Encryption and Decryption| What is Encryption and Decryption| Concept Explained| S2CS
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the basics of encryption and decryption are explained in simple terms. The script introduces key concepts such as plaintext, ciphertext, public key, and private key, emphasizing their roles in securing data during transmission. Viewers learn how encryption converts readable messages into unreadable data for secure transmission, and how decryption reverses this process to make the message readable again. The video also covers where encryption and decryption take place, the use of keys, and the importance of these processes in ensuring data security.
Takeaways
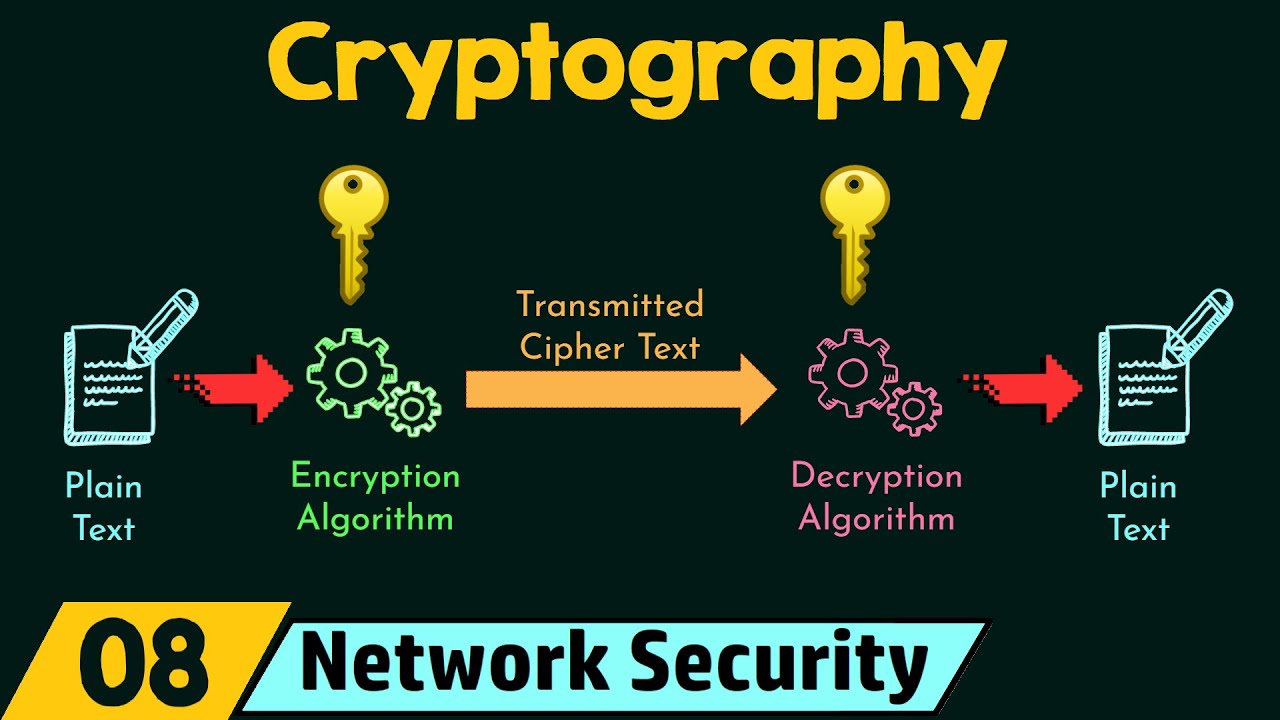
- 😀 Plain text is the readable, unencrypted message that the sender intends to send.
- 😀 Ciphertext is the unreadable, encrypted message that cannot be understood by humans without decryption.
- 😀 Public key is used by the sender to encrypt the message, making it secure during transmission.
- 😀 Private key is used by the recipient to decrypt the message and turn ciphertext back into readable plain text.
- 😀 Encryption is the process of converting plain text into ciphertext, ensuring secure communication.
- 😀 Decryption is the process of converting ciphertext back into plain text, allowing the recipient to read the message.
- 😀 Encryption ensures that only authorized parties can access sensitive data, preventing unauthorized access.
- 😀 Decryption ensures that only the intended recipient can read the message by using the private key.
- 😀 Encryption is essential for the secure transmission and storage of sensitive information.
- 😀 Both encryption and decryption processes are crucial for maintaining privacy and security in digital communication.
Q & A
What is plain text in the context of encryption and decryption?
-Plain text refers to data that is unencrypted and readable. It is the original, readable message that the sender wants to transmit to the recipient.
What does ciphertext mean?
-Ciphertext is the result of encrypting plain text. It is an unreadable, scrambled version of the original message that appears as a string of random characters, which can't be interpreted without decryption.
How does encryption work?
-Encryption involves converting readable plain text into ciphertext using an encryption algorithm. This process ensures that the message is secure and cannot be read by unauthorized individuals during transmission.
What is the role of the public key in encryption?
-The public key is used by the sender to encrypt the message. It ensures that only the intended recipient, who possesses the corresponding private key, can decrypt and read the message.
What is a private key used for?
-The private key is used by the recipient to decrypt the ciphertext back into plain text. It is kept secret and only the recipient should have access to it.
What happens during the decryption process?
-Decryption is the process of converting ciphertext back into plain text using a private key or secret key. The recipient can read the original message only after decryption.
Why is encryption necessary?
-Encryption is used to secure sensitive data during transmission or storage. It ensures that unauthorized parties cannot read or modify the data, protecting privacy and confidentiality.
What is the difference between encryption and decryption?
-Encryption converts readable plain text into unreadable ciphertext using a key, while decryption converts ciphertext back into readable plain text using a private key or secret key.
Who are the participants involved in encryption and decryption?
-The sender and recipient are the primary participants in the encryption and decryption process. The sender encrypts the message, and the recipient decrypts it.
What is the purpose of using a private key for decryption?
-The private key ensures that only the intended recipient, who possesses it, can decrypt and read the encrypted message, maintaining security and confidentiality.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Proteksi Data & File (Enkripsi) - Informatika Kelas 7 SMP/ MTs (Jaringan Komputer dan Internet)

Kripto 13: Kriptografi modern (Bagian 1: Representasi bit dan operasi XOR)

Algoritma Atbash Chipers
Cryptography

types of cryptography explain in Telugu 1.symmetric 2. Asymmetric #types#cryptography#telugu#

RSA Algorithm - How does it work? - I'll PROVE it with an Example! -- Cryptography - Practical TLS
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)