Diferenciación de funciones lineales | Cálculo | Khan Academy en Español
Summary
TLDRThis video script compares two attempts at finding the derivative of similar mathematical expressions. Abril makes an error by omitting the negative sign when differentiating, which affects her final answer. Ana, on the other hand, incorrectly applies the product rule to a simple linear term, leading to the wrong derivative. Both examples highlight common mistakes in derivative rules, emphasizing the importance of correctly handling constants, terms of first degree, and applying the right derivative properties. The video aims to clarify these errors and provide guidance on how to avoid them in future derivative problems.
Takeaways
- 😀 Abril made an error in the first step of differentiating `7 - 5x` by incorrectly omitting the minus sign for the derivative of `-5x`.
- 😀 Abril's final result should have been `-5` instead of `5`, had she correctly applied the minus sign in the first step.
- 😀 Constants, like `7`, always have a derivative of 0, and this is correctly handled by Abril in subsequent steps.
- 😀 The derivative of `-5x` is simply the coefficient `-5`, but Abril mistakenly left out the negative sign.
- 😀 Ana made an error in the third step by incorrectly using the product rule to differentiate `8x`, which was unnecessary because `8` is a constant.
- 😀 The derivative of a constant multiplied by a variable, such as `8x`, is simply the constant (`8`) times the derivative of the variable (`x`), which is `1`.
- 😀 Ana mistakenly concluded that the derivative of `8x` was 0 by incorrectly applying the product rule.
- 😀 The correct derivative of `8x` should be `8`, but Ana's method led to an incorrect answer of `0`.
- 😀 When differentiating terms involving constants, the product rule should not be used if one term is a constant and the other is a variable.
- 😀 Both Abril and Ana made their errors in different steps but used similar types of basic derivative principles, highlighting the importance of careful application of rules.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

KALKULUS | TURUNAN | APA ITU TURUNAN?

Derivatives of Parametric Functions

1. Eulerian and Lagrangian Descriptions in Fluid Mechanics
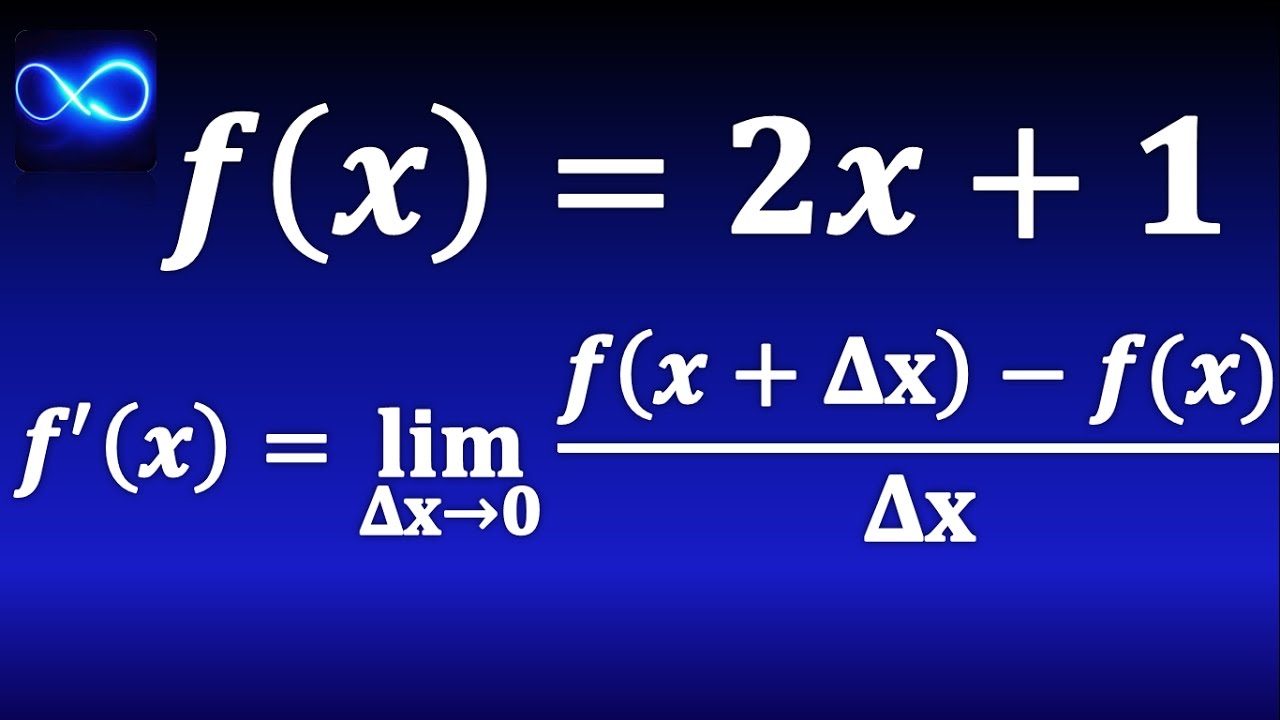
Derivative by increment method (By definition with limit)
Module 2 Lesson 1 Characteristics of Mathematical Language
Worked example: motion problems (with definite integrals) | AP Calculus AB | Khan Academy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)