HR Diagram Explained - Star Color, Temperature and Luminosity
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Janine from *Learn the Sky* guides viewers through the HR diagram, a key tool for understanding star evolution. She explains how the diagram illustrates the relationship between star temperature, color, and brightness, helping astronomers classify stars. The video covers stellar life cycles, from main-sequence stars to red giants, supergiants, and white dwarfs. Janine also shares an interactive teaching method using a 3D model to help students visualize the HR diagram. The video is sponsored by Skillshare, with Janine encouraging viewers to explore a variety of courses to enhance their skills.
Takeaways
- 😀 The HR diagram is a critical tool used by astronomers to classify stars based on their temperature, luminosity, and spectral class.
- 😀 Stars' positions on the HR diagram change over time, reflecting their evolution from molecular clouds to white dwarfs or supernovae.
- 😀 The HR diagram has two key axes: temperature (measured in Kelvin) and luminosity, which help categorize stars by their brightness and heat.
- 😀 The mnemonic 'Oh Be A Fine Girl, Kiss Me' helps remember the spectral classes of stars, which range from O-type (hot and blue) to M-type (cool and red).
- 😀 Stars on the main sequence are in a stable phase where the pressure from fusion balances the force of gravity pulling inward.
- 😀 Stellar evolution involves stages like main sequence, red giants, supergiants, and eventually white dwarfs, or black holes for massive stars.
- 😀 Red dwarfs are cooler, dimmer stars, while blue giants are much hotter and more luminous, though both can exist on the main sequence.
- 😀 Low-mass stars, like our Sun, eventually become red giants and then white dwarfs, while high-mass stars end as supernovae or black holes.
- 😀 The HR diagram also visually illustrates the size and temperature of stars, which can range from small red stars to large, hot blue supergiants.
- 😀 The process of stellar fusion plays a major role in determining a star's classification and its position on the HR diagram.
- 😀 Skillshare is highlighted as a resource for learning new skills, including topics like astronomy, photography, and social media platforms like TikTok.
Q & A
What is the HR diagram and why is it important?
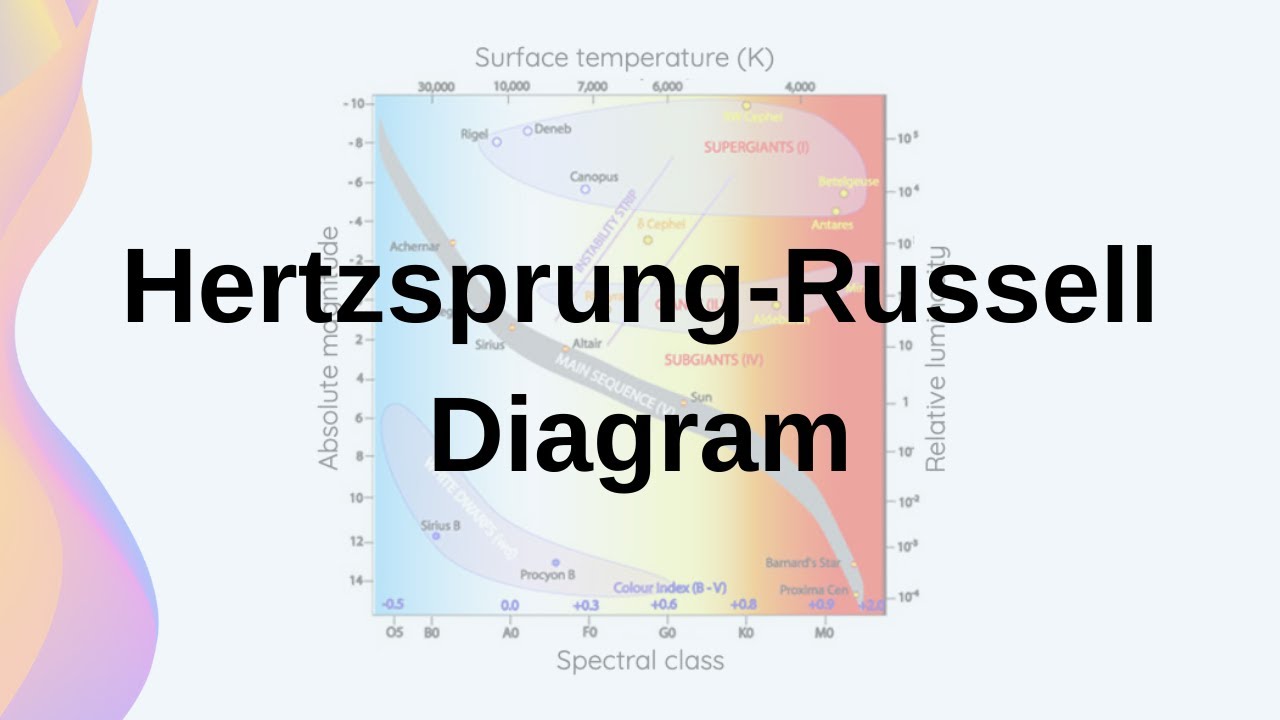
-The HR diagram, or Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, is a tool used by astronomers to classify stars based on their temperature, color, and luminosity. It shows the relationship between a star's surface temperature and its brightness, which helps astronomers understand star evolution and lifecycle.
How did the HR diagram come to be developed?
-The HR diagram was developed in 1911 by Danish astronomer Enjar Hertzsprung and American astronomer Henry Russell. Their work was crucial in advancing the understanding of how stars evolve over time.
What does the temperature axis on the HR diagram represent?
-The temperature axis on the HR diagram represents the surface temperature of stars, measured in Kelvin. Stars on the left side of the diagram are hotter (up to 25,000 Kelvin or higher), while stars on the right side are cooler (around 3,000 Kelvin).
What is the significance of the spectral class in the HR diagram?
-The spectral class categorizes stars based on their temperature and color. The mnemonic 'Oh Be A Fine Girl/Guy, Kiss Me' is used to help remember the order of spectral types, ranging from O-type stars (the hottest and blue) to M-type stars (the coolest and red).
What is the relationship between a star's color and its temperature?
-A star's color is directly related to its temperature. Hotter stars tend to be blue, while cooler stars are red or orange. This relationship helps astronomers classify stars on the HR diagram.
What is the main sequence on the HR diagram?
-The main sequence is a long band on the HR diagram where most stars spend the majority of their life. Stars in this region are stable, with a balance between the pressure from nuclear fusion and the gravitational pull trying to collapse the star.
What happens to a star as it ages on the HR diagram?
-As a star ages, its position on the HR diagram changes. It starts in the main sequence, then can evolve into a red giant or supergiant, and finally may end as a white dwarf, supernova, or even a black hole, depending on its mass.
What are red dwarf stars and where are they located on the HR diagram?
-Red dwarf stars are low-mass, cool stars that appear red. They are located in the lower-right portion of the HR diagram, with low luminosity and relatively low surface temperatures.
How do massive stars evolve compared to smaller stars?
-Massive stars evolve differently than smaller stars. They may become supergiants, and after exhausting their fuel, they can explode as supernovae, leading to the formation of a neutron star or black hole. Smaller stars, like the Sun, become red giants before eventually cooling down into white dwarfs.
What is a white dwarf, and why is it dim yet hot?
-A white dwarf is the remnant core of a star that has exhausted its nuclear fuel. Despite being very hot (often exceeding 100,000 Kelvin), it is dim because it is very small in size and no longer undergoes fusion.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Stars and Galaxies: The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram

How to Find Lyra The Harp Constellation
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram // HSC Physics

Create a Rigorous Physical Process Model as an Easy Start to a Data Flow Diagram

SWOT Analysis Explained Step by Step

Cara menggunakan PRISMA Flow Diagram untuk pembuatan Systematic Literature Review (SLR)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)