Human Reproduction Oogenesis #missangler
Summary
TLDRThis video explains oogenesis, the process by which egg cells are produced in the ovaries. It details the stages of follicular development, from primordial follicles to Graafian follicles, and how hormones like FSH and LH regulate the process, culminating in ovulation. The video contrasts oogenesis with spermatogenesis, highlighting that only one viable egg is produced, with polar bodies as byproducts. The role of the corpus luteum and progesterone in maintaining pregnancy is also discussed. This video serves as an essential guide to understanding the hormonal control and cellular events of egg cell production.
Takeaways
- 😀 Oogenesis is the process by which egg cells (ova) are produced in the ovaries.
- 😀 The process starts with primordial follicles, which develop into larger Graafian follicles containing the oocyte.
- 😀 Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimulates the growth and maturation of follicles in the ovary.
- 😀 Luteinizing hormone (LH) triggers ovulation, causing the oocyte to be released from the ovary into the fallopian tube.
- 😀 After ovulation, the empty Graafian follicle becomes the corpus luteum, which secretes progesterone.
- 😀 Progesterone prepares the uterus for potential pregnancy and is essential in maintaining early pregnancy.
- 😀 If no fertilization occurs, the corpus luteum shrinks, leading to a drop in progesterone levels and the start of a new cycle.
- 😀 Oogenesis differs from spermatogenesis by producing only one viable egg cell and three polar bodies, which degenerate.
- 😀 The polar bodies produced during meiosis have little cytoplasm and do not become egg cells.
- 😀 The final product of oogenesis is a large haploid egg cell (ovum) that contains most of the cytoplasm necessary for early development.
Q & A
What is oogenesis?
-Oogenesis is the process by which egg cells (ova) are produced in the ovaries. It involves the maturation of follicles and the release of a haploid egg cell through meiotic divisions.
What is the role of the ovary in oogenesis?
-The ovary is the site where oogenesis takes place. It contains the follicles that grow and mature into Graafian follicles, which eventually release the oocyte (egg cell) during ovulation.
How do the primordial follicles develop in the ovary?
-Primordial follicles are undifferentiated cells that, under the influence of hormones like FSH, grow into primary follicles. These follicles continue to mature and eventually become Graafian follicles.
What is the Graafian follicle, and what is its role?
-The Graafian follicle is a mature follicle in the ovary that contains the oocyte. It is responsible for the release of the egg cell during ovulation.
What hormones are involved in oogenesis, and what are their roles?
-FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone) stimulates the growth of follicles, while LH (Luteinizing Hormone) triggers ovulation, causing the release of the egg cell. Progesterone, secreted by the corpus luteum, helps prepare the uterus for potential pregnancy.
What happens to the Graafian follicle after ovulation?
-After ovulation, the Graafian follicle transforms into the corpus luteum, which secretes progesterone to support pregnancy. If no fertilization occurs, the corpus luteum shrinks and eventually disappears.
What is the corpus luteum, and how does it affect the menstrual cycle?
-The corpus luteum is the structure formed after the Graafian follicle releases the egg. It secretes progesterone, which prepares the uterus for implantation. If no pregnancy occurs, the corpus luteum shrinks, leading to a decrease in progesterone and the start of a new cycle.
How does oogenesis differ from spermatogenesis?
-In oogenesis, only one functional egg cell is produced from a diploid cell, with the other three cells becoming polar bodies. In spermatogenesis, four functional sperm cells are produced from one diploid cell.
What are polar bodies, and why are they formed during oogenesis?
-Polar bodies are small, non-functional cells produced during meiosis in oogenesis. They are the result of unequal division during the meiotic stages, with most of the cytoplasm going to the larger egg cell.
What is the significance of progesterone in oogenesis and pregnancy?
-Progesterone, secreted by the corpus luteum after ovulation, plays a crucial role in preparing the uterus for implantation. If fertilization occurs, progesterone helps maintain the pregnancy; if not, progesterone levels drop, leading to menstruation.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

PEMBELAHAN SEL | GAMETOGENESIS HEWAN DAN MANUSIA | BIOLOGI KELAS 12

Oogenesis (Formation of Egg Cells) - Reproductive System In Humans

PERNYATAAN YANG BENAR MENGENAI OOGENESIS ADALAH? SIMAK ULASANNYA BERIKUT INI || MATERI BIOLOGI
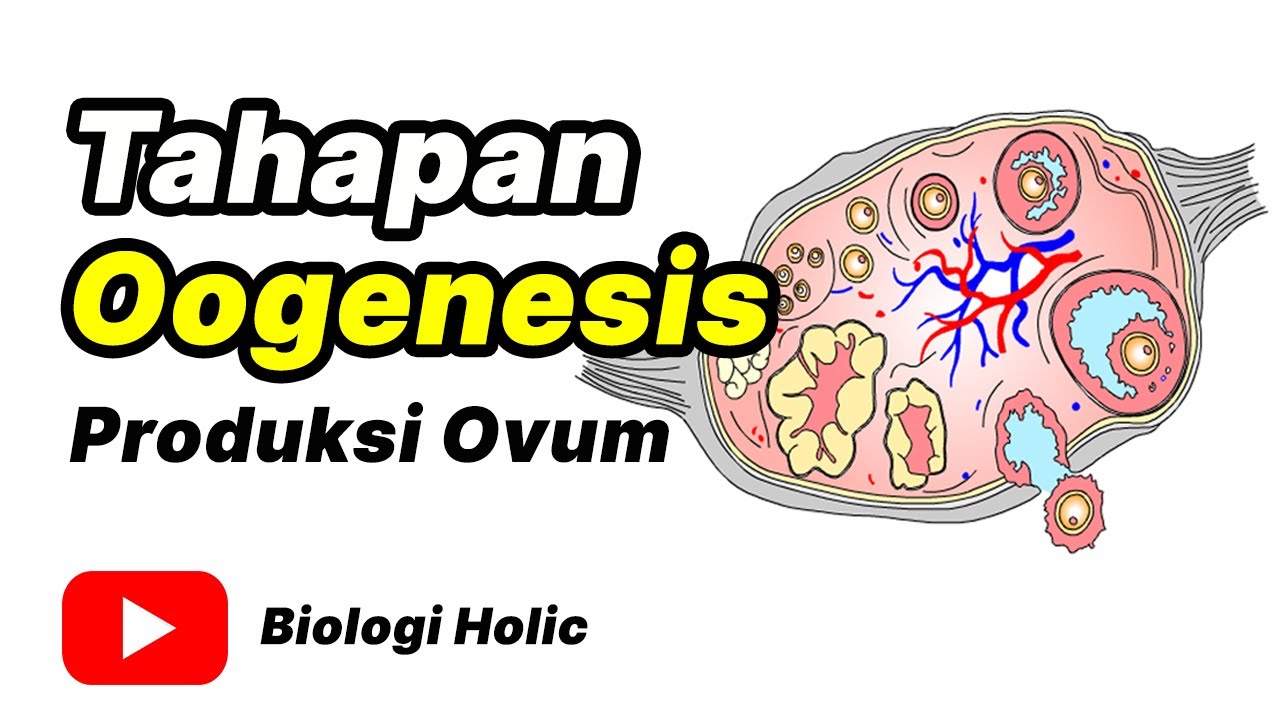
Tahap oogenesis | Produksi ovum (Animasi)

Oogenesis and Spermatogenesis | Reproductive

Cara Pintar | Memahami Konsep Oogenesis
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)