Speciation Allopatric, Sympatric, Peripatric, & Parapatric Speciation Evolution I CSIRNET NEET GATE
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the concept of speciation, focusing on the processes of allopatric and sympatric speciation. The script discusses how geographical barriers can lead to reproductive isolation between populations, causing them to evolve into distinct species. It also covers the factors contributing to this isolation, including environmental changes, genetic mutations, and geographic separation. The presenter explains the intricacies of these biological processes using examples like the migration of populations and the formation of new species due to ecological and biological isolation. Overall, it provides an in-depth look at the mechanisms driving evolution and the creation of species.
Takeaways
- 😀 Speciation is the process by which new species are formed due to evolutionary changes in isolated populations.
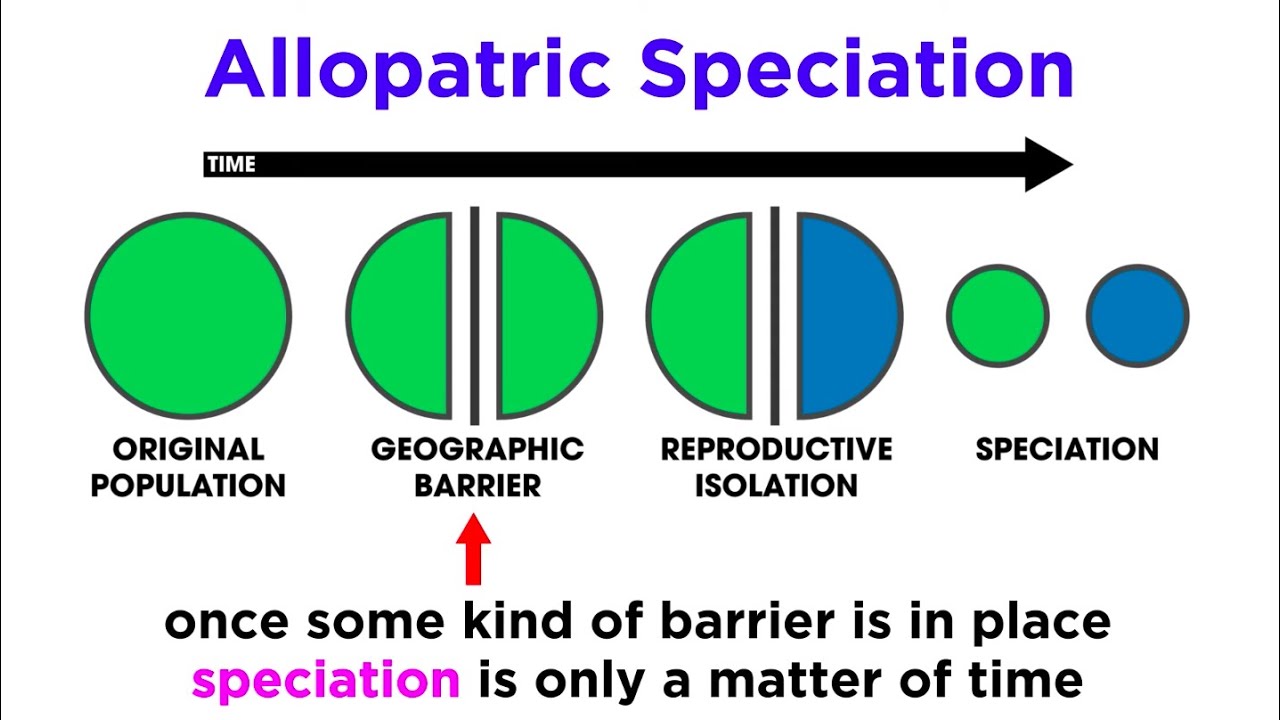
- 😀 Geographical isolation occurs when physical barriers like mountains or rivers divide a population, leading to speciation over time.
- 😀 Reproductive isolation happens when two populations of the same species can no longer interbreed due to genetic or behavioral differences.
- 😀 Ecological isolation occurs when populations live in the same geographic area but occupy different habitats or ecological niches.
- 😀 Biological isolation can arise from genetic or physiological barriers, such as incompatible chromosomes, preventing interbreeding.
- 😀 Examples of speciation include Darwin’s finches, which evolved into different species due to geographical isolation on the Galápagos Islands.
- 😀 Isolation can be caused by physical barriers like mountains or rivers, but also by behavioral factors like mating rituals or timing.
- 😀 Mutations and natural selection play important roles in speciation, especially when populations are isolated for long periods.
- 😀 When two populations become reproductively isolated, they may evolve into separate species and cannot produce viable offspring.
- 😀 Speciation can occur in both plants and animals, with plants experiencing geographical isolation leading to the development of new species.
- 😀 Understanding speciation helps scientists grasp how biodiversity develops and evolves over time.
Q & A
What is speciation?
-Speciation is the process by which a population of organisms divides into two or more distinct groups that can no longer interbreed, leading to the formation of new species.
How does geographic isolation contribute to speciation?
-Geographic isolation occurs when a physical barrier, such as a mountain or ocean, separates a population into distinct groups. These groups evolve separately, and eventually, they may develop reproductive isolation, preventing them from interbreeding even if they come into contact again.
What is reproductive isolation?
-Reproductive isolation occurs when two populations of the same species can no longer produce fertile offspring together due to genetic differences or physical barriers, marking the point where they are considered separate species.
What is the founder effect in speciation?
-The founder effect occurs when a small group of individuals from a larger population migrates or becomes isolated in a new environment. Over time, this small group may undergo different evolutionary pressures, leading to speciation.
What is the difference between geographic and ecological isolation?
-Geographic isolation involves physical barriers that separate populations, while ecological isolation occurs when populations share the same geographical area but occupy different ecological niches, reducing their interaction and potential for breeding.
How can mutations contribute to speciation?
-Mutations can introduce genetic changes that lead to variations in traits. If these mutations help individuals adapt to different environments or conditions, they can contribute to the process of speciation by making populations genetically distinct.
What role does reproductive isolation play in the evolution of new species?
-Reproductive isolation is essential for speciation because it prevents different populations from interbreeding. Over time, this isolation allows genetic differences to accumulate, leading to the formation of distinct species.
Can two populations evolve into separate species without geographic isolation?
-Yes, two populations can evolve into separate species without geographic isolation if other factors, such as ecological isolation or reproductive isolation, prevent them from interbreeding and lead to genetic divergence.
What is the significance of the 'biological isolation' concept in speciation?
-Biological isolation refers to mechanisms, such as genetic or reproductive barriers, that prevent different populations from interbreeding, even if they occupy the same geographic area. This isolation is crucial for the evolution of new species.
What happens when populations from different geographic areas meet after being isolated for a long time?
-When populations from different geographic areas meet after long isolation, they may no longer be able to interbreed due to reproductive isolation. This can confirm that they have evolved into distinct species during their period of isolation.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)