Materi Biologi Zygomycota Kelas 10 | Bab Kingdom Fungi
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a comprehensive explanation of Zygomycota fungi, focusing on their structure, reproduction, and ecological roles. The fungi are introduced with examples like *Rhizopus stolonifer*, found on rotting bread, and *Rhizopus oryzae*, used in tempe fermentation. Key structural features like hyphae, sporangium, and rhizoids are discussed. The video highlights both sexual and asexual reproduction in Zygomycota, including spore formation and the process of conjugation. It also covers the role of Zygomycota as saprophytic organisms, breaking down organic matter. Viewers are encouraged to ask questions for further clarification.
Takeaways
- 😀 Zygomycota fungi, such as *Rhizopus stolonifer*, are commonly found on rotting organic materials like bread.
- 😀 The structure of Zygomycota fungi includes hyphae, sporangia, sporangiofores, rhizoids, and stolons.
- 😀 Hyphae are the main structures that absorb nutrients, and rhizoids help anchor the fungus to the substrate.
- 😀 Sporangia are the spore-producing structures, with spores developing in a protective box called a sporangium.
- 😀 Zygomycota fungi reproduce both sexually and asexually, with asexual reproduction involving spore formation and germination.
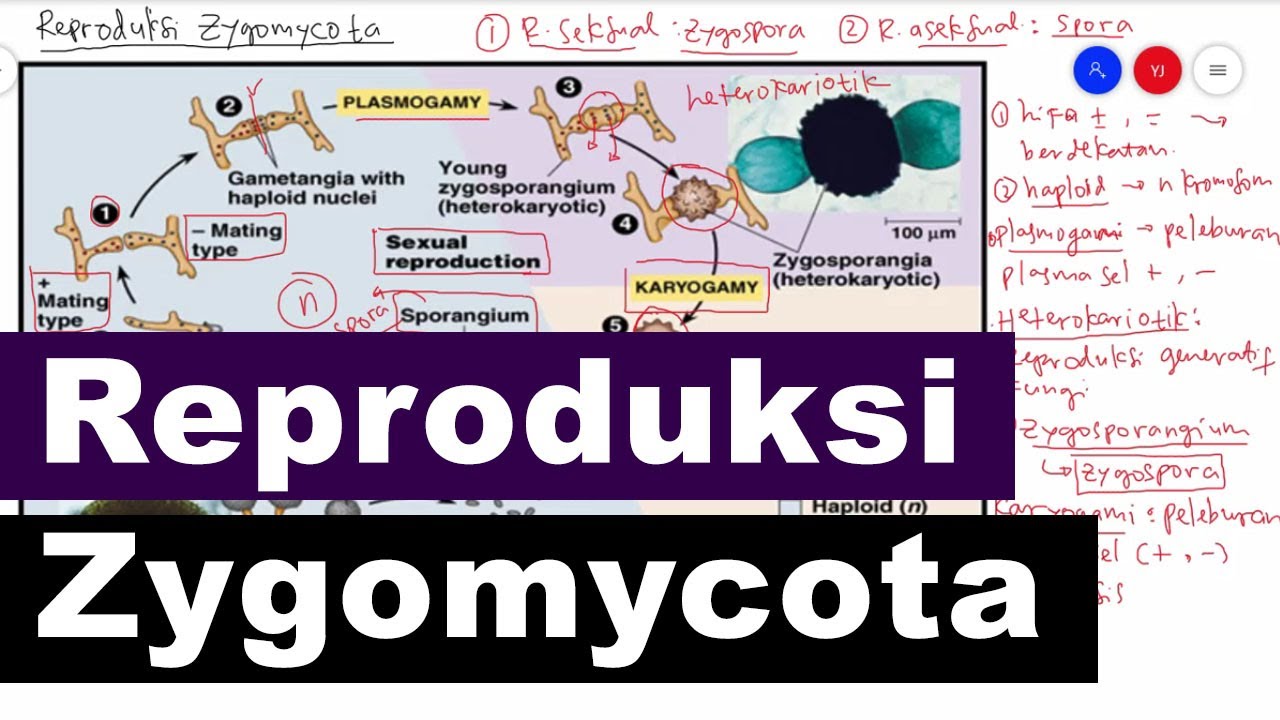
- 😀 Sexual reproduction in Zygomycota involves the fusion of two different haploid hyphae, leading to the formation of a zygospore.
- 😀 The zygospore undergoes meiosis to create new haploid spores, ready to germinate when conditions are favorable.
- 😀 The fungi are saprophytic, meaning they decompose dead organic matter, contributing to nutrient recycling in ecosystems.
- 😀 *Rhizopus oryzae* is used in the production of tempeh, showcasing the role of Zygomycota in food production.
- 😀 Zygomycota fungi can survive harsh conditions due to their thick-walled spores that protect them during dormancy.
- 😀 Environmental factors like humidity and temperature influence the germination and growth of Zygomycota spores.
Q & A
What are the main components of Zygomycota fungi?
-The main components of Zygomycota fungi are hyphae and sporangia. Hyphae form the fungal body, while sporangia are specialized reproductive organs containing spores.
What is the function of rhizoids in Zygomycota fungi?
-Rhizoids in Zygomycota fungi function like root structures, anchoring the fungus to its substrate and absorbing nutrients from the environment.
How does the structure of Zygomycota fungi differ from other fungi?
-Zygomycota fungi have hyphae that are not separated by septa, meaning they are multinucleate. This distinguishes them from other fungi that typically have septate hyphae.
What is the role of stolons in Zygomycota fungi?
-Stolons are horizontal hyphae that connect different fungal colonies, helping the fungus spread across its substrate.
What are the two main types of reproduction in Zygomycota fungi?
-Zygomycota fungi reproduce both sexually and asexually. Asexual reproduction involves the formation of spores in sporangia, while sexual reproduction involves the fusion of two different types of hyphae to form a zygospore.
How does asexual reproduction occur in Zygomycota fungi?
-In asexual reproduction, spores are produced in sporangia. These spores mature, rupture the sporangium, and germinate, forming new fungal growth.
What happens during sexual reproduction in Zygomycota fungi?
-In sexual reproduction, two types of hyphae (positive and negative) fuse. This results in the formation of a zygospore, which undergoes meiosis to produce haploid spores.
What is a zygospore and how is it formed in Zygomycota fungi?
-A zygospore is a thick-walled spore formed when two compatible hyphae (positive and negative) undergo plasmogamy and karyogamy, fusing their cytoplasm and nuclei. It eventually undergoes meiosis to produce haploid spores.
Can Zygomycota fungi survive in unfavorable conditions?
-Yes, Zygomycota fungi can survive in unfavorable conditions due to their thick-walled spores, which enter dormancy until conditions improve, allowing them to germinate and grow.
What are some practical examples of Zygomycota fungi?
-Some practical examples of Zygomycota fungi include **Rhizopus oryzae**, which is used in tempe fermentation, and **Rhizopus stolonifer**, which causes mold growth on decaying bread.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Reproduksi Zygomycota Secara Seksual dan Aseksual - Kingdom Fungi Biologi Kelas 10

Kingdom Fungi - Kelas X SMA

Kingdom Fungi - Biologi kelas 10 SMA

BIOLOGI SMA KELAS X: FUNGI (JAMUR)
KINGDOM FUNGI ( JAMUR ), CIRI KHAS, KLASIFIKASI DAN STRUKTUR TUBUH JAMUR

KLASIFIKASI JAMUR ( ZYGOMYCOTA DAN DEUTEROMYCOTA)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)