Fixed-Bias Configuration of JFET (Mathematical Approach)
Summary
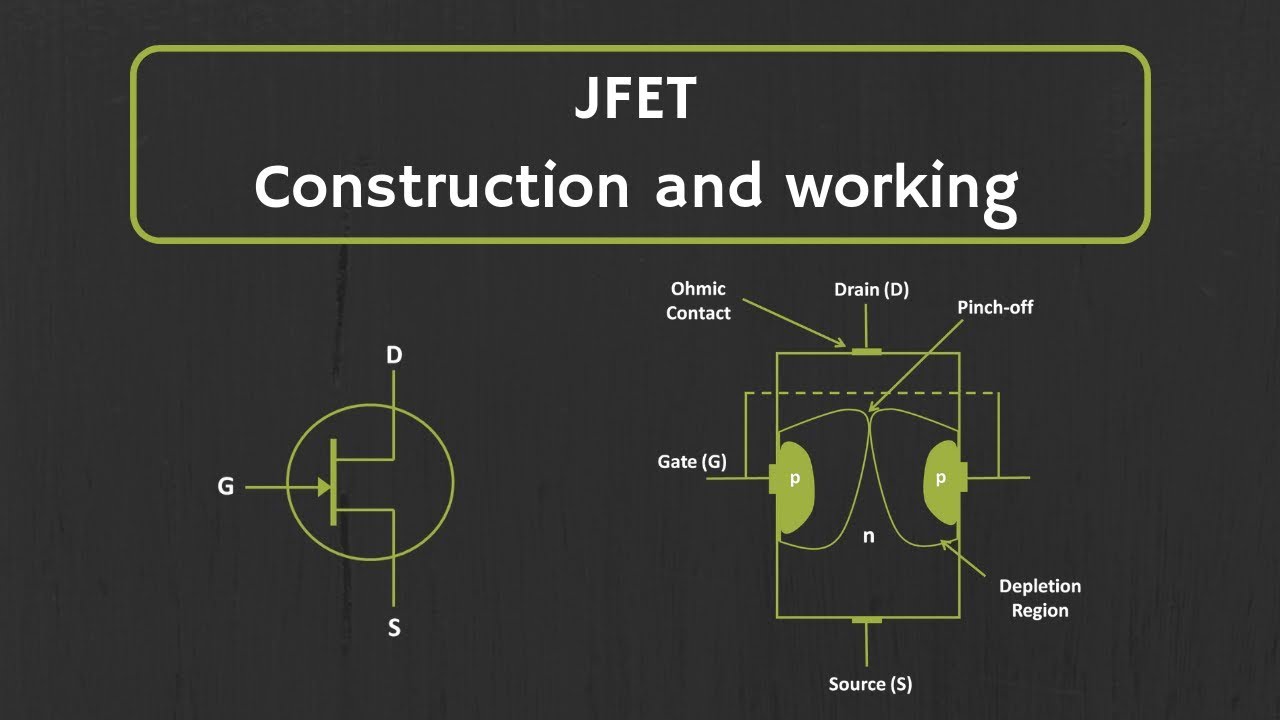
TLDRThis lecture provides an introduction to the fixed bias configuration in N-channel JFETs, focusing on how to determine the operating point using a mathematical approach. Key concepts include simplifying the circuit for DC analysis, calculating input voltage (V_GS), drain current (I_D), and output voltage (V_DS). The process involves using Shockley’s equation for drain current and Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law to find the output voltage. The session compares JFETs with BJTs, highlighting differences in input and output parameters, and sets the stage for exploring graphical methods in future lectures.
Please replace the link and try again.
Q & A
What is the main objective of the lecture?
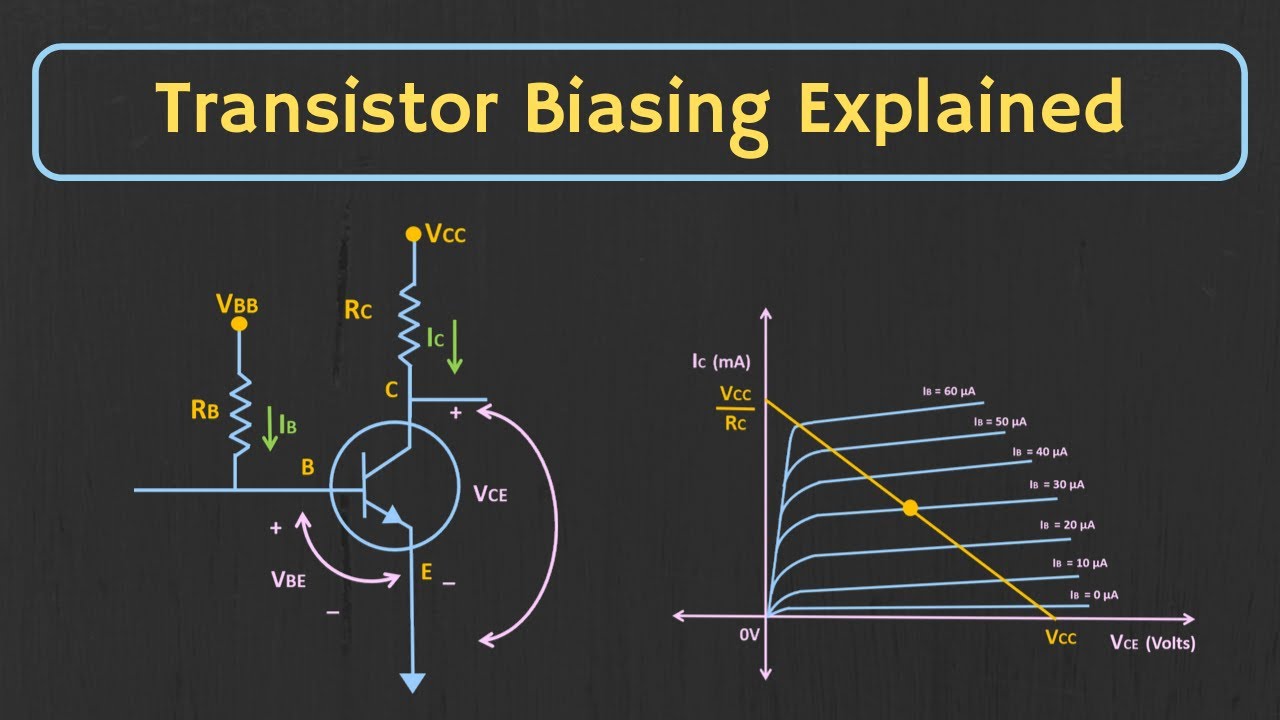
-The main objective of the lecture is to explain the fixed bias configuration of a JFET and to determine the operating point using a mathematical approach.
What are the two approaches to finding the operating point?
-The two approaches are the mathematical approach, which is covered in this lecture, and the graphical approach, which will be covered in the next lecture.
Why can capacitors C1 and C2 be replaced with open circuits for DC analysis?
-C1 and C2 can be replaced with open circuits because the reactance of capacitors to DC signals is infinite, as the frequency of DC signals is 0 Hz.
What is the importance of resistance RG in this circuit?
-Resistance RG is important as it connects to the gate branch, but since the gate current (IG) is zero, the voltage drop across RG is also zero, allowing it to be short-circuited.
How is the input voltage (Vgs) calculated?
-The input voltage (Vgs) is calculated by applying Kirchhoff’s voltage law, and it is given by the equation Vgs = -Vgg.
What does the term 'fixed bias configuration' refer to?
-'Fixed bias configuration' refers to the setup where Vgs is determined by a fixed voltage source (Vgg), making the gate-source voltage constant.
What equation is used to calculate the drain current (Id)?
-The drain current (Id) is calculated using Shockley's equation: Id = Ids(s) * (1 - Vgs / Vp)².
What are the two coordinates of the operating point for the JFET?
-The two coordinates of the operating point are Vgs (the x-coordinate) and Id (the y-coordinate).
How is the output voltage (Vds) found?
-The output voltage (Vds) is found by applying Kirchhoff’s voltage law in the output loop: Vds = Vdd - IdRd.
How does the analysis for JFET differ from that of bipolar junction transistors (BJTs)?
-The analysis for JFETs differs from BJTs in the input and output parameters, such as the absence of a gate current in JFETs and the different relationships for voltage and current in the equations.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)