CHEMICAL AND NERVOUS CONTROL
Summary
TLDRThis transcript delves into the workings of the nervous and endocrine systems, explaining how both regulate bodily functions. The nervous system is responsible for fast, short-term actions through the brain, spinal cord, and nerves, including voluntary and involuntary actions. In contrast, the endocrine system handles long-term regulation using hormones. Topics covered include the structure of neurons, neurotransmitter function, types of nerves, and key hormones like insulin and adrenaline. Additionally, the transcript explores plant hormones and their role in processes such as growth, flowering, and response to stimuli, offering a comprehensive look at physiological control in both animals and plants.
Takeaways
- 😀 The body regulates chemical processes through the endocrine system, which controls long-term effects using hormones.
- 😀 The nervous system is fast-acting, but its effects are generally short-term, though it can contribute to long-term memory and behavior.
- 😀 The central nervous system (CNS) consists of the brain and spinal cord, while the peripheral nervous system (PNS) connects to various body parts.
- 😀 The nervous system has two major divisions: the somatic nervous system (voluntary control) and the autonomic nervous system (involuntary control).
- 😀 The autonomic nervous system has two branches: the sympathetic (fight or flight) and parasympathetic (rest and digest).
- 😀 Neurons are the basic structural and functional units of the nervous system, responsible for transmitting electrical signals.
- 😀 Action potentials travel through neurons, with synapses facilitating the transfer of signals between neurons or to muscles and organs.
- 😀 Sensory neurons carry impulses towards the CNS, while motor neurons carry responses away from the CNS to effectors.
- 😀 There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves, each with distinct functions like smell, vision, and hearing.
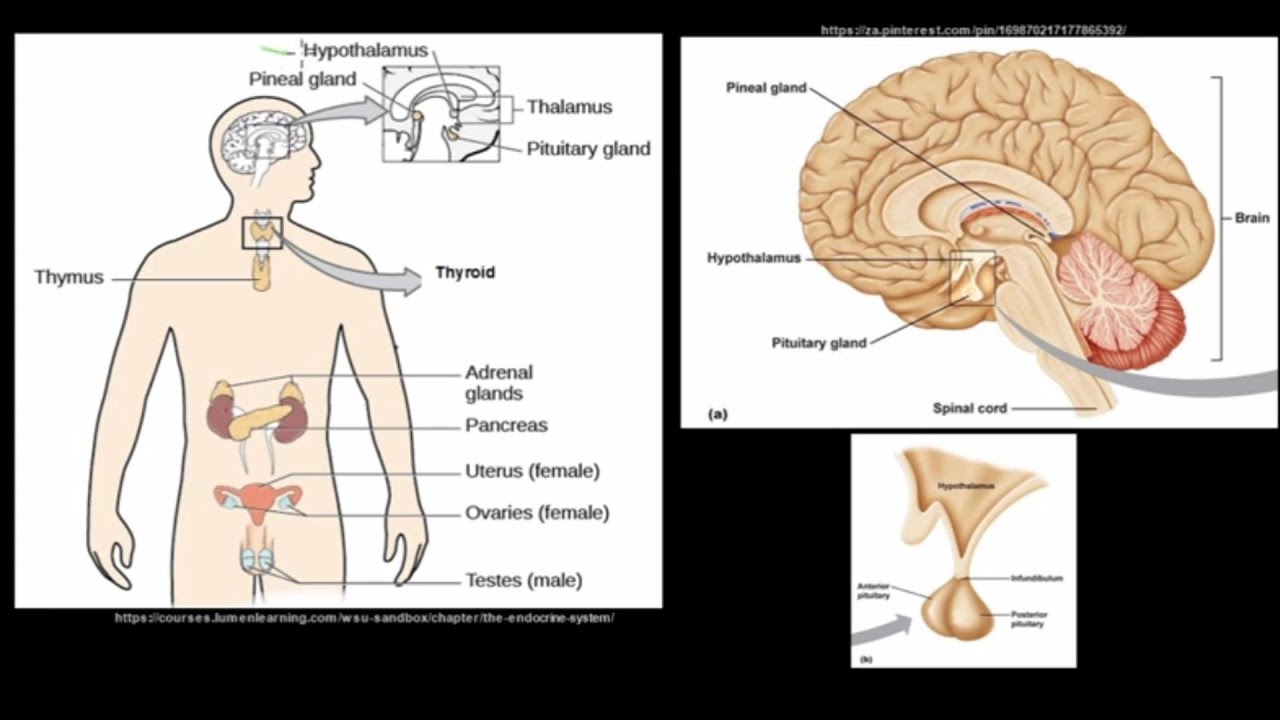
- 😀 The endocrine system produces hormones, which regulate processes like growth, metabolism, and homeostasis in both animals and plants.
Q & A
What system controls the chemical processes in the human body?
-The chemical processes in the human body are controlled by the endocrine system, which regulates hormones that act as chemical messengers.
How does the nervous system differ from the endocrine system in terms of speed and effects?
-The nervous system is fast-acting with short-term effects, while the endocrine system is slower but has long-term effects.
What are the two main divisions of the nervous system?
-The two main divisions of the nervous system are the central nervous system (CNS), consisting of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), which includes sensory and motor nerves.
What is the role of the sympathetic nervous system?
-The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for the 'fight or flight' response, preparing the body to handle stress or danger, such as increasing heart rate and strength.
What is the function of neurons in the nervous system?
-Neurons are the basic structural and functional units of the nervous system. They receive information from stimuli, transmit signals, and produce appropriate responses that are sent to muscles or organs.
What is the role of the myelin sheath in neurons?
-The myelin sheath is a fatty layer around the axon of neurons that helps speed up the transmission of electrical signals, ensuring efficient communication within the nervous system.
What are the different types of neurons, and what are their functions?
-There are sensory (afferent) neurons that carry impulses toward the CNS, motor (efferent) neurons that carry responses away from the CNS to muscles or organs, and interneurons that connect neurons within the CNS.
How do hormones regulate various processes in the body?
-Hormones, produced by the endocrine glands, are chemical messengers that regulate processes like metabolism, growth, mood, and reproductive functions. They help maintain homeostasis by coordinating different physiological activities.
What is the connection between the hypothalamus and the pancreas in hormone regulation?
-The hypothalamus signals the pancreas to release insulin to regulate blood sugar levels. If the blood sugar level drops, the hypothalamus may trigger the release of other hormones to raise the sugar level back to normal.
What is the function of plant hormones, and how do they influence plant growth?
-Plant hormones are chemical messengers that regulate processes like seed germination, flowering, fruit ripening, and root development. Examples include auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, ethylene, and abscisic acid.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Control and Coordination Class 10 Full Chapter (Animation) | Class 10 Science Chapter 7 | CBSE
Grade 12 Life Sciences Responding to the Environment The Endocrine System

Os Sistemas do Corpo Humano

Sistem Hormon_(Sistem Koordinasi Bagian 2 )_Biologi SMA XI

Sistema endócrino - Introdução - Fisiologia veterinária - Aula 1

Biologi Bab. sistem endokrin /hormonal - perkenalan apa itu sistem endokrin kelas 11
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)