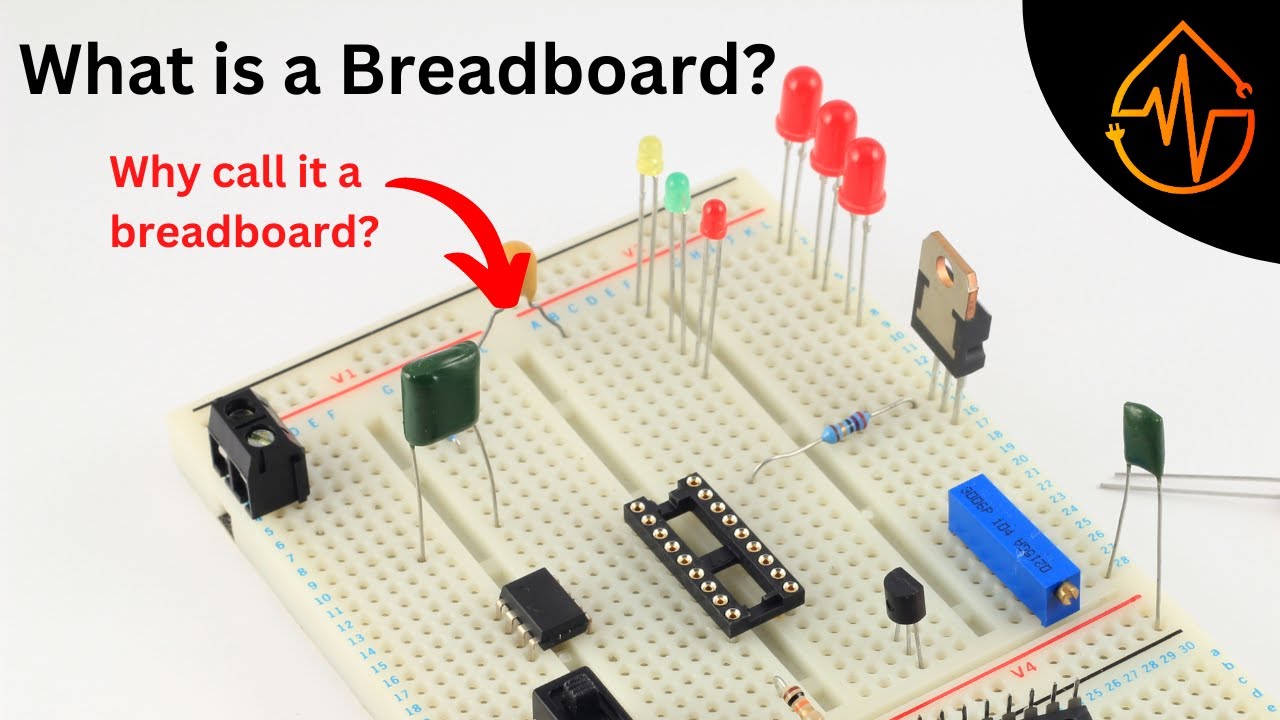
How to use a BreadBoard - Electronics Basics 10
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, the host introduces viewers to breadboards, explaining their function as a simple, non-permanent way to prototype electronic circuits without soldering. The video covers how breadboards work, with rows and columns that are electrically common and how to use jumper wires for connections. The tutorial demonstrates building a basic LED circuit powered by an Arduino, showing both series and parallel connections. It’s an ideal starting point for beginners looking to understand breadboards and start experimenting with electronics.
Takeaways
- 😀 Breadboards are an easy, solder-free alternative for prototyping and building circuits.
- 😀 The rows on a breadboard are electrically common, meaning all the holes in a row are connected.
- 😀 Columns on a breadboard are electrically isolated from each other unless connected by a wire.
- 😀 Power rails on a breadboard are typically marked for positive and negative connections, making power distribution easier.
- 😀 It’s important to note that on many breadboards, the power rails are divided, and can be bridged to create a continuous connection across the board.
- 😀 Jumper wires are used to make connections on a breadboard, and they can be purchased or handmade with solid core wire.
- 😀 Components like LEDs are polarized, meaning they have a positive (longer leg) and negative side, which must be correctly connected.
- 😀 To create a simple LED circuit, the positive leg of the LED connects to the positive rail, and the negative leg goes through a resistor to the negative rail.
- 😀 In a parallel circuit, multiple LEDs can be connected, with each LED having its own resistor connected to the negative power rail.
- 😀 A basic example circuit with an Arduino can be used to power a breadboard, showing how to light up multiple LEDs in parallel.
Q & A
What is the main purpose of using a breadboard in electronics?
-A breadboard provides an easy and straightforward platform for prototyping and building circuits without the need for soldering or circuit board design.
How are the rows and columns on a breadboard electrically connected?
-On a breadboard, the rows going vertically are electrically common, meaning that all the holes in a single row are connected together. Similarly, individual columns are also electrically common within each column, but not between adjacent columns.
What are the power rails on a breadboard, and what are they used for?
-The power rails on a breadboard are typically located along the sides and are used to distribute power (positive and negative) to the circuit. These rails are electrically common, allowing easy connections for powering components.
How can you bridge the break in the power rail to make it electrically common across the entire breadboard?
-You can bridge the break in the power rail by using a wire to connect the two sides, ensuring that the entire rail is electrically common and can distribute power throughout the breadboard.
What are jumper wires, and why are they important when working with breadboards?
-Jumper wires are breadboard-compatible wires that allow you to make connections across the breadboard. They are essential for linking components and creating circuits on the breadboard.
What does it mean when an LED is described as 'polarized'?
-An LED is polarized, meaning it has a positive (anode) and a negative (cathode) leg. The positive side is typically marked by a longer leg, while the negative side may be indicated by a flat edge on the LED housing.
How do you connect an LED to a breadboard circuit?
-To connect an LED to a breadboard, insert the positive leg into one column and the negative leg into another column. Then, complete the circuit with a resistor on the negative side and connect the other components to the power rails.
What is the role of the resistor in the LED circuit on the breadboard?
-The resistor limits the current flowing through the LED to prevent it from burning out. It is connected in series with the LED, with one leg attached to the negative side of the LED and the other leg connected to the negative power rail.
What happens when you connect multiple LEDs in parallel on a breadboard?
-When you connect multiple LEDs in parallel, each LED shares the same positive connection but has its own current-limiting resistor connected to the negative power rail. This allows each LED to light up independently while sharing the same power source.
How do you ensure the LEDs are connected correctly when placed in parallel?
-Ensure that all the positive legs of the LEDs are connected to the same positive rail, and that each LED's negative leg is connected to its own resistor, with the resistors then linked to the negative power rail.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)