How Is Stainless Steel Made?
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the fascinating journey of stainless steel production, from the extraction of iron ore to the final finished product. It delves into the complex stages, including the addition of alloying elements like chromium, nickel, and manganese to create steel with unique properties such as corrosion resistance and high strength. The script details the refining process, including argon-oxygen decarbonization, casting, rolling, and surface finishing, highlighting the precision required in each step. It emphasizes the versatile applications of stainless steel, which ranges from construction to medical devices, and the importance of quality control in ensuring the material's durability and aesthetics.
Takeaways
- 😀 Stainless steel is a versatile and widely used material, essential in industries like construction, automotive, medical, and kitchenware.
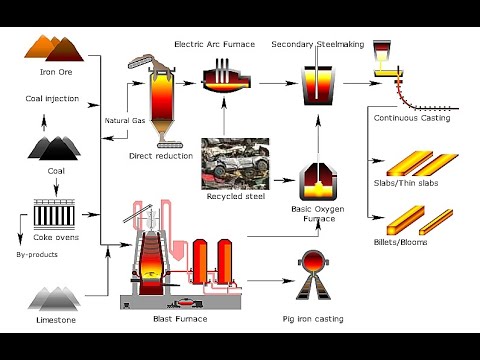
- 😀 The production of stainless steel starts with iron extracted from iron ore, which is then refined in a blast furnace at extremely high temperatures.
- 😀 Chromium is the key element added to steel to give it its stainless, rust-resistant properties by forming an oxide layer on the surface.
- 😀 Stainless steel typically contains at least 10.5% chromium, though other elements like nickel, molybdenum, and manganese may also be added for specific properties.
- 😀 The AOD (Argon Oxygen Decarburization) process removes impurities from molten steel, ensuring a clean, refined material.
- 😀 Continuous casting is used to shape the molten steel into slabs or billets, a process that ensures consistent quality and allows for mass production.
- 😀 Hot rolling reduces the thickness of steel slabs and shapes it into the desired forms, while improving its mechanical properties.
- 😀 Pickling is a crucial process where the steel is immersed in acid to remove oxide scale and surface impurities, leaving a smooth finish.
- 😀 Cold rolling, annealing, and various surface finishing techniques refine the steel's thickness, strength, and appearance for specific uses.
- 😀 Quality control throughout the production process involves rigorous testing, ensuring the steel meets required strength and corrosion resistance standards.
- 😀 After production, stainless steel is used in a wide range of applications, from kitchen appliances to medical devices, buildings, and jewelry.
Q & A
What is the primary component used in the production of stainless steel?
-The primary component in the production of stainless steel is iron, which is extracted from iron ore.
Why is chromium added to molten iron in the production of stainless steel?
-Chromium is added to create a thin, invisible layer of chromium oxide on the surface of the steel, which protects it from rust and corrosion.
What role does nickel play in the production of stainless steel?
-Nickel enhances the corrosion resistance of stainless steel and provides a more lustrous, shiny finish.
What are some other elements that may be added to stainless steel, and what do they do?
-Other elements such as molybdenum and manganese may be added. Molybdenum increases resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion, while manganese improves the steel's strength and hardness.
What is the AOD process, and why is it important?
-The Argon Oxygen Decarbonization (AOD) process involves injecting a mixture of argon and oxygen into molten steel to remove impurities. It helps create a pure form of stainless steel with a controlled composition.
How does continuous casting differ from traditional casting methods?
-Continuous casting involves pouring molten steel into a water-cooled mold to solidify into long billets or slabs, allowing for consistent quality and large-scale production, unlike traditional casting, which may produce individual castings.
Why is hot rolling important in the production of stainless steel?
-Hot rolling is important because it shapes the steel into various forms and improves its mechanical properties by refining its grain structure, making it stronger and more durable.
What is the purpose of pickling in stainless steel production?
-Pickling is a cleaning process where the steel is immersed in an acid bath to remove oxide scales and other surface impurities, leaving the steel with a smooth, clean surface.
What finishing processes are used to prepare stainless steel for its final use?
-After pickling, stainless steel may undergo cold rolling, annealing (for stress relief and improved ductility), and surface finishing techniques like brushing, grinding, or polishing to achieve the desired texture and appearance.
How is quality control integrated into the stainless steel production process?
-Quality control is integrated by testing samples at various stages of production. These tests include chemical analysis, mechanical testing, and microstructural examination to ensure the steel meets strength, corrosion resistance, and other standards.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)