Cardiovascular Disorders - Part 2 (arteries)
Summary
TLDRThis comprehensive video script covers a range of arterial diseases, focusing primarily on hypertension, a leading cause of cardiovascular issues like strokes, heart attacks, and kidney disease. The script explains the significance of blood pressure readings, the causes and risk factors for hypertension, and treatments including lifestyle changes and medications. It also delves into conditions like atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease, which involve plaque buildup and narrowing arteries, leading to life-threatening conditions. The importance of early diagnosis and interventions like stenting, bypass surgery, and lifestyle adjustments to prevent further complications is emphasized.
Takeaways
- 😀 Hypertension is a major cause of cardiovascular diseases, including strokes, heart attacks, and kidney diseases.
- 😀 A normal blood pressure is around 120/80 mmHg, with hypertension diagnosed at values over 140/90 mmHg.
- 😀 Blood pressure is influenced by cardiac output (stroke volume x heart rate) and peripheral vascular resistance.
- 😀 Primary hypertension is idiopathic, meaning its cause is unknown, but risk factors include heredity, diet, age, obesity, smoking, and stress.
- 😀 Lifestyle changes such as a low-salt diet, regular exercise, stress reduction, and smoking cessation can help manage hypertension.
- 😀 Arteriosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) results from plaque buildup, which can restrict blood flow and increase blood pressure.
- 😀 Coronary artery disease is the leading cause of death in the U.S., often due to arteriosclerosis, and can lead to heart attacks.
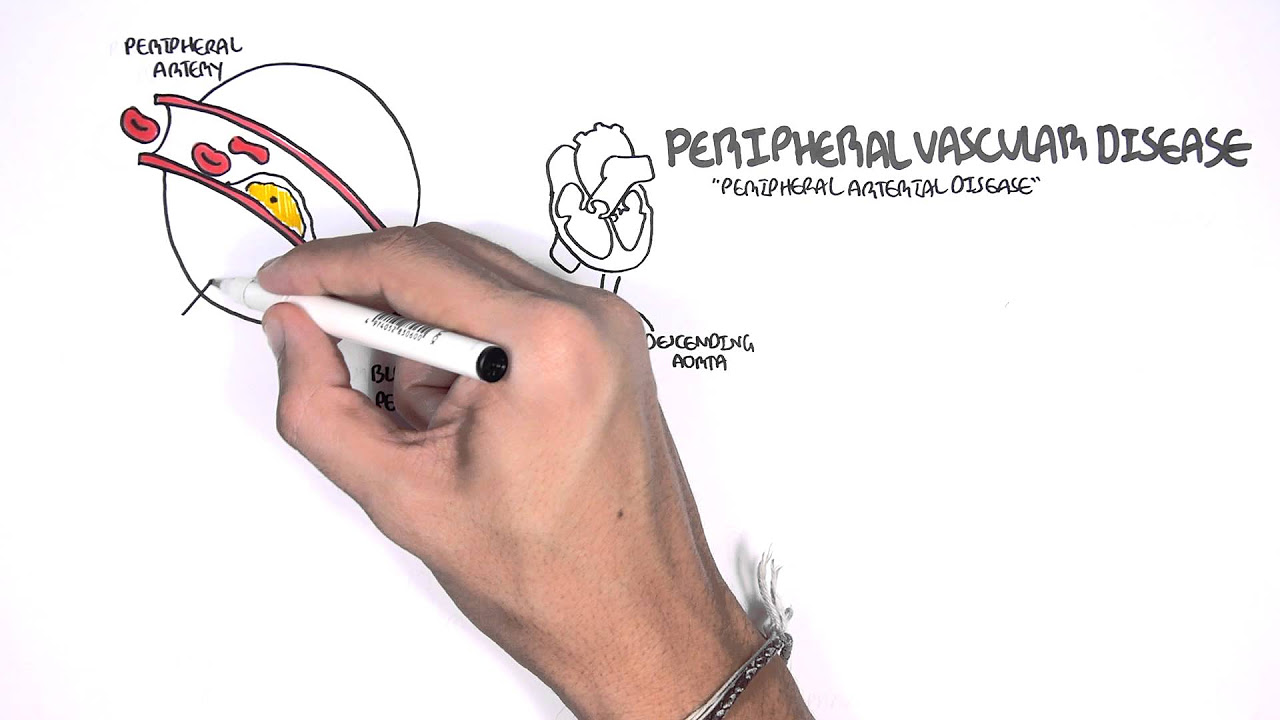
- 😀 Intermittent claudication, a symptom of peripheral vascular disease, causes muscle cramps that are relieved with rest and worsened with activity.
- 😀 Peripheral vascular disease may lead to tissue necrosis and amputation if blood flow is not restored in time.
- 😀 An aneurysm is a weakening in an artery wall, often asymptomatic until it ruptures, which can lead to rapid bleeding and death.
- 😀 Coronary artery disease can be diagnosed through an ECG, history, and angiogram, with treatments including stents, bypass surgery, and lifestyle changes to prevent plaque buildup.
Q & A
What is hypertension and why is it considered dangerous?
-Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a chronic condition where the force of the blood against the artery walls is consistently too high. It is dangerous because it can lead to serious cardiovascular problems, including strokes, heart attacks, and kidney diseases. Over time, it puts additional strain on the heart and arteries, increasing the risk of these complications.
What do the numbers in a blood pressure reading represent?
-In a blood pressure reading, the top number (systolic) measures the pressure in the arteries when the heart contracts, while the bottom number (diastolic) measures the pressure when the heart is at rest between beats. A normal reading is around 120/80 mmHg, with high blood pressure being defined as a reading over 140/90 mmHg.
How does blood viscosity affect blood pressure?
-Blood viscosity refers to the thickness of the blood. Thicker blood, like syrup, flows more slowly, causing increased resistance in the blood vessels, which can raise blood pressure. If the blood is too viscous, the heart has to work harder to pump it through the vessels.
What is the difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure?
-Systolic pressure is the higher number in a blood pressure reading, representing the pressure in the arteries when the heart contracts and pumps blood. Diastolic pressure is the lower number, representing the pressure in the arteries when the heart relaxes between beats.
What are the major risk factors for developing hypertension?
-The major risk factors for hypertension include heredity, a high-fat or high-salt diet, obesity, smoking, stress, and aging. Certain conditions like diabetes can also contribute to the development of hypertension.
What lifestyle changes can help manage hypertension?
-Managing hypertension can involve a variety of lifestyle changes such as reducing salt intake, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, reducing stress, maintaining a healthy weight, and limiting alcohol consumption. Diuretics and antihypertensive medications may also be prescribed.
What is arterial sclerosis, and how does it affect the arteries?
-Arterial sclerosis, or hardening of the arteries, occurs when the arteries lose their elasticity and become thickened due to the buildup of plaque. This reduces the ability of the arteries to expand and contract, which impairs blood flow and can increase the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular problems.
What causes the buildup of plaque in arteries?
-Plaque buildup in arteries is often caused by damage to the artery walls, where fat, cholesterol, and other substances accumulate. This process is influenced by factors like high blood pressure, smoking, poor diet, and lack of exercise.
What is an aneurysm, and why is it a serious condition?
-An aneurysm is a bulging or weakened area in the wall of an artery, typically in the aorta. It can be asymptomatic, making it difficult to detect, but if it ruptures, it can lead to rapid and severe bleeding, which can be fatal. Early detection and surgical repair are crucial to prevent rupture.
What is coronary artery disease, and what are its main causes?
-Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart muscle. It is primarily caused by plaque buildup due to atherosclerosis, but can also result from blood clots (thrombosis) or embolisms (fat globules or air bubbles blocking the arteries). CAD can lead to chest pain (angina) and heart attacks.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

MENGERIKAN! INI 5 PENYAKIT PENYEBAB KEMATIAN TERTINGGI DI INDONESIA

Atherosclerosis - Pathophysiology

10 INCRÍVEIS ALIMENTOS que TRANSFORMAM sua CIRCULAÇÃO | LIMPAM até 95,6% seus VASOS SANGUÍNEOS?
Cardiovascular Disease Overview

Gangguan/Kelainan pada Sistem Peredaran Darah & Upaya Mencegah serta Menanggulanginya | IPA Kelas 8
Angiotensin 2 Receptor Blockers (ARBS) Pharmacology Nursing NCLEX Quick Review
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)