Metode Penugasan Kasus Maksimasi
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Septia Wulandari explains how to apply the Hungarian Method for solving assignment problems, focusing on maximization. The method involves converting a profit table into an opportunity loss table, subtracting maximum row values and minimum column values, then marking and adjusting zeros to find the optimal assignments. Using a real-world example with 5 employees and 5 tasks, the video demonstrates how to maximize profit through task assignments, arriving at a maximum profit of 68. The process is thoroughly explained with step-by-step guidance on how to handle both normal and non-normal cases.
Takeaways
- 😀 The Hungarian Method can be used to solve both minimization and maximization assignment problems, but the approach differs for each case.
- 😀 In maximization problems, the goal is to assign tasks to maximize profits or productivity.
- 😀 The method works for both 'normal' maximization cases (where the number of rows equals columns) and 'non-normal' cases (where rows do not equal columns).
- 😀 For non-normal maximization cases, dummy variables are added to balance the matrix of tasks and employees.
- 😀 The first step in solving a maximization problem is converting the performance table into an opportunity loss table.
- 😀 After creating the opportunity loss table, the next step is to subtract the maximum value from each row.
- 😀 For each column in the table, subtract the minimum value from every entry in that column.
- 😀 The method minimizes opportunity loss by adjusting values to ensure that the smallest uncovered values are identified and subtracted.
- 😀 Zeros are then crossed out in the table, and the maximum number of zeros is removed either horizontally or vertically.
- 😀 The final assignment of tasks to employees is made by evaluating uncovered values and ensuring that the solution is optimal, which is indicated when no further adjustments can be made.
- 😀 In the example problem, the maximum possible profit that can be obtained is 68, and the problem has multiple valid solutions for task assignments.
Q & A
What is the main objective of the maximization assignment problem discussed in the script?
-The main objective of the maximization assignment problem is to allocate tasks to employees in a way that maximizes the total profit or productivity, as opposed to minimizing cost or loss.
What method is used to solve both minimization and maximization assignment problems?
-The Hungarian method is used to solve both minimization and maximization assignment problems.
How do you adjust the performance matrix for a maximization assignment problem?
-For a maximization problem, the performance matrix is transformed into an opportunity loss matrix by subtracting each element in a row from the maximum value of that row, and similarly subtracting the minimum value of each column from the elements in that column.
What is the difference between a normal and non-normal maximization problem?
-A normal maximization problem occurs when the number of rows equals the number of columns. A non-normal maximization problem occurs when the number of rows does not equal the number of columns, requiring the addition of dummy variables to balance the rows and columns.
What step follows the creation of the opportunity loss table in the Hungarian method?
-After creating the opportunity loss table, the next step is to find the maximum value in each row and subtract it from every element in that row to minimize the opportunity loss.
How are zeros used in the Hungarian method for assignment problems?
-Zeros are identified in the matrix after row and column reductions. The largest number of zeros is then crossed out, either horizontally or vertically, to optimize the assignment process. The remaining non-crossed zeros are used to form the optimal assignment.
What should you do if a value in the opportunity loss table is negative after performing row reductions?
-If the result is negative after row reductions, the negative value should be written as positive since it represents the absolute difference, and only positive values are used in the process.
What does crossing out zeros in the matrix represent in the Hungarian method?
-Crossing out zeros in the matrix represents potential assignments that should be considered for the optimal solution. This process helps to identify which tasks should be assigned to which employees based on the opportunity loss minimization.
How do you know when the assignment problem is optimal in the Hungarian method?
-The assignment problem is considered optimal when all rows and columns are either crossed out or assigned to a task, and no further reductions can be made to the matrix without violating the constraints of the problem.
Can the maximization assignment problem have multiple optimal solutions?
-Yes, the maximization assignment problem can have multiple optimal solutions, which is referred to as a 'multiple solution case'. This happens when there are multiple combinations of assignments that yield the same maximum profit.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Lec-32 Maximization Assignment Problem | Unbalanced Example | In Hindi | In Operation Research

MK Kuantitatif - Metode Penugasan
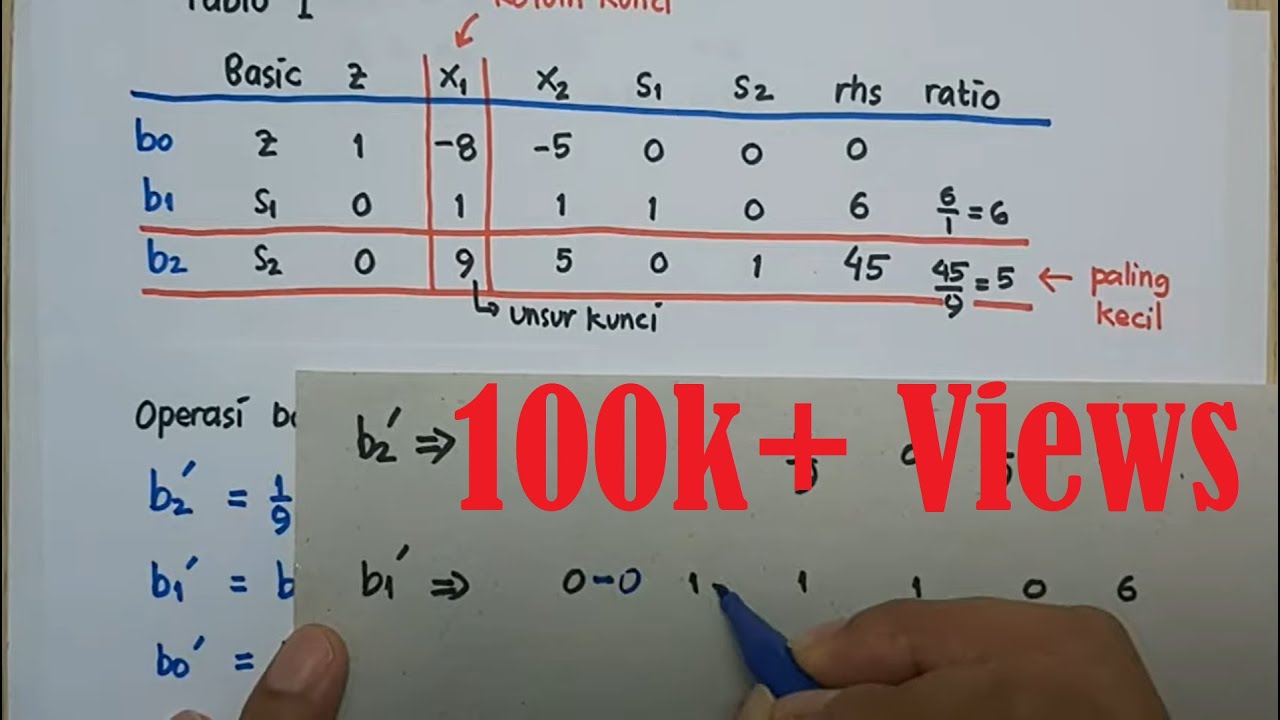
Metode Simpleks (Contoh soal untuk kasus maksimisasi)

Elimination Method

IKATAN ION( ELEKTROVALEN)
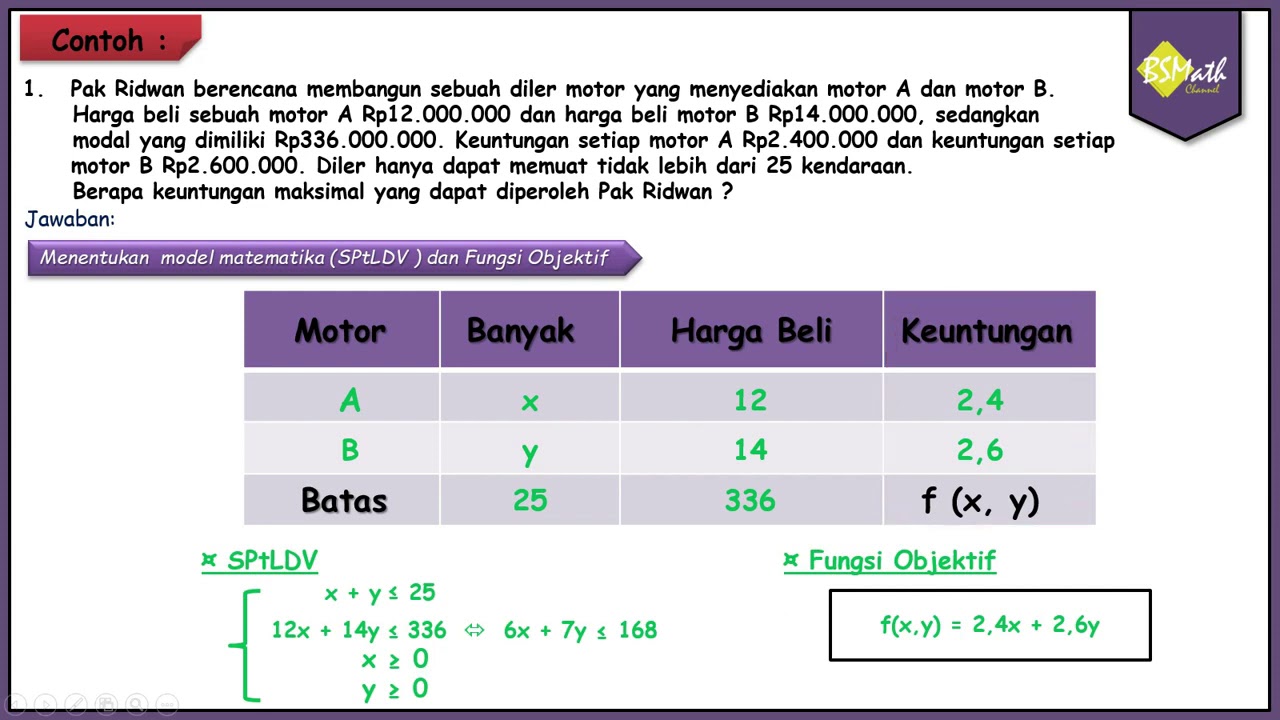
Menyelesaikan Permasalahan Program Linear Menentukan Nilai Optimum dengan Metode Uji Titik Pojok
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)