioGeoKimia (Siklus Air, Karbon, Nitrogen, Fosfor, Sulfur)

Repaso de los ciclos biogeoquímicos | Ecología | Biología | Khan Academy en Español
How the Earth Recycles Elements: Biogeochemical Cycles
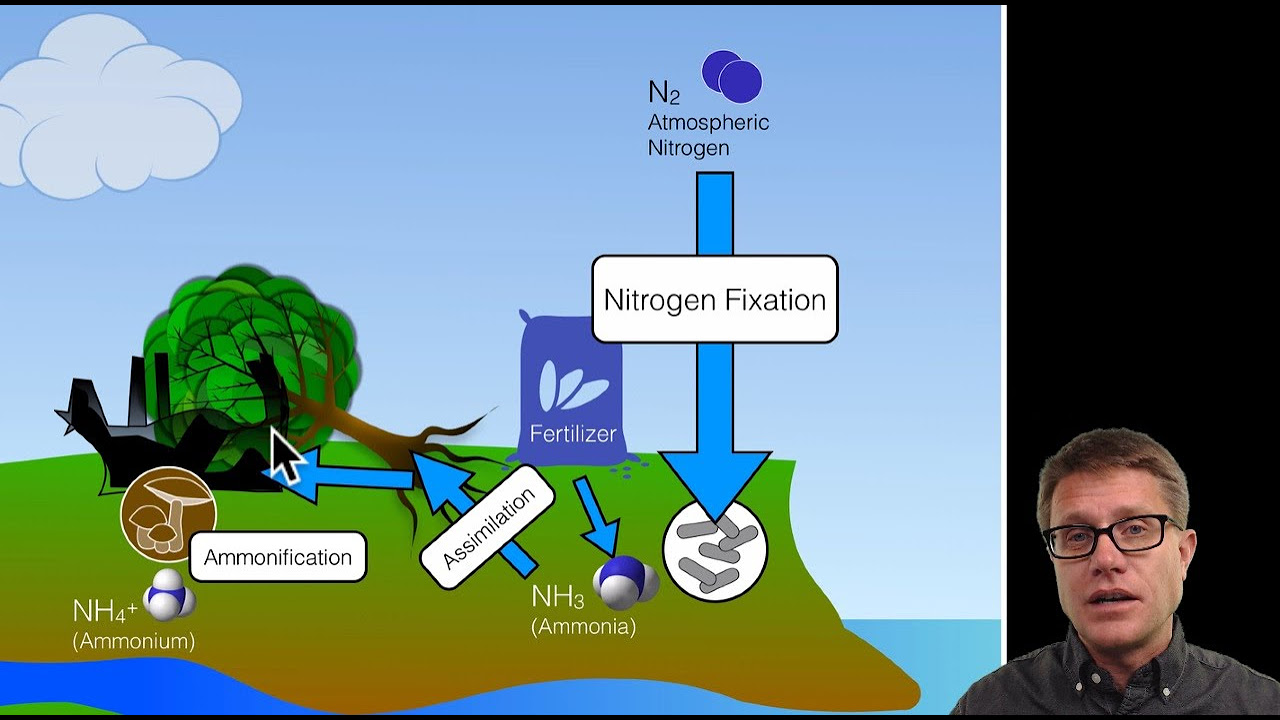
Biogeochemical Cycles
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)