ADFS: The Complete Guide to Active Directory Federation Service and Claim-Based Identity Model
Summary
TLDRThis video introduces Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS), explaining its role in providing secure Single Sign-On (SSO) across organizational boundaries. It covers the claims-based identity model, where ADFS customizes authentication tokens based on the application's needs, allowing organizations to share resources securely. The video discusses key concepts such as Federation Trust, security token service (STS), claims provider, and identity provider. Practical examples clarify the need for ADFS in handling user access while minimizing security risks. The series will continue with detailed deployment scenarios and certificate requirements for ADFS installation.
Takeaways
- 😀 ADFS (Active Directory Federation Services) is a component of Windows Server that provides Single Sign-On (SSO) access to applications across different organizational boundaries.
- 😀 ADFS works based on the **claims-based identity model**, allowing users to authenticate once and access multiple applications without logging in repeatedly.
- 😀 In ADFS, a **federation trust** is established between organizations to allow users to access specific applications hosted across organizational borders, without exposing all resources.
- 😀 ADFS reduces security risks by only requiring **Port 443** to be open between organizations, unlike traditional methods that might require multiple ports.
- 😀 ADFS allows for the customization of authentication tokens, adapting the claims sent to an application based on the application’s specific attribute requirements.
- 😀 The key advantage of ADFS is its ability to send customized tokens to applications, based on attributes such as **email address** or **department**, tailored to the application’s needs.
- 😀 **Claims** in ADFS are pieces of identity information, such as **user principal name**, **email address**, or **department**, that are issued as part of authentication.
- 😀 ADFS is a **Security Token Service (STS)**, issuing tokens to applications for secure authentication and authorization.
- 😀 The **Identity Provider** (such as ADFS) authenticates users and provides the necessary tokens for SSO access to applications, acting as the intermediary between users and resource providers.
- 😀 The **Relying Party** is the entity hosting an application and validating tokens sent by ADFS to grant user access.
- 😀 Federation trust in ADFS is comparable to how airport security trusts ID proofs (like passports or driver’s licenses) issued by trusted authorities, allowing users access based on their identity tokens.
Q & A
What is Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS)?
-ADFS is a component of the Windows Server operating system that provides users with Single Sign-On (SSO) access to systems and applications across organizational boundaries using a claims-based identity model.
What is the claims-based identity model in ADFS?
-The claims-based identity model allows ADFS to authenticate users and authorize access by issuing tokens based on claims (user attributes like email or department), instead of using static Kerberos tickets, enabling more flexible authentication for different applications.
Why do organizations need ADFS?
-ADFS allows organizations to securely share resources across domains or networks without opening multiple ports, by creating a federation trust between organizations and passing only necessary user information (claims) to minimize security risks.
What is a federation trust in ADFS?
-A federation trust is a relationship between two organizations that enables secure resource sharing. ADFS allows organizations to establish this trust, so users from one organization can access applications hosted by another, while minimizing security risks.
What are claims in the context of ADFS?
-Claims are pieces of identity information, such as a user's email address, department, or user principal name, that are passed within tokens issued by ADFS to facilitate authentication and authorization across systems.
How does ADFS customize tokens for different applications?
-ADFS can customize tokens based on the specific claims required by an application. For example, if an application needs a user's email address for authentication, ADFS will construct a token with the email address claim and send it to the application.
What role does the Security Token Service (STS) play in ADFS?
-The Security Token Service (STS) in ADFS is responsible for issuing security tokens to authenticated users. It processes user credentials, generates tokens, and ensures they contain the necessary claims for accessing applications.
What is the difference between a Kerberos ticket and an ADFS token?
-A Kerberos ticket issued by Active Directory contains a fixed set of attributes, such as user SID and group SID. In contrast, an ADFS token is customizable and can include specific claims required by an application, allowing for more flexible authentication.
How does the federation process work between an identity provider and a resource provider in ADFS?
-In ADFS, when a user wants to access an application hosted by a different organization, the identity provider authenticates the user and issues a token. This token is forwarded to the resource provider, which then validates the token and grants access to the application.
What are relying parties in ADFS?
-Relying parties in ADFS are the entities hosting the applications that consume the tokens issued by the ADFS server. These parties trust the identity provider to authenticate users and validate the tokens before granting access to resources.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Lecture 03 Introduction to Active Directory

CompTIA Security+ SY0-701 Course - 4.6 Implement and Maintain Identity & Access Management - PART A

¿Qué es Active Directory y para qué sirve? | ManageEngine LATAM

What Is Single Sign-on (SSO)? How It Works

Installing and Configuring Active Directory, DNS, DHCP
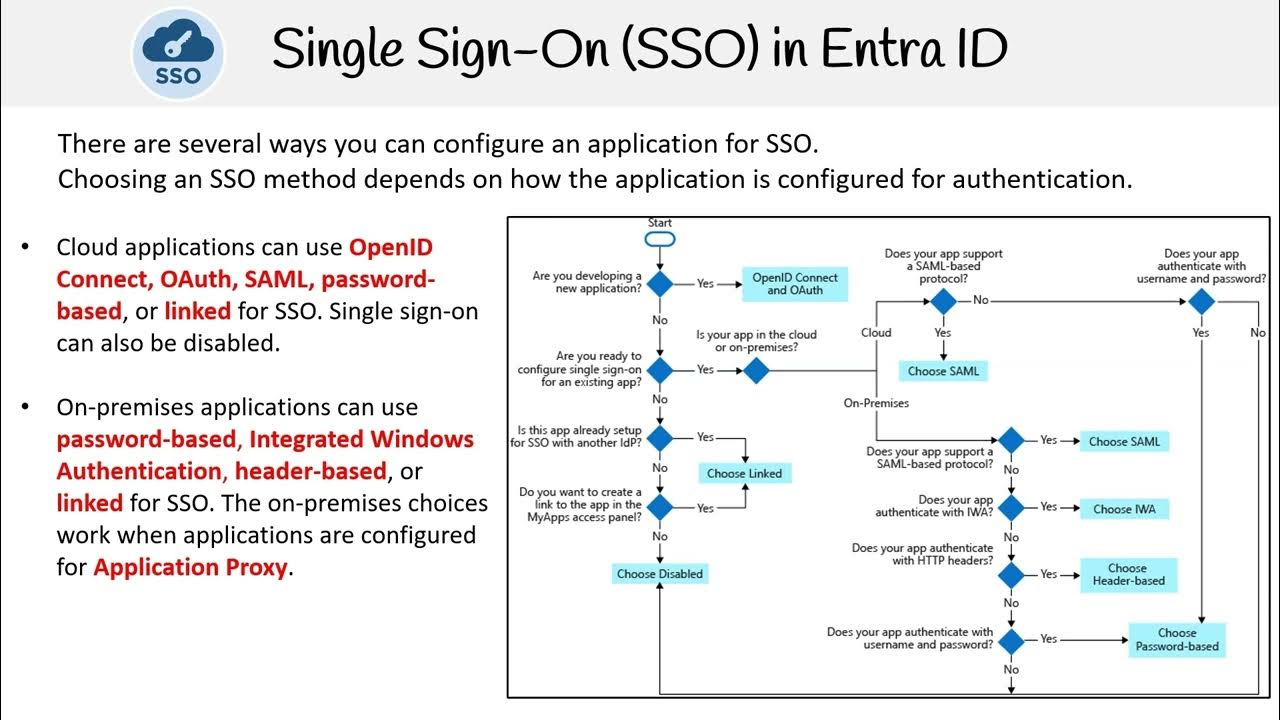
AZ 305 — Single Sign On SSO
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)