Permintaan dan Penawaran Uang - Indeks Harga dan Inflasi Part 3 - Materi Ekonomi Kelas 11
Summary
TLDRThis video lesson covers key concepts in economics related to money demand and supply, tailored for high school students. It explains the factors influencing money demand, including transaction, precautionary, and speculative motives. The script highlights Keynesian and Classical theories of money demand, as well as how to calculate money circulation using formulas. The lesson also covers the supply of money, the role of central banks, and factors such as interest rates, inflation, and government needs. The video engages students in understanding the fundamental relationship between money, interest rates, and economic stability.
Takeaways
- 😀 Money demand refers to the amount of money needed by individuals and businesses for transactions, savings, or speculation.
- 😀 The four main sources of money demand are individuals (consumers), businesses, investors, and the government.
- 😀 Factors affecting money demand include income levels, interest rates, future expectations, and investment needs.
- 😀 Keynes' theory of money demand focuses on three main motives: transaction, precautionary, and speculative motives.
- 😀 The classical theory of money demand emphasizes the relationship between the money supply and the number of transactions in the economy.
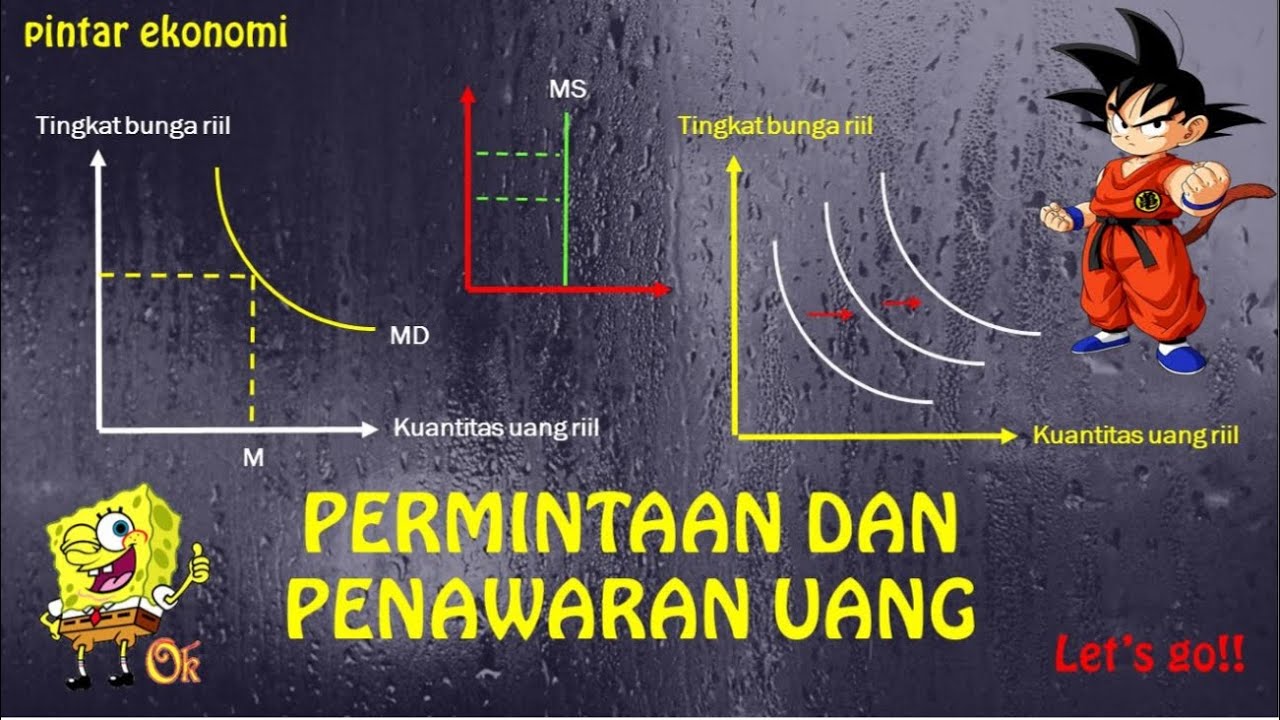
- 😀 The money supply equation is MV = PT, where M is money supply, V is velocity, P is price level, and T is transaction quantity.
- 😀 Higher income levels lead to increased demand for money as people need more money for transactions and savings.
- 😀 Higher interest rates typically lead to lower money demand, as people prefer saving their money rather than holding it for transactions.
- 😀 Central banks control the money supply through monetary policies to prevent inflation and ensure economic stability.
- 😀 The money supply is influenced by various factors including government policies, inflation, and the banking sector's credit offerings.
- 😀 Money demand curves show how income and interest rates affect the need for money in the economy, influencing both consumer behavior and investment decisions.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the video lesson?
-The main focus of the video lesson is the Demand and Supply of Money, as part of Chapter 4: Price Index and Inflation in economics for high school students.
What are the four sources of demand for money mentioned in the transcript?
-The four sources of demand for money are individuals (consumers), entrepreneurs, investors, and the government.
What factors influence the demand for money according to the lesson?
-The factors influencing the demand for money include the desire to hold money for transactions, precautionary motives, speculation, interest rates, investment needs, market prices, and future expectations.
What is the key difference between the Keynesian and Classical theories of money demand?
-The Keynesian theory focuses on the motives for holding money (transaction, precaution, speculation), while the Classical theory focuses on the total amount of money circulating in the economy.
How is the formula for money circulation (MV = PT) explained in the transcript?
-The formula MV = PT represents the relationship between money supply (M), velocity of money (V), price level (P), and the number of transactions (T). It helps calculate the total money circulating in the economy.
What does the money demand curve for transaction and precautionary motives show?
-The money demand curve for transaction and precautionary motives shows that as income increases, the demand for money increases as well, since higher income leads to more spending and precautionary savings.
What is the relationship between interest rates and speculative money demand?
-The relationship between interest rates and speculative money demand is inverse: as interest rates increase, the demand for money decreases because people tend to save more, reducing the amount of money held for speculative purposes.
Why is controlling the supply of money important in an economy?
-Controlling the supply of money is important because excessive money circulation can lead to inflation. Managing the money supply helps stabilize prices and prevent economic instability.
What factors affect the supply of money according to the video?
-The supply of money is affected by factors like real income, government spending, interest rates, market prices, public preferences, and monetary policies.
How does the supply of money curve behave with changes in interest rates?
-The supply of money curve shifts to the right when the money supply increases and shifts to the left when the money supply decreases. Higher interest rates typically lead to an increase in the money supply offered by banks.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

PENINJAUAN TOPIK DAN PENILAIAN MAPEL EKONOMI | PERTEMUAN 1 [PART 1/2]

Applied Economics - Intro - Part 1 - Senior High School and College Students
Permintaan dan Penawaran Uang | Ekonomi SMA Kelas 11

📌 Supply and Demand🖊A Level Business - Practice How To Draw Demand And Supply Diagrams - Revision

EKONOMI MIKRO DAN EKONOMI MAKRO (Materi EKONOMI XI BAB 5 Semester Genap) KURIKULUM MERDEKA

Supply and Demand Tips- Macro and Micro
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)