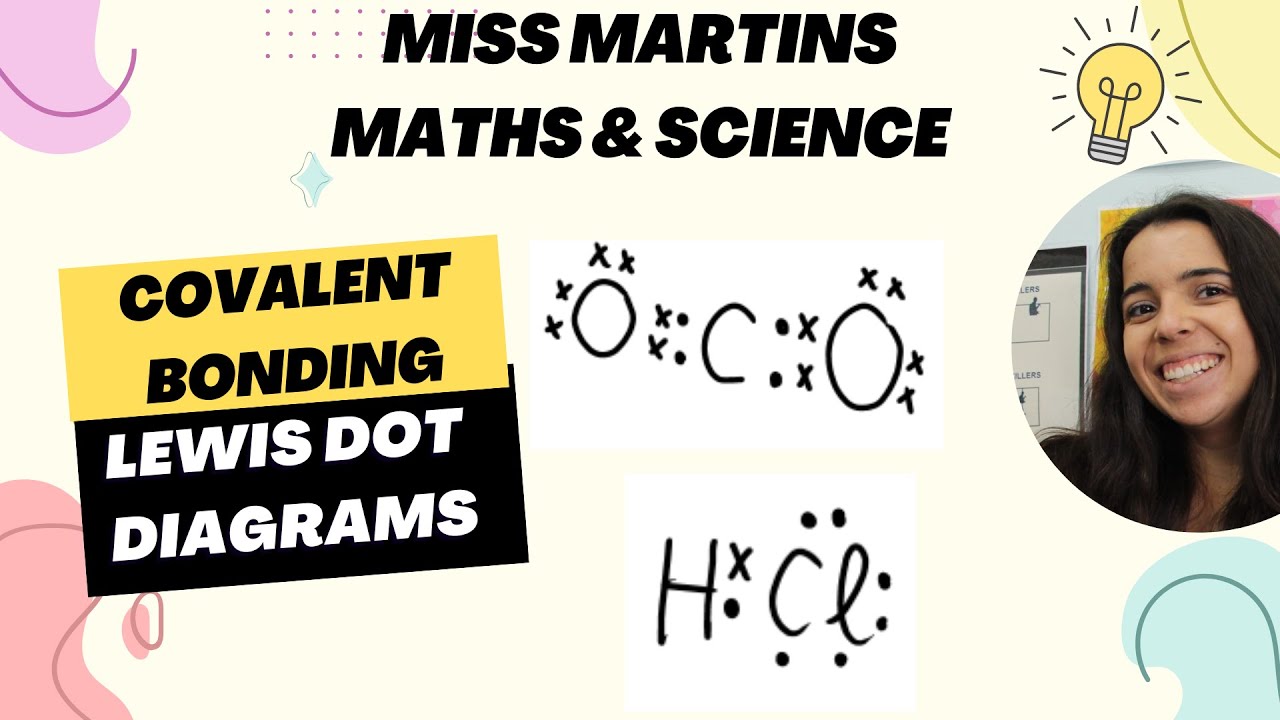Ikatan Kovalen | Kimia SMA | Tetty Afianti
Summary
TLDRThis video tutorial covers the basics of covalent bonding, focusing on its definition, types, and examples. It explains how covalent bonds form when two atoms share electron pairs to achieve stability, as opposed to ionic bonds where electrons are transferred. Key examples include water (H2O), methane (CH4), and oxygen (O2), with detailed illustrations of electron sharing. The video also introduces the concept of coordinate covalent bonds, where one atom donates both electrons. Additionally, it contrasts polar and nonpolar covalent bonds and discusses their properties, such as electrical conductivity and solubility. The lesson concludes with practice problems for better understanding.
Takeaways
- 😀 Covalent bonds occur when two atoms share electron pairs to achieve stability, unlike ionic bonds where electrons are transferred.
- 😀 Covalent bonds are formed between non-metal atoms, and these can be single, double, or triple bonds depending on the number of electron pairs shared.
- 😀 In the water molecule (H2O), hydrogen (H) shares electrons with oxygen (O), leading to a stable configuration similar to noble gases.
- 😀 The formation of methane (CH4) involves carbon (C) sharing its electrons with four hydrogen (H) atoms, resulting in a stable molecule.
- 😀 In the hydrogen molecule (H2), two hydrogen atoms share a single pair of electrons to achieve stability.
- 😀 The oxygen molecule (O2) forms a double bond where each oxygen atom shares two pairs of electrons, creating a stable structure.
- 😀 In the hydrogen bromide (HBr) molecule, hydrogen (H) shares one electron with bromine (Br) to complete its electron configuration.
- 😀 Nitrogen molecules (N2) form a triple bond, with each nitrogen atom sharing three pairs of electrons to achieve a full electron shell.
- 😀 Covalent bonds can also be categorized into coordination bonds, where the electron pair comes from only one atom, as seen in ammonia (NH3) reacting with H+ to form NH4+.
- 😀 Polar covalent bonds occur when electrons are shared unevenly due to differences in electronegativity, creating partial positive and negative charges.
- 😀 Nonpolar covalent bonds occur when electrons are shared equally, with no partial charges formed, as seen in molecules like H2 or Cl2.
Q & A
What is a covalent bond?
-A covalent bond is formed when two atoms share a pair of electrons. This occurs between non-metal atoms, where neither atom fully gives up electrons, but both share them in order to achieve stability.
How does a covalent bond differ from an ionic bond?
-In an ionic bond, electrons are transferred from one atom to another, resulting in the formation of positively and negatively charged ions. In a covalent bond, the electrons are shared between the atoms.
What are the different types of covalent bonds?
-Covalent bonds can be single, double, or triple. A single bond shares one pair of electrons, a double bond shares two pairs, and a triple bond shares three pairs of electrons.
How is the covalent bond in H2O formed?
-In H2O (water), oxygen has six valence electrons and needs two more to be stable. Hydrogen has one valence electron and needs one more to be stable. Oxygen shares its electrons with two hydrogen atoms to form two covalent bonds, achieving stability for both atoms.
What is the role of valence electrons in covalent bonding?
-Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell of an atom. They play a crucial role in covalent bonding as atoms share or use these electrons to achieve stability.
What is a coordinate covalent bond?
-A coordinate covalent bond occurs when both electrons in the shared pair come from the same atom. This is different from a regular covalent bond, where each atom contributes one electron to the shared pair.
How is the covalent bond in NH3 (ammonia) and H+ (hydrogen ion) formed?
-In this case, NH3 (ammonia) donates a pair of electrons to form a bond with the hydrogen ion (H+), which has no electrons. This creates a coordinate covalent bond.
What are the key differences between polar and nonpolar covalent bonds?
-In a polar covalent bond, the electrons are more attracted to one atom because it has higher electronegativity, creating a dipole with a positive and negative side. In a nonpolar covalent bond, the electrons are shared equally between atoms, and there is no dipole.
What determines whether a covalent bond is polar or nonpolar?
-The electronegativity difference between the two atoms determines if the bond will be polar or nonpolar. If the difference is significant, the bond is polar; if it's small or nonexistent, the bond is nonpolar.
What are the general properties of covalent compounds?
-Covalent compounds typically have lower melting and boiling points, can exist as gases, liquids, or solids, and are poor conductors of electricity. Polar covalent compounds can dissolve in polar solvents, while nonpolar covalent compounds dissolve in nonpolar solvents.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)