Types of Chemical Reactions
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the six main types of chemical reactions are explained with simple examples from daily life. The types include combination reactions (e.g., photosynthesis), decomposition reactions (e.g., electrolysis of water), displacement reactions (e.g., table salt formation), combustion reactions (e.g., burning of petrol in car engines), redox reactions (e.g., rusting of iron), and neutralization reactions (e.g., toothpaste neutralizing mouth acids). Each type is clearly defined with relatable instances to help viewers understand their significance in everyday occurrences.
Takeaways
- 😀 Combination reaction (also known as addition reaction) occurs when two or more substances combine to form a single product, such as carbon + oxygen to form carbon dioxide.
- 😀 Photosynthesis is a real-life example of a combination reaction, where carbon dioxide and water combine to form glucose.
- 😀 Decomposition reactions involve the breakdown of a compound into simpler substances, like the electrolysis of water to produce hydrogen and oxygen gases.
- 😀 Hydrogen peroxide decomposes into water and oxygen, and silver bromide decomposes into silver and bromine gas under light.
- 😀 Decomposition reactions can occur spontaneously or be initiated by heat, like the breakdown of carbonic acid into water and carbon dioxide.
- 😀 Displacement reactions involve one element replacing another in a compound. For example, zinc displaces hydrogen in hydrochloric acid to form zinc chloride and hydrogen gas.
- 😀 Displacement reactions only occur when the replacing element is more reactive, as seen when sodium replaces calcium in the formation of table salt.
- 😀 Combustion reactions occur when oxygen reacts with a compound to produce heat and light. In complete combustion, methane reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water.
- 😀 Incomplete combustion occurs with limited oxygen, resulting in products like carbon monoxide and carbon in addition to water.
- 😀 Redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons. In the reaction of magnesium with oxygen, magnesium is oxidized (loses electrons) and oxygen is reduced (gains electrons).
- 😀 Neutralization reactions occur when an acid and a base react to form salt and water, such as the reaction of hydrochloric acid with sodium hydroxide to form sodium chloride and water.
- 😀 Everyday examples of neutralization reactions include using toothpaste to neutralize acids in the mouth and magnesium hydroxide to reduce stomach acid.
Q & A
What is a combination reaction?
-A combination reaction occurs when two or more substances combine to form a single product. For example, carbon reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide (CO₂).
Can you give a real-life example of a combination reaction?
-Yes, photosynthesis is a real-life example of a combination reaction, where carbon dioxide and water combine to form glucose and oxygen.
What is a decomposition reaction?
-A decomposition reaction involves the breakdown of a chemical compound into simpler substances. For example, when water undergoes electrolysis, it decomposes into hydrogen and oxygen gases.
How does a displacement reaction work?
-In a displacement reaction, one element displaces another in a compound. For instance, when zinc reacts with hydrochloric acid, zinc displaces hydrogen, forming zinc chloride and hydrogen gas.
What is the difference between complete and incomplete combustion?
-In complete combustion, there is a plentiful supply of oxygen, resulting in the formation of carbon dioxide and water. In incomplete combustion, oxygen is limited, and carbon monoxide or carbon may also be produced along with water.
How does a redox reaction occur?
-A redox reaction involves the transfer of electrons between two species. One species is oxidized (loses electrons), and the other is reduced (gains electrons). For example, magnesium is oxidized and oxygen is reduced when they react to form magnesium oxide.
What is the significance of the reactivity of elements in a displacement reaction?
-In a displacement reaction, a more reactive element will displace a less reactive element from its compound. For example, sodium displaces calcium in a displacement reaction because sodium is more reactive than calcium.
How is the burning of petrol in a car engine related to a combustion reaction?
-The burning of petrol in a car engine is an example of a combustion reaction, where oxygen reacts with fuel to produce heat, light, and typically carbon dioxide and water.
What happens during a neutralization reaction?
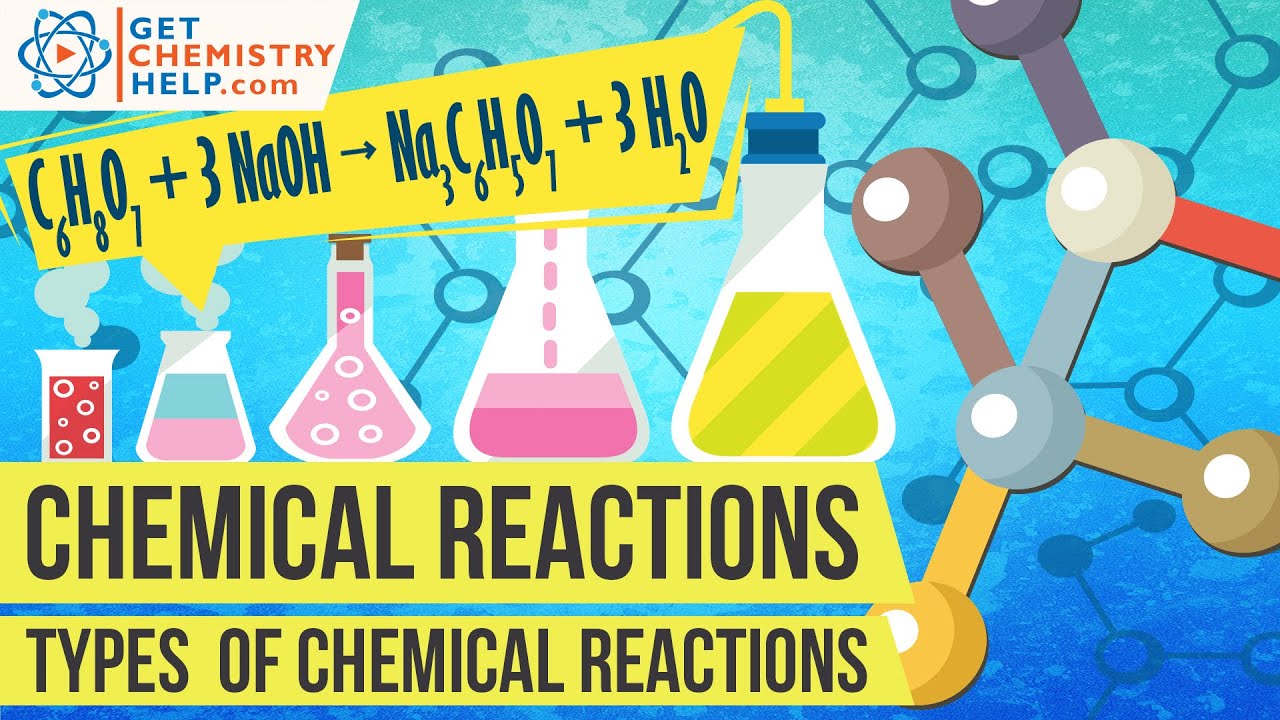
-In a neutralization reaction, an acid reacts with a base to form a salt and water. For example, hydrochloric acid (HCl) reacts with sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to form sodium chloride (NaCl) and water.
How does toothpaste act as an example of a neutralization reaction?
-Toothpaste neutralizes the acids produced by bacteria in the mouth, as toothpaste is basic in nature. This neutralization helps to protect teeth from the harmful effects of acids.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Chemistry Lesson: Types of Chemical Reactions

BAB 5 REAKSI - REAKSI KIMIA DAN DINAMIKANYA PART 1 (IPA Kelas 9 Kurikulum Merdeka)

Chemical reactions and equations Full chapter in animation | CBSE Class 10 | NCERT Science ch -1

Video Pembelajaran Model Problem Based Learning Materi Persamaan Reaksi Kimia

KESETIMBANGAN KIMIA KELAS 11_PART 1

CHEMICAL WEATHERING
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)