Hall Effect and it's Applications | English to Telugu
Summary
TLDRThis video explains complex concepts in electromagnetism, focusing on electric fields, magnetic fields, and current-carrying conductors. It introduces the relationship between voltage, current, and magnetic fields in conductors, including the impact of different semiconductors and electrical charges. The script also includes repeated calls to subscribe to the channel, emphasizing the importance of following for more educational content. Despite the technical nature, the tone remains accessible and casual, aiming to simplify advanced topics for a general audience interested in electronics and physics.
Takeaways
- 😀 High voltage is directly proportional to the current flowing through a conductor and the magnetic field produced.
- 😀 Magnetic fields around current-carrying conductors influence the forces acting on nearby charged particles.
- 😀 The script mentions the discovery of a half-inch house, though the context is unclear; it could be part of an educational example.
- 😀 The relationship between electric and magnetic fields is explored, with an emphasis on their influence on each other.
- 😀 The script refers to semiconductors, discussing both types and their applications in electrical systems.
- 😀 The concept of potential difference is highlighted, describing how it affects the flow of electric current.
- 😀 A significant part of the content is dedicated to the electromagnetic field, particularly its role in producing force on electric charges.
- 😀 The importance of maintaining a proper voltage-to-current ratio in electrical systems is stressed.
- 😀 References to 'subscribe' and 'channel' suggest the content is likely part of an educational or promotional video for a platform like YouTube.
- 😀 The script includes several technical terms such as 'perpendicular magnetic field,' 'electric field,' and 'current-carrying conductors,' indicating a focus on electrical and electromagnetic theory.
Q & A
What is a current-carrying conductor, and how does it relate to electromagnetic fields?
-A current-carrying conductor is a material that allows electric current to flow through it. When a current flows through a conductor, it generates a magnetic field around the conductor due to the movement of charged particles (electrons). This magnetic field is perpendicular to the direction of the current flow and is a fundamental principle of electromagnetism.
What is the relationship between electric current and magnetic fields?
-Electric current produces magnetic fields around conductors. This is known as Ampère's Law, which states that the magnetic field around a conductor is directly proportional to the current flowing through it and is perpendicular to the direction of the current.
How do semiconductor materials behave in electrical circuits?
-Semiconductors are materials that have electrical conductivity between conductors and insulators. The script mentions P-type and N-type semiconductors, which are created by doping materials to create an excess of positive (holes) or negative (electrons) charge carriers. These semiconductors are crucial in the functioning of various electronic devices such as diodes and transistors.
What does it mean when the script mentions 'magnetic field induced by current-carrying conductors'?
-The magnetic field induced by current-carrying conductors refers to the magnetic field that forms around a conductor when it carries an electric current. The strength and direction of this magnetic field depend on the amount of current flowing and the orientation of the conductor.
What role does voltage play in the generation of electromagnetic fields?
-Voltage is the electric potential difference between two points in a circuit, which drives the flow of current. The current, in turn, generates an electromagnetic field. The voltage controls the amount of current that flows, and hence, the strength of the electromagnetic field produced around conductors.
What is the significance of the statement 'one liter of milk' in the script?
-The mention of 'one liter of milk' appears to be an unrelated, possibly metaphorical or misplaced phrase within the context of a technical discussion. It may be a transcription error or part of an example used to illustrate a concept, but it does not directly relate to the scientific content discussed.
How is the force on a charged particle in an electromagnetic field determined?
-The force on a charged particle moving through an electromagnetic field is determined by the Lorentz force law. This law states that the force is the sum of two components: the electric force (due to the electric field) and the magnetic force (due to the magnetic field). The magnetic force is proportional to the velocity of the charged particle and the strength of the magnetic field.
What does it mean for a force to be 'perpendicular' to the conductor and current?
-When a force is described as 'perpendicular' to the conductor and current, it means that the direction of the force is at a 90-degree angle to both the direction of the current flow and the conductor. This is characteristic of the magnetic force acting on moving charges in a conductor, which always acts perpendicular to both the current direction and the magnetic field.
Why is high voltage important in the context of electrical systems and conductors?
-High voltage is essential in electrical systems because it enables the transmission of large amounts of power over long distances with reduced energy loss. In the script, references to high voltage emphasize its role in the functioning of electrical circuits, where the current flowing through conductors is proportional to the voltage applied.
What is the significance of the term 'high voltage' in terms of electric field strength?
-In the context of electrical fields, high voltage is significant because it leads to stronger electric fields, which can influence the behavior of charged particles and current flow through conductors. The electric field strength is directly related to the voltage difference between two points; a higher voltage results in a stronger electric field.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Magnetic effect of electric current in one shot (Animation) | CLASS 10 CBSE boards | NCERT Science

Class 10 CBSE Physics - Magnetic Effect of Electric Current | Concept Revision | Xylem Class 10 CBSE

Magnetic Effect of Electric Current

All of MAGNETIC FIELDS in 15 mins - A-level Physics

25. Physik - Elektromagnetische Induktion
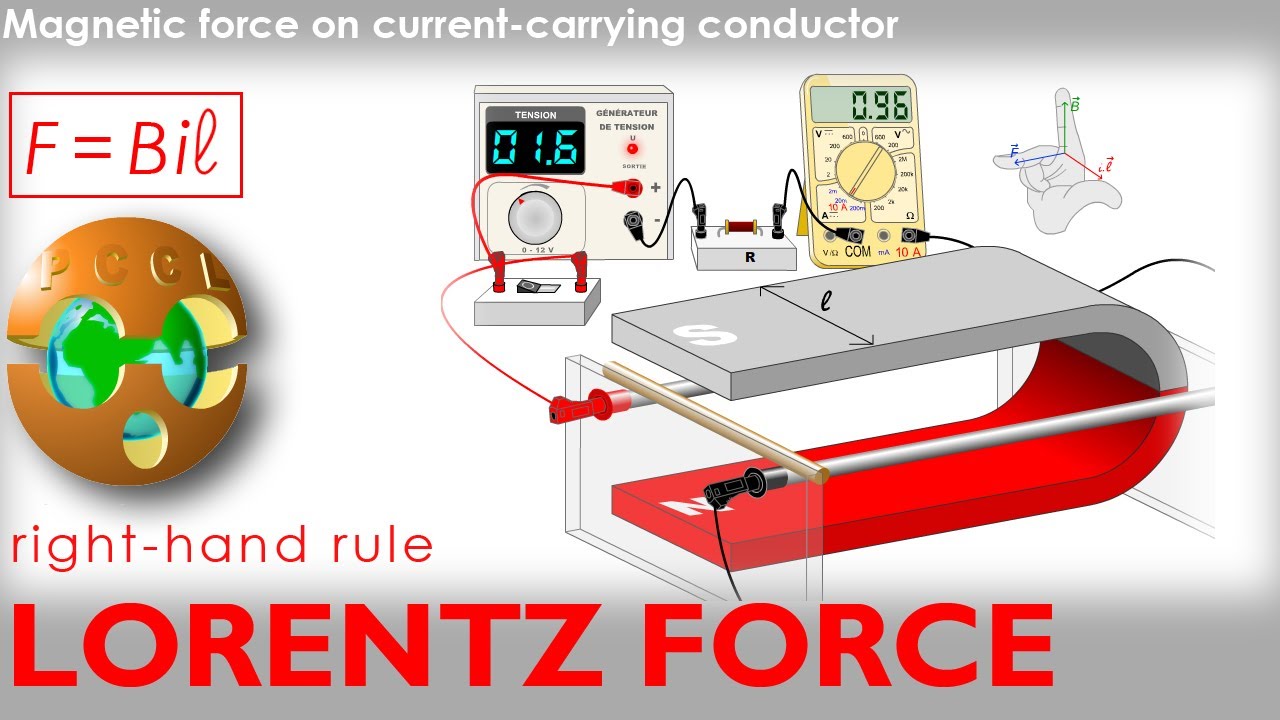
LORENTZ FORCE Rail + Rolling Conductor + i + Magnetic Field 🧲 + 3 Fingers Right Hand Rule 👆 PCCL
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)