What are States' Rights and What Is Federalism? | Your Democracy
Summary
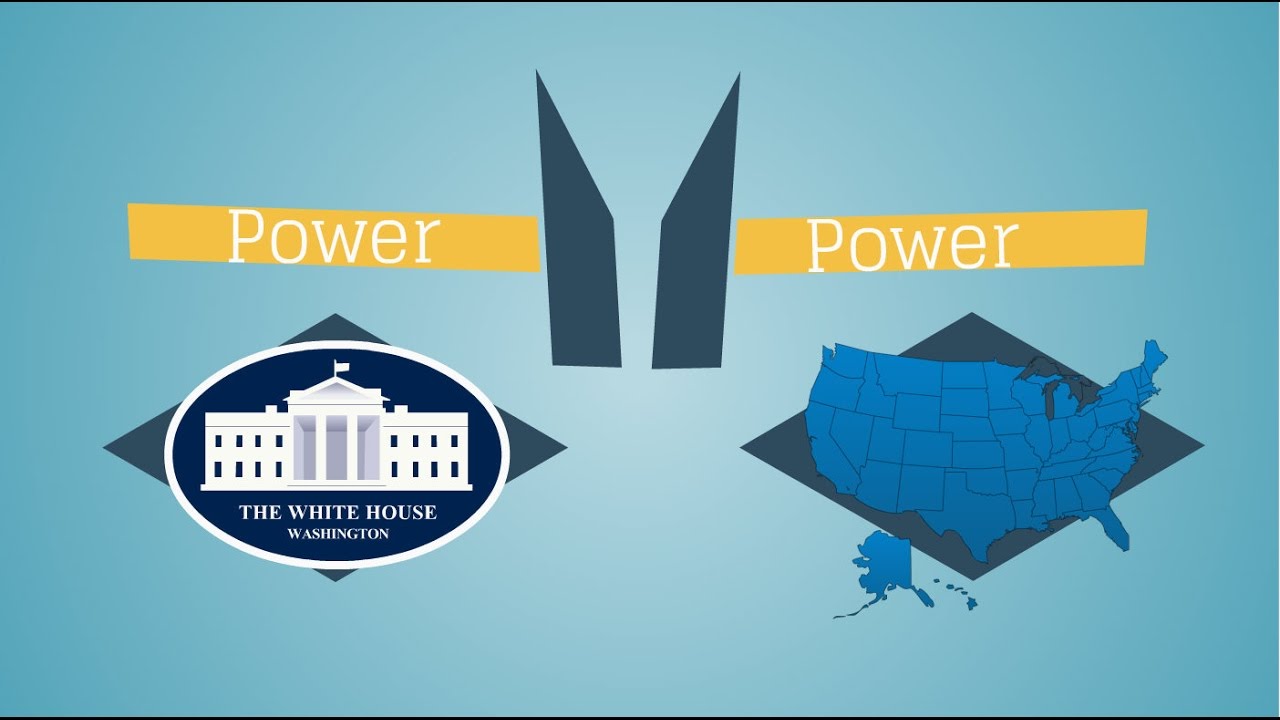
TLDRThis video explains the concept of federalism in the United States, focusing on the balance of power between state governments and the federal government. It highlights the rights of states, as defined by the 10th Amendment, and their authority to make laws in areas like education, real estate, and taxes. The video also explains the Supremacy Clause, which asserts that federal law takes precedence over state law. Additionally, the video covers the history of the Articles of Confederation and the creation of the US Constitution, illustrating how state and federal governments work together to serve the people.
Takeaways
- 😀 States are united under the US Constitution, including territories like Guam, Puerto Rico, and the Virgin Islands.
- 😀 Every state has its own constitution, governor, capital, laws, and landmarks, reflecting the diversity of its people.
- 😀 States possess 'states' rights,' which allow them to control local matters like education, driver's licenses, and real estate transactions.
- 😀 Federalism is the balance of power between state governments and the federal government, as outlined by the 10th Amendment.
- 😀 The 10th Amendment reserves powers for the states and people, except those explicitly delegated to the federal government.
- 😀 Federal law and state law must coexist, but in the case of conflict, federal law takes precedence due to the Supremacy Clause in Article VI of the US Constitution.
- 😀 The Supremacy Clause makes the US Constitution and federal laws the 'supreme law of the land,' overriding state laws when necessary.
- 😀 Historically, before the US Constitution, states were more powerful, and the federal government was weak under the Articles of Confederation.
- 😀 The creation of the US Constitution in 1787 shifted the balance of power, giving more authority to the federal government over individual states.
- 😀 While the federal government plays a significant role in national matters like defense and immigration, states still maintain substantial responsibilities for their local governance.
- 😀 Despite occasional conflicts between state and federal law, both levels of government must work together to serve the people and strengthen democracy.
Q & A
What is the main purpose of the United States Constitution in relation to the states?
-The US Constitution binds the states together, establishing a framework for federalism, which balances the power between the states and the federal government.
What territories are considered part of the United States under the Constitution?
-The territories that are considered part of the United States under the Constitution include Guam, Puerto Rico, and the Virgin Islands.
What powers do states have under the US Constitution?
-States have powers known as 'states' rights,' which allow them to govern things like driver's licenses, marriages, real estate transactions, education, state highways, and taxes.
What is the role of the federal government in relation to the states?
-The federal government handles national matters such as military, immigration, and printing money. It also makes laws that states must follow, particularly in cases of conflict with state laws.
What is federalism?
-Federalism is the system of government that defines the balance of power between the federal government and the individual states.
How does the 10th Amendment relate to state powers?
-The 10th Amendment states that any powers not specifically granted to the federal government are reserved for the states or the people, thus protecting state powers.
What happens when a state and the federal government disagree on a law?
-In the event of a conflict between state laws and federal laws, the Supremacy Clause of the US Constitution dictates that federal laws take precedence over state laws.
What was the significance of the case Brown v. Topeka Board of Education?
-Brown v. Topeka Board of Education was a landmark case where the federal government overruled state laws that enforced racial segregation in schools, affirming federal authority over states in matters of civil rights.
What was the situation before the US Constitution, under the Articles of Confederation?
-Before the US Constitution, the Articles of Confederation created a weak federal government with states acting almost like independent countries, leading to issues such as insufficient military power and financial instability.
What led to the creation of the US Constitution in 1787?
-The need for a stronger federal government, capable of maintaining order and defending the country, led to the Philadelphia Convention in 1787, where the US Constitution was created to address the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation.
What is the Supremacy Clause and why is it important?
-The Supremacy Clause, found in Article VI of the US Constitution, states that the US Constitution, along with federal laws and treaties, is the supreme law of the land, meaning federal law takes priority over conflicting state laws.
How do state and federal governments work together in the US?
-While the federal government has authority over national issues, state governments handle local matters and services. Despite occasional conflicts, they must cooperate to serve the needs of the people.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
What is federalism?

Federalism: Crash Course Government and Politics #4

FEDERALISM Explained [AP Government Review]

US Federalism For Dummies: American Government Review

AP Gov | 1.7 Relationship Between the States and National Government | NEW!

McCulloch v Maryland, EXPLAINED [AP Gov Required Supreme Court Cases]
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)