KOMPONEN TANAH | TANAH DAN KEBERLANGSUNGAN KEHIDUPAN
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explains the process of soil formation, including physical, chemical, and biological weathering factors. It covers the role of climate, sunlight, rainfall, and microorganisms in the creation of soil, as well as the formation of soil horizons: A, B, and C. The video highlights the importance of humus, minerals, and organic components in enriching soil quality, and explains how soil fertility is influenced by pH, color, and the presence of essential nutrients. It also discusses the impact of erosion and other natural disasters on soil health and the environment.
Takeaways
- 😀 Physical, chemical, and biological weathering affect the Earth's conditions, contributing to soil formation.
- 😀 Climate, sunlight, and rainfall impact temperature, accelerating rock weathering and soil formation.
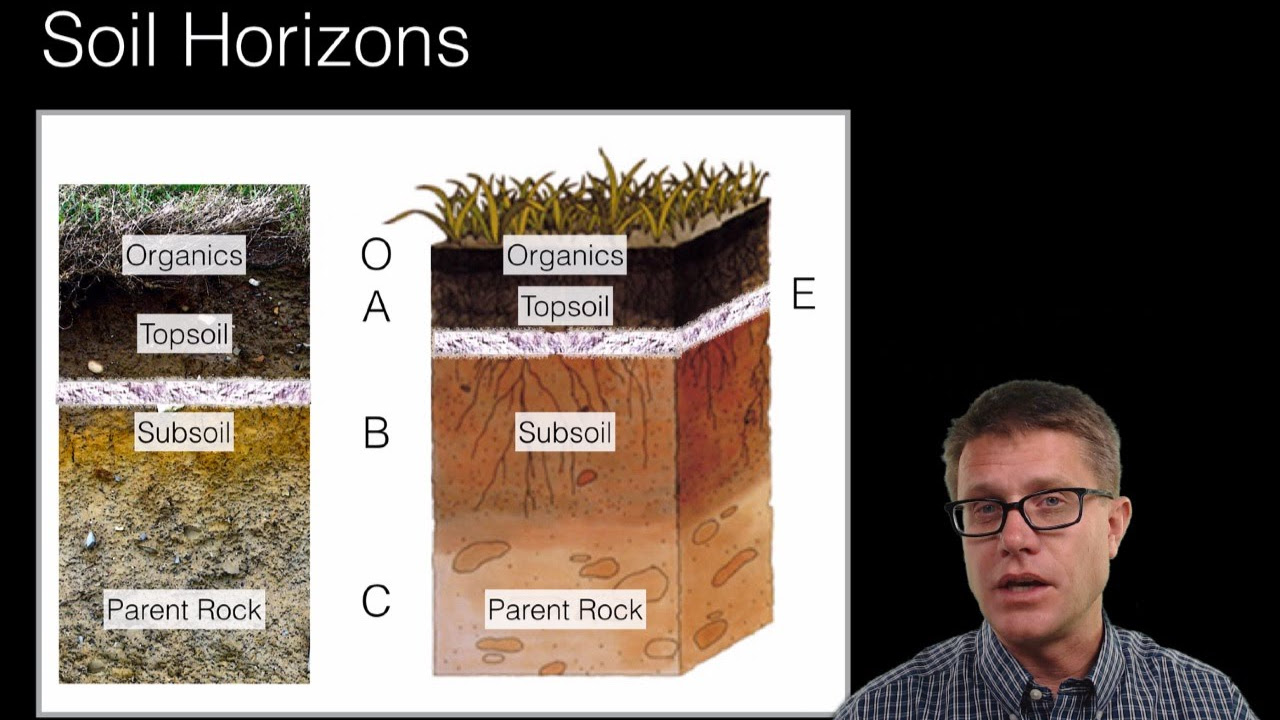
- 😀 Soil formation occurs over thousands of years, resulting in different soil horizons (layers).
- 😀 Horizon A is the topsoil layer, composed of weathered rocks, organic matter, and living organisms.
- 😀 Horizon B contains fewer organic materials compared to Horizon A and is deeper in the soil profile.
- 😀 Horizon C is composed of weathered rock, which provides essential materials for soil formation.
- 😀 Plants extract nutrients such as water and minerals from the soil, but erosion, floods, and landslides can deplete soil quality.
- 😀 Erosion occurs when topsoil is removed by forces like water, resulting in less fertile land.
- 😀 Soil is made up of important components like rocks, air, humus, water, and minerals, which are necessary for plant growth.
- 😀 Humus, created from the decomposition of plants and animals, enriches the soil with nutrients, promoting soil fertility.
- 😀 The acidity or pH of the soil, along with its color, influences plant nutrient absorption and soil quality.
Q & A
What are the main types of weathering that affect the Earth's surface?
-The main types of weathering that affect the Earth's surface are physical, chemical, and biological weathering.
What physical factors influence weathering and soil formation?
-The physical factors influencing weathering and soil formation include climate, sunlight, and rainfall, which affect the Earth's temperature and accelerate rock weathering.
How does weathering contribute to soil formation?
-Weathering helps in the breakdown of rocks, which contributes to soil formation by creating smaller particles that mix with organic materials, forming the soil.
What are the different soil horizons, and what do they consist of?
-There are three main soil horizons: Horizon A (the top layer, consisting of a mix of weathered rock, various textures, living organisms, and organic matter), Horizon B (which has fewer organic materials than the layer above it), and Horizon C (composed of weathered rock, providing primary materials for soil formation).
What role does erosion play in soil degradation?
-Erosion is the process by which the topsoil, rich in nutrients and organisms, is displaced by natural events like heavy rain and floods. This leaves behind poor soil that is less fertile and unable to support plant life.
What are the main components that make up soil?
-Soil consists of several important components: rocks, air, humus, water, and organic material, all of which contribute to its fertility and structure.
How does humus contribute to soil fertility?
-Humus is an organic component formed by the decomposition of plant and animal matter. It enriches the soil by making it loose, porous, and able to retain moisture, and it also supplies essential nutrients for plant growth.
How does air in the soil benefit plants and organisms?
-The air present in soil fills the spaces between particles and provides oxygen to plant roots and soil organisms. This is essential for plant growth and maintaining the health of soil ecosystems.
What types of minerals are found in soil, and why are they important for plants?
-Soil contains essential minerals like potassium, calcium, magnesium, nitrates, phosphates, and sulfates. These minerals provide vital nutrients that plants need for growth and development.
How does the pH of the soil affect plant growth?
-The pH level of soil affects how well plants can absorb nutrients. Soils with a pH level of around 7 (neutral) are most suitable for plant growth, as they allow plants to absorb nutrients optimally.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Geografi Kelas X (21) Dinamika Pedosfer | Jenis Tanah, Proses Terbentuknya dan persebaran Tanah

PEDOSFER : PENGERTIAN DAN PROSES TERBENTUKNYA TANAH

Proses Pembentukan Tanah | mata kuliah ilmu tanah | FKT UGM | 2024

APES Topic 4.2, Soil Formation & Erosion
Soil and Soil Dynamics

Geo X. 25. Profil Tanah & Pembentukan Tanah.
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)