What is Electricity? Voltage, Current and Resistance Explained!
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explains the fundamentals of electricity, focusing on concepts like voltage, current, and their practical uses. The script highlights the movement of electrons, the role of conductors and insulators, and the differences between direct and alternating current. It also covers how to measure voltage with a multimeter and the importance of understanding power requirements for electrical appliances. The video engages viewers by simplifying complex ideas and using relatable analogies, such as the water tank analogy for voltage. The goal is to equip viewers with a solid understanding of electricity in everyday life.
Takeaways
- 😀 Electricity is one of the most important inventions in human history, as it powers much of modern life, from appliances to technology.
- 😀 Understanding basic concepts like voltage and current is essential, as they are fundamental to how electricity works.
- 😀 Atoms are made of electrons, which are negatively charged and can flow through certain materials called conductors, such as metals.
- 😀 Non-conductors (insulators) like rubber, glass, and plastic do not allow electrons to flow freely, preventing electric current.
- 😀 A battery has two sides: a negative side full of electrons and a positive side with a lack of electrons. Connecting them allows electrons to flow and power devices.
- 😀 Electric current refers to the movement of electrons from high pressure (negative side) to low pressure (positive side) in a circuit.
- 😀 The unit of electric current is the ampere (amp), which measures the number of electrons passing a point in one second.
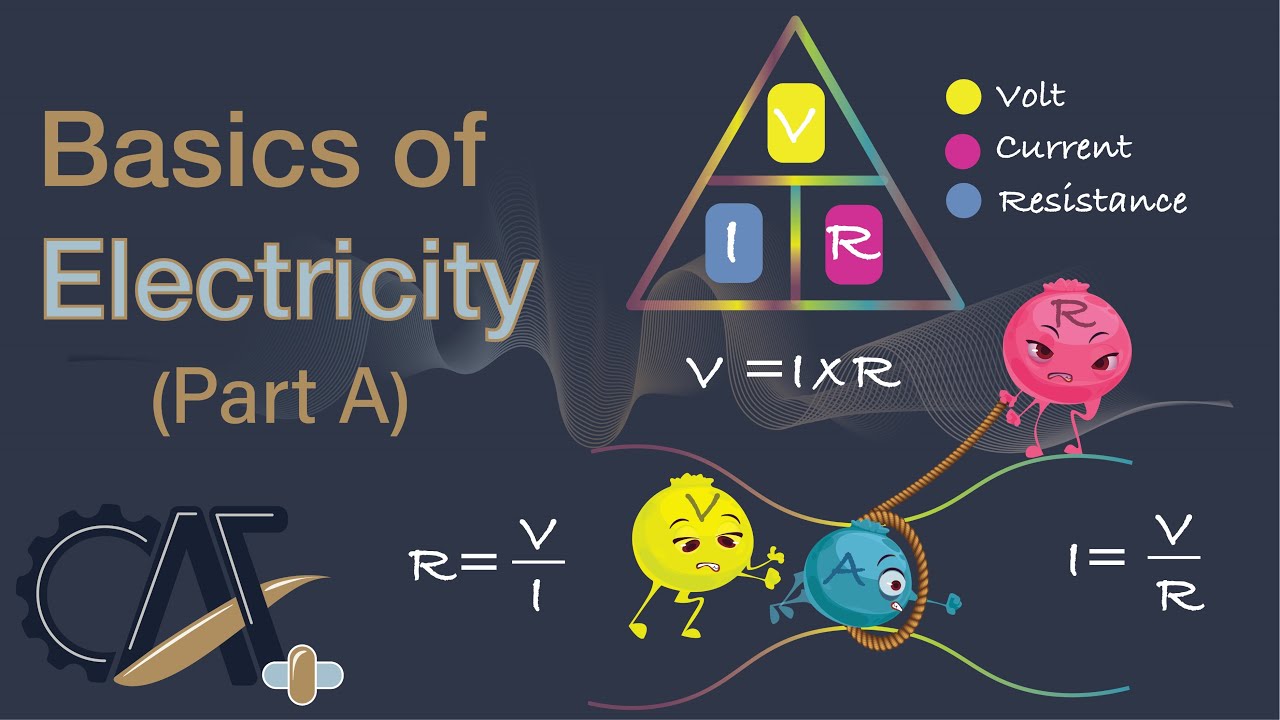
- 😀 Voltage, or electric potential difference, is the measure of the difference in electron pressure between two points in a circuit, and is measured in volts.
- 😀 The water tank analogy is helpful for understanding electricity: high water pressure (voltage) causes water (electrons) to flow, similar to how electric current works.
- 😀 There are two types of electric current: direct current (DC), where electrons flow in one direction, and alternating current (AC), where the direction of flow changes rapidly.
- 😀 Devices are designed to work with specific voltage, current, and type of electric current (AC or DC), so it’s important to check labels to ensure compatibility.
Q & A
Why is electricity considered one of the most important inventions in human history?
-Electricity powers almost all modern devices and systems, making life more convenient and efficient, from daily appliances to industrial operations. Without it, living would be far more challenging.
What are the two most fundamental concepts of electricity?
-The two fundamental concepts of electricity are voltage and current. These concepts are crucial to understanding how electricity works and powers devices.
What role do atoms and electrons play in electricity?
-Electricity is based on the movement of electrons within atoms. Electrons, which are negatively charged, flow through conductive materials to create an electric current.
What is the difference between conductors and insulators?
-Conductors, such as metals like iron and copper, allow electrons to flow easily through them, while insulators like rubber, glass, and plastic prevent the flow of electrons.
How does a battery generate electricity?
-A battery has two sides, positive and negative, where a high pressure of electrons (negative side) and low pressure (positive side) create an electron flow when connected by a conductor like copper wire.
Why do we say current flows in the opposite direction to the electron movement?
-The convention is to define current flow in the opposite direction of electron flow. This is a historical convention established before the discovery of the electron.
How is electric current measured?
-Electric current is measured in amperes (amps), which represents the number of electrons passing a specific point in one second.
What is the water tank analogy in relation to electricity?
-The water tank analogy compares the flow of water through pipes to the flow of electrons through a conductor. Water pressure (voltage) causes the flow, just like the electric potential difference causes electron flow.
What is the difference between direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC)?
-In direct current (DC), electrons flow in one direction, while in alternating current (AC), the direction of electron flow reverses periodically, typically 60 times per second in many homes.
How do you measure voltage using a multimeter?
-To measure voltage, insert the black lead into the common jack and the red lead into the voltage jack of the multimeter. Set the multimeter to either AC or DC voltage range and place the leads at the points where voltage needs to be measured.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Grade 8 Science Q1 Ep 10
Basics of Electricity-Part A [Voltage, Current, Resistance, and Ohm's Law]

Elettricità. Principi fondamentali, in 10 minuti

PRINSIP KELISTRIKAN DAN SISTEM INSTALASI LISTRIK ~ MATERI PRAKARYA KELAS 9 BAB 2

KELISTRIKAN PART 2 : LISTRIK DINAMIS (IPA KELAS 9 SMP)

FISIKA Kelas 12 - Listrik Bolak Balik (AC) | GIA Academy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)