Digestive System Part 1 - Oral Cavity
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a comprehensive introduction to the digestive system, focusing on the oral cavity and its role in digestion. It explains the path food takes through the gastrointestinal tract, from the mouth to the anus, while highlighting the importance of accessory organs such as salivary glands. The script also covers the functions of teeth, including the difference between primary and adult teeth, and discusses the salivary glands’ contribution to breaking down food. Additionally, it explores the tongue's role in food manipulation and taste perception, setting the stage for further exploration of digestion in future videos.
Takeaways
- 😀 The digestive system involves both the gastrointestinal tract and accessory digestive organs, which assist in digestion without directly interacting with food.
- 😀 The gastrointestinal tract (alimentary canal) starts in the oral cavity and includes the pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine (duodenum, jejunum, ileum), large intestine, rectum, and anus.
- 😀 The accessory digestive organs, like salivary glands, do not have food pass through them but play crucial roles in chemical breakdown.
- 😀 Teeth play a vital role in mechanical digestion by breaking food into smaller pieces, making it easier for enzymes in saliva to act.
- 😀 In children, the primary (deciduous) set of teeth consists of 20 teeth, and in adults, there are 32 permanent teeth, including premolars and wisdom teeth.
- 😀 Wisdom teeth (third molars) often need to be removed because they can cause overcrowding or are hard to clean properly.
- 😀 Salivary glands (parotid, submandibular, and sublingual) produce saliva, which starts the chemical breakdown of food with digestive enzymes and mucus.
- 😀 Saliva contains enzymes like amylase that begin the breakdown of carbohydrates, aiding in digestion from the very start of the process.
- 😀 Exocrine glands like salivary glands have ducts that carry their secretions (e.g., saliva) directly to the oral cavity, unlike endocrine glands which release hormones into the bloodstream.
- 😀 The tongue is integral to both mechanical digestion (helping move food around for efficient crushing) and sensation (with papillae that help detect taste).
Q & A
What is the function of the accessory digestive organs mentioned in the video?
-The accessory digestive organs, such as salivary glands, liver, and pancreas, contribute important substances, such as digestive enzymes or bile, which assist in the chemical breakdown of food, although food does not pass through them directly.
What is the difference between the gastrointestinal tract and the accessory digestive organs?
-The gastrointestinal tract is the pathway food travels through, from the mouth to the anus. In contrast, the accessory digestive organs are involved in digestion but food does not pass through them directly. They contribute substances like enzymes or bile that aid in breaking down food.
What are the three components of the small intestine and their order?
-The three components of the small intestine are the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. The duodenum is the first part, followed by the jejunum, and then the ileum.
Why is it difficult to identify the different parts of the small intestine in an image?
-The small intestine consists of the jejunum and ileum, which are coiled and difficult to distinguish from each other in an image. It’s important to know the order of these sections, but you won’t be expected to identify them visually.
How many teeth do children and adults typically have, and what are the differences between primary and permanent teeth?
-Children typically have 20 primary (milk) teeth, while adults have 32 permanent teeth. The adult set includes additional premolars and molars that are not present in the primary set. Wisdom teeth, or third molars, are the last to emerge, typically around the age of 20.
What are wisdom teeth and why are they often removed?
-Wisdom teeth, or third molars, are the last set of molars to emerge, usually in early adulthood. They are often removed because they can crowd other teeth, make them crooked, or be difficult to clean due to their position.
What is the role of the salivary glands in digestion?
-Salivary glands produce saliva, which begins the chemical breakdown of food. Saliva contains digestive enzymes that help break down food chemically, and its water content helps moisten food for easier swallowing.
What is the difference between exocrine and endocrine glands?
-Exocrine glands, like the salivary glands, have ducts that transport their secretions (like saliva) to specific locations. Endocrine glands, on the other hand, release hormones directly into the bloodstream without using ducts.
What are the three pairs of salivary glands mentioned in the video?
-The three pairs of salivary glands are the parotid glands (located near the ears), the submandibular glands (under the jaw), and the sublingual glands (under the tongue).
How does the tongue contribute to the mechanical breakdown of food?
-The tongue helps by moving food around in the mouth, ensuring it comes in contact with the teeth for proper crushing. It also helps in pushing larger food pieces closer to the teeth for better grinding.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
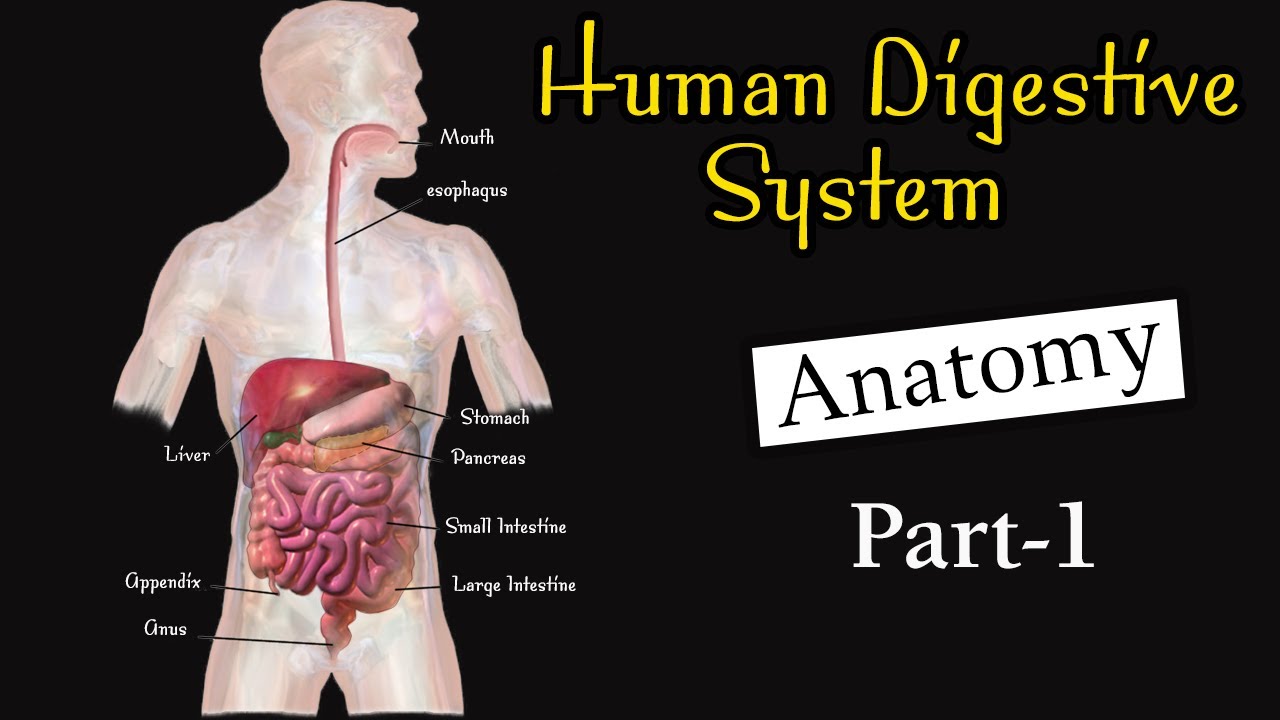
Anatomy of human digestive system I Digestive system I Digestive system class 11

Digestive System (Part 1) - Digestive Tract

Anatomi Lengkap Sistem Pencernaan (Traktus Digestivus / Alimentary Tract) | Sistem Pencernaan

Die Verdauung des Menschen (Animation)

Avaliação Semiológica e Diagnóstico em Pequenos Animais - Aula 4.2

Überblick über die Mundhöhle (Vorschau) - Anatomie des Menschen | Kenhub
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)