Dasar Sistem Digital | 09 - Register & Counter
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the speaker introduces the fundamentals of digital systems, focusing on registers and counters. They explain how registers store data using flip-flops, such as D flip-flops for both parallel and serial inputs. The speaker then delves into the workings of counters, highlighting both asynchronous and synchronous types, including how clock cycles influence the operation of JK and T flip-flops. The video concludes with a thank-you message to the students and a reminder to subscribe for more content. This serves as the final module in a digital systems practicum series.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video focuses on explaining how to design and implement a digital counter using flip-flops.
- 😀 The counter circuit discussed uses a T flip-flop rather than a JK flip-flop for its design.
- 😀 The T flip-flop is chosen because of its ability to function effectively in the desired configuration.
- 😀 The counter in the video is a down-counter, meaning it counts backward.
- 😀 The practical experiment is part of a larger course on digital systems and includes a hands-on component.
- 😀 Viewers are encouraged to visit the website for more learning materials related to digital systems.
- 😀 The speaker provides contact information for further questions and support from their team.
- 😀 This video is the final part of a 9-module series focused on basic digital systems practicals.
- 😀 The speaker expresses gratitude to viewers for participating in the course and following along with the content.
- 😀 The video encourages viewers to subscribe for more educational content in the future.
- 😀 The script includes both instructional content and closing remarks aimed at engaging and thanking the audience.
Q & A
What is a register in digital systems?
-A register in digital systems is a storage location or container used to hold data. It stores data in binary form (bits), typically using flip-flops like D flip-flops to save individual bits of information.
How is data stored in a register?
-Data is stored in a register by utilizing flip-flops. Each flip-flop stores one bit of data, and multiple flip-flops are used to store a multi-bit value. The data is retained until a clock pulse triggers an update.
What is the function of a D flip-flop in a register?
-The D flip-flop in a register captures and stores the input data at the moment of a clock pulse. It holds the data stable until the next clock pulse, enabling sequential data storage in a register.
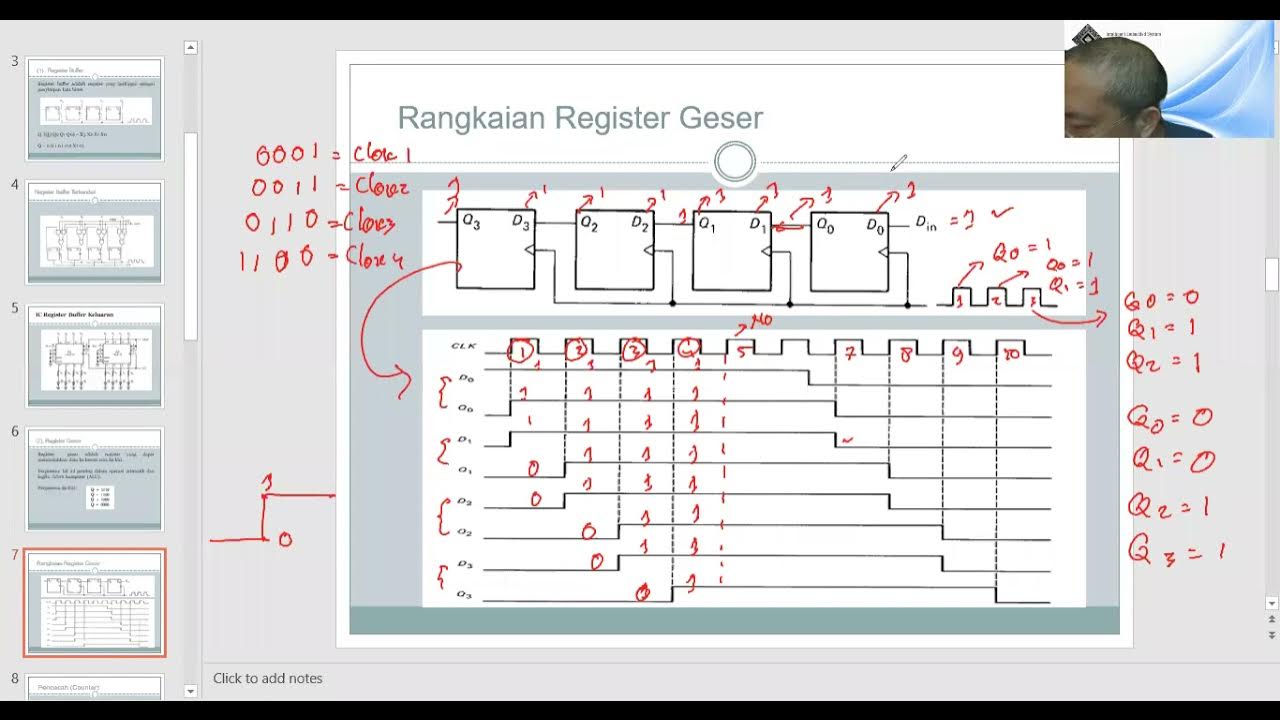
What is the difference between parallel input/output and serial input/output registers?
-In parallel input/output registers, each bit has its own input and output, allowing simultaneous data storage and retrieval. In serial input/output registers, data is stored and read sequentially, one bit at a time, which takes more clock cycles.
How does a serial input register work?
-A serial input register stores data bit by bit. Each bit is shifted into the register sequentially, and the data is transferred through flip-flops with each clock cycle, starting from the least significant bit.
What is a 'shift' in a serial input register?
-A shift in a serial input register refers to the process of moving the input data through the flip-flops sequentially. As each clock pulse occurs, the data from one flip-flop moves to the next, effectively shifting the data bit by bit.
What is the primary characteristic of a synchronous counter?
-A synchronous counter uses a common clock signal for all flip-flops in the counter. All flip-flops receive the clock pulse simultaneously, enabling the counter to operate faster with no internal delay between flip-flops.
How does an asynchronous counter differ from a synchronous counter?
-In an asynchronous counter, each flip-flop is triggered by the output of the previous one, creating a delay between the flip-flops. In contrast, a synchronous counter has a shared clock signal for all flip-flops, eliminating this delay and allowing for faster counting.
What is the function of a T flip-flop in a counter circuit?
-A T flip-flop in a counter circuit toggles its output on every clock pulse. It can be used to create binary counters that increment with each clock cycle, with each flip-flop representing a bit in the binary count.
Why is a rising edge or falling edge important in flip-flops and counters?
-The rising edge (0 to 1) or falling edge (1 to 0) of the clock signal determines when a flip-flop updates its output. Depending on the edge used, flip-flops can be configured to activate and change their state at specific times during the clock cycle.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)